Root nodule endophyte S43 with phosphate solubilizing function and application of root nodule endophyte S43
An endophyte and phosphorus solution technology, applied in the field of agricultural microorganisms, can solve the problems of few and few and lack of research on plant endophytes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The isolation of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
[0039] (1) Sample collection
[0040] The samples came from Nahui Village (Lat.24.514341N, Lon.104.590378E) in Xingyi City, Guizhou Province.
[0041] (2) Surface disinfection of root nodule samples
[0042] Collect the fresh root nodules of the green leafy locust in a clean triangular flask, soak in sterile water for 5 minutes and rinse 3 to 5 times, add 75% alcohol to soak for 3 minutes and shake slightly, rinse with sterile water for 3 to 5 times, then add 3.5% The surface was disinfected with NaClO for 8 minutes, and finally rinsed with sterile water for 5 to 8 times.
[0043] (3) Isolation and culture of endophytic bacteria in rhizobia
[0044] Place the sterilized nodule samples in a 5ml centrifuge tube, crush the nodules with a sterilized glass rod, and squeeze to obtain nodule juice. Under sterile conditions, the root nodule juice after detoxification treatment was diluted to obtain 10 -3 、10 -4 and 10 -5 S...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The identification of embodiment 2 bacterial strains
[0048] (1) Colony characteristics of the strain
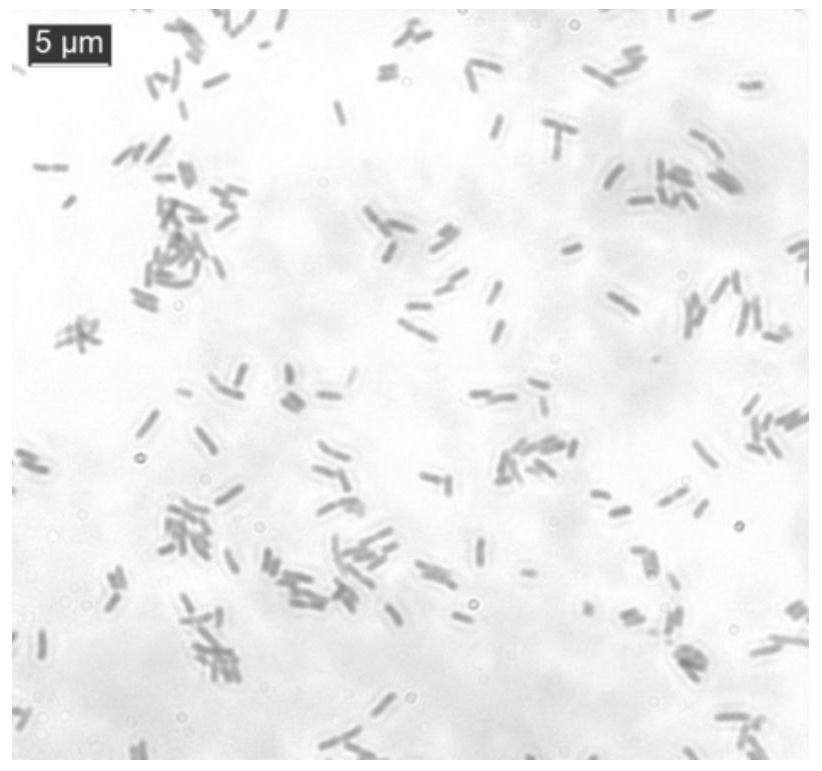
[0049] The strain S43 isolated above was identified to be rod-shaped, with a colony length of 1 μm-2.5 μm and a width of about 0.5 μm. It is a regular circle on the YMA plate, the surface is wet and sticky, shiny, and the whole is white.
