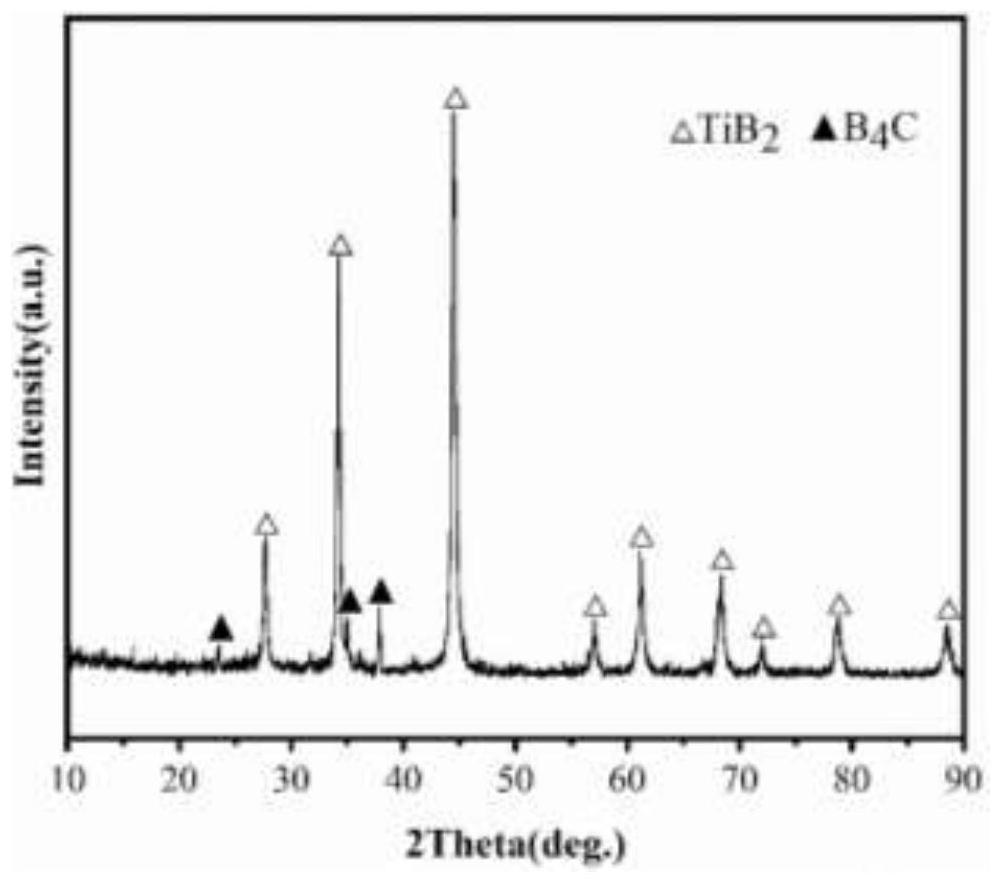
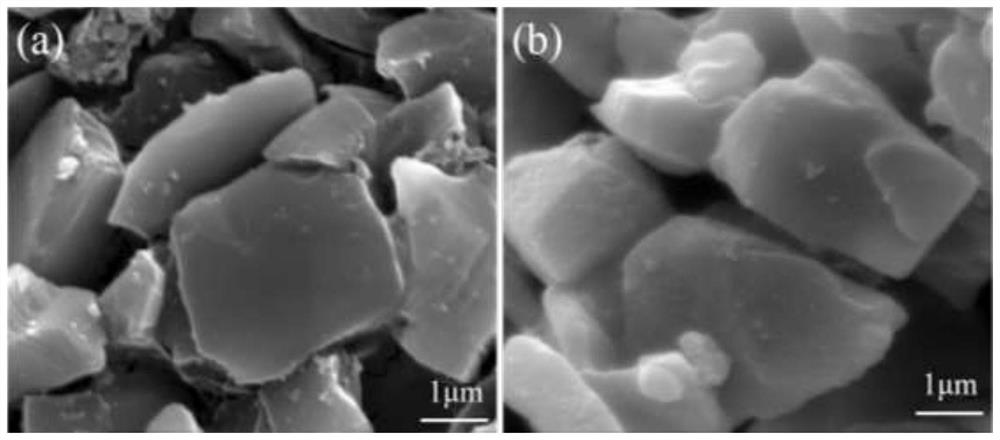
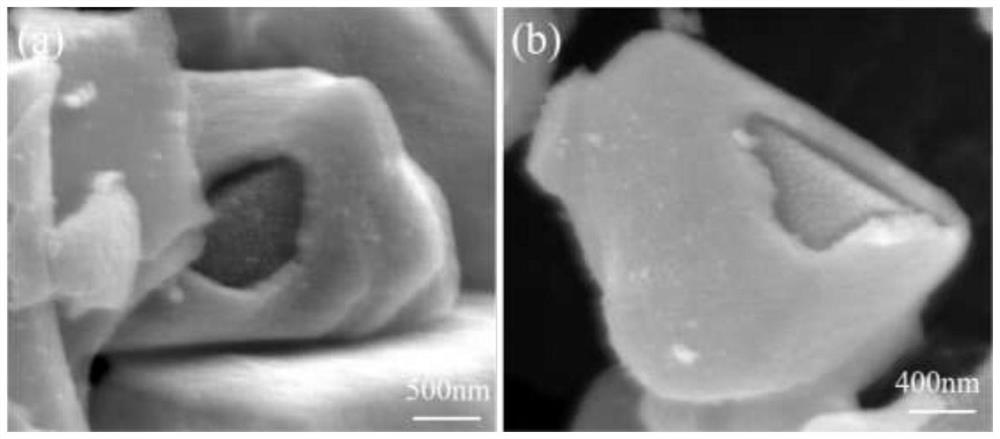
Molten salt preparation method of B4C-coated TiB2 composite powder with core-shell structure
A core-shell structure and composite powder technology, which is applied in the field of molten salt preparation of B4C@TiB2 composite powder, can solve the problems of high sintering temperature, low fracture toughness and low bending strength of single-phase boron carbide, and achieves low cost, The effect of good electrical conductivity and excellent sintering performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] A B with a core-shell structure 4 C@TiB 2 The molten salt preparation method of composite powder comprises the following steps:
[0044] 1) Add 10g of boron carbide into a mixed acid containing 10mL of hydrofluoric acid (concentration: 40wt%) and 10mL of nitric acid (concentration: 65wt%), soak for 12h; then wash with deionized water for 3 times and absolute ethanol for 3 times, after filtration, dry in an 80°C blast drying oven;
[0045] 2) Weigh 7g of acid-corroded boron carbide and 3g of titanium powder, and mix them uniformly to obtain mixed reaction raw materials;
[0046] 3) take by weighing 25g sodium chloride and 25g potassium chloride, mix uniformly to obtain alkali metal base molten salt raw material;
