Biomass-based phenolic resin adhesive and preparation method thereof
A technology based on phenolic resin and based phenolic resin, applied in the field of biomass-based phenolic resin adhesive and its preparation, can solve the problems of harsh reaction conditions, complicated production process, increased production cost, etc., and achieve high bonding strength and production The effect of cost reduction and increase of production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Step 1: Take 10g of corn stalks and add them to 100g of 0.7mol / L sulfuric acid solution, and react at 130°C for 3 hours at a stirring rate of 500rpm to obtain a corn stalk hydrolyzate, add alkali to adjust to neutral, and set aside;
[0036] Step 2: Take 3.4g of corn stalk hydrolyzate and 175.7g of 37% formaldehyde in step 1 (mass ratio of corn stalk hydrolyzate to formaldehyde is 1:19) and stir at room temperature for 10min to make a mixture; take two-thirds The mixed solution, 94g phenol and 56g 8mol / L sodium hydroxide solution were added to the reactor, and reacted for 10min at 65°C; continue to add the remaining mixed solution and 24g 8mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to the reactor, React at 85° C. for 3.5 hours; add 13.5 g of urea into the reactor, react at 85° C. for 30 minutes, and rapidly cool to room temperature to obtain a biomass-based phenolic resin adhesive.
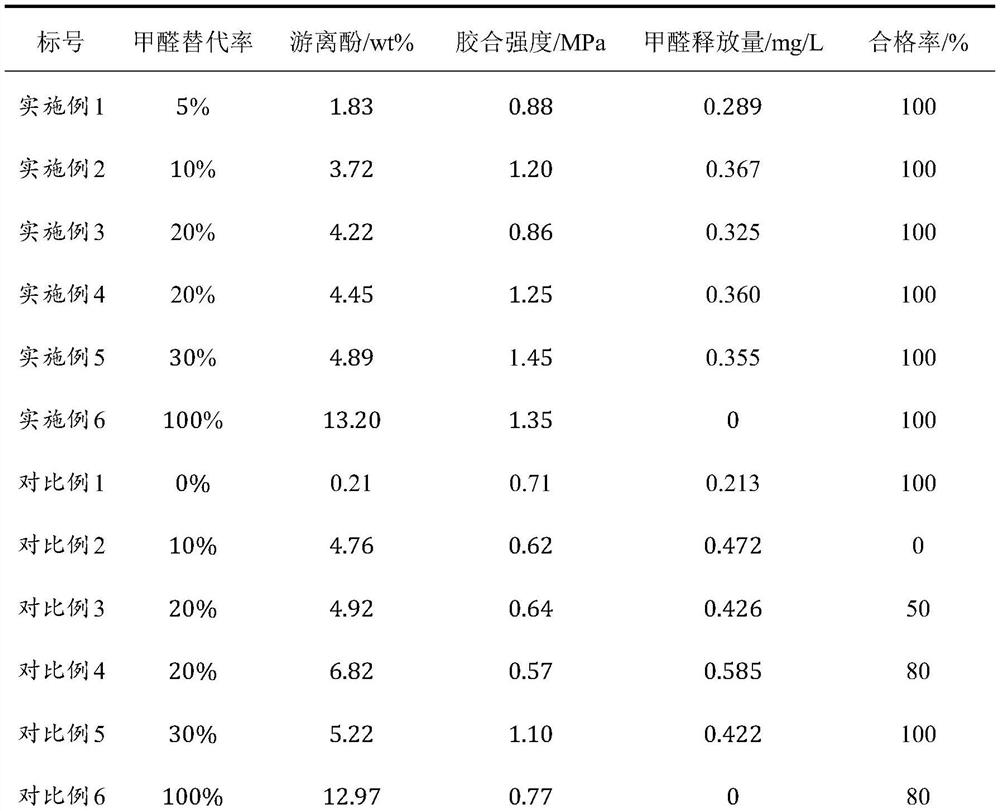
[0037] Two-layer poplar plywood was pressed, and its performance was tested. The results are liste...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Step 1: Take 20g of corncobs and add them to 200g of 1mol / L sulfuric acid solution, react at 150°C with a stirring rate of 600rpm for 2 hours to obtain a corncob hydrolyzate, add alkali to adjust to neutral, and set aside;
[0040] Step 2: Take 5.8g of corncob hydrolyzate and 140g of 37% formaldehyde in step 1 (mass ratio of corncob hydrolyzate to formaldehyde is 1:9) and stir at room temperature for 15min to make a mixed solution; take two-thirds of Add the mixed solution, 54g phenol and 30g 8mol / L sodium hydroxide solution into the reactor, and react at 70°C for 15min; continue to add the remaining mixed solution and 15g 8mol / L sodium hydroxide solution in the reactor, React at ℃ for 4 hours; add 8g of ammonia water to the reactor, react at 85℃ for 30min, and rapidly cool to room temperature to obtain a biomass-based phenolic resin adhesive.
[0041] Two-layer poplar plywood was pressed, and its performance was tested. The results are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Step 1: Take 25g of corncobs and add 500g of sodium hydroxide / urea mixed solution (sodium hydroxide: urea: water: 7:12:81) and stir for 3 hours at -10°C, centrifuge the obtained product to obtain the supernatant, and upward 50 mL of distilled water was added dropwise to the clear liquid, dialyzed to neutrality, and the obtained product was dried to obtain nanocellulose.
[0044] Step 2: Take 11g of nanocellulose in step 1 and 118.8g of 37% formaldehyde (mass ratio of nanocellulose to formaldehyde is 1:4) and stir at room temperature for 20min to make a mixed solution; take two-thirds of the mixed solution , 94g phenol and 44.8g 8mol / L sodium hydroxide solution were added to the reactor, and reacted for 10min at 70°C; continue to add the remaining mixed solution and 22.4g 8mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to the reactor, and React at 85°C for 3h; add 13.5g of urea into the reactor, react at 90°C for 35min, and cool down to room temperature rapidly to obtain a biomass-base...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| impact strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com