[0050] (2) Biochemical indicators of bacterial strains
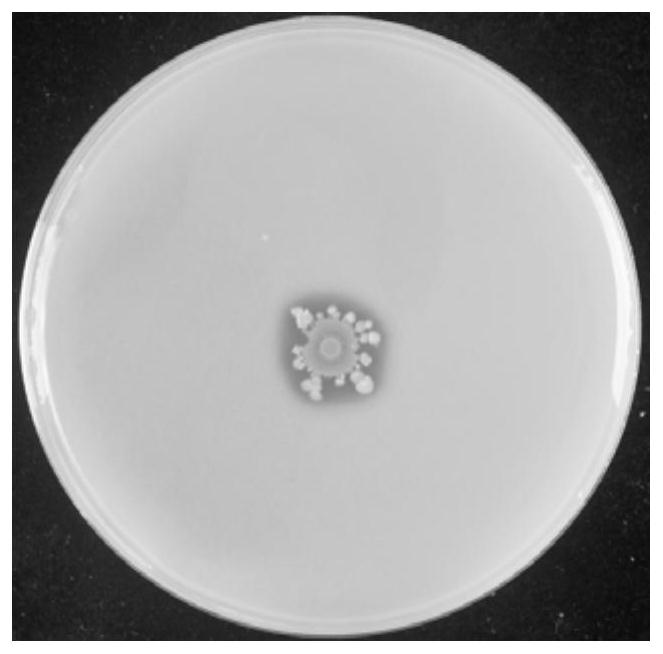
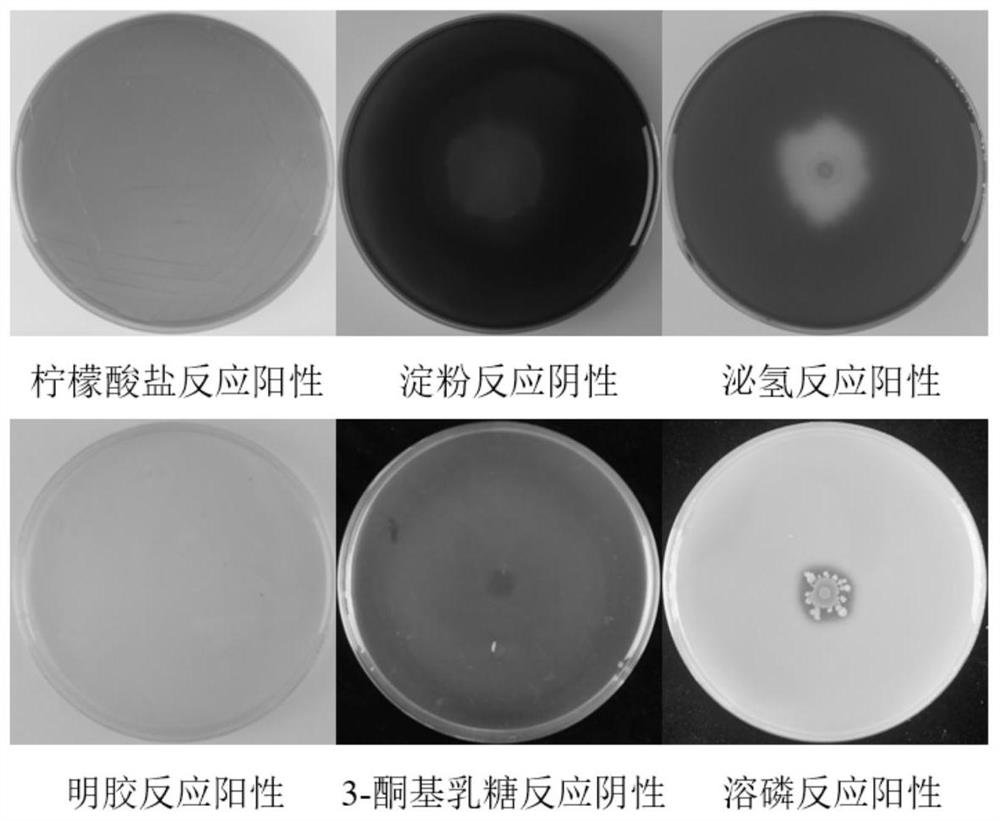
[0051] Physiological and biochemical index determination of the bacterial strain shows that the bacterial strain S43 is negative for Gram staining, and the results are as follows: figure 2 Shown; strain S43 is positive for citrate, negative for starch hydrolysis, positive for hydrogen secretion, positive for gelatin, negative for 3-ketolactose, the results are as follows image 3 shown.
[0052] (3) Identification of strains
[0053] Extract the genomic DNA of bacterial strain S43 isolated in Example 1, and use the extracted DNA as a template to perform 16SrDNA PCR ampl...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Phosphate-dissolving and hydrogen-releasing performance identification of bacterial strain S43
[0061] (1) Identification of Phosphorus Solubilizing Ability of Strain S43
[0062] In Example 1, the inorganic phosphorus medium was used for preliminary screening, and the obtained bacterial strain S43 with obvious phosphorus-dissolving circle was further measured, and the content of soluble phosphorus in the medium was determined by the molybdenum-antimony anti-colorimetric method to determine its phosphorus-dissolving ability. .
[0063] Inoculate the strain S43 into a Erlenmeyer flask containing 50ml of inorganic phosphorus liquid medium, adjust the initial pH to 7.0, place it in a shaker at 28°C and 180rpm for cultivation, and measure the culture at 6h, 12h, 24h and 48h respectively. The soluble phosphorus content in the base was measured every 48 hours thereafter. Determination result takes cultivation time as abscissa, and soluble phosphorus content is or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com