[0047] 4) Mix the alkali metal salt-based molten salt raw material and the mixed reaction raw material evenly, then put it into a graphite crucible, place it in a box-type atmosphere furnace protected by an argon atmosphere, and heat the box-type atmosphere ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] A B with a core-shell structure 4 C@TiB 2 The molten salt preparation method of the composite powder is roughly the same as that of Example 1, except that the temperature of the box-type atmosphere furnace is raised to 800° C. and then kept for 6 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0053] A B with a core-shell structure 4 C@TiB 2 The molten salt preparation method of composite powder comprises the following steps:
[0054] 1) Add 10g of boron carbide into a mixed acid containing 10mL of hydrofluoric acid (mass concentration: 40%) and 10mL of nitric acid (mass concentration: 65%), soak for 12h; then wash with deionized water for 3 times and absolute ethanol 3 times, after filtering, dry in an 80°C blast drying oven;
[0055] 2) Weigh 6g of acid-etched boron carbide and 4g of titanium powder, and mix them uniformly to obtain mixed reaction raw materials;
[0056] 3) take by weighing 50g sodium sulfate and 50g potassium sulfate, mix uniformly to obtain alkali metal base molten salt raw material;
[0057] 4) Mix the alkali metal salt-based molten salt raw material and the mixed reaction raw material evenly, then put it into a graphite crucible, place it in a box-type atmosphere furnace protected by an argon atmosphere, and heat the box-type atmosphere fur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com