Nitrogen-doped carbon-coated aluminum material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A nitrogen-doped carbon, aluminum-coated technology, applied in transportation and packaging, metal processing equipment, reduced water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption and aluminum consumption, reduce side reactions, improve efficiency, Wide application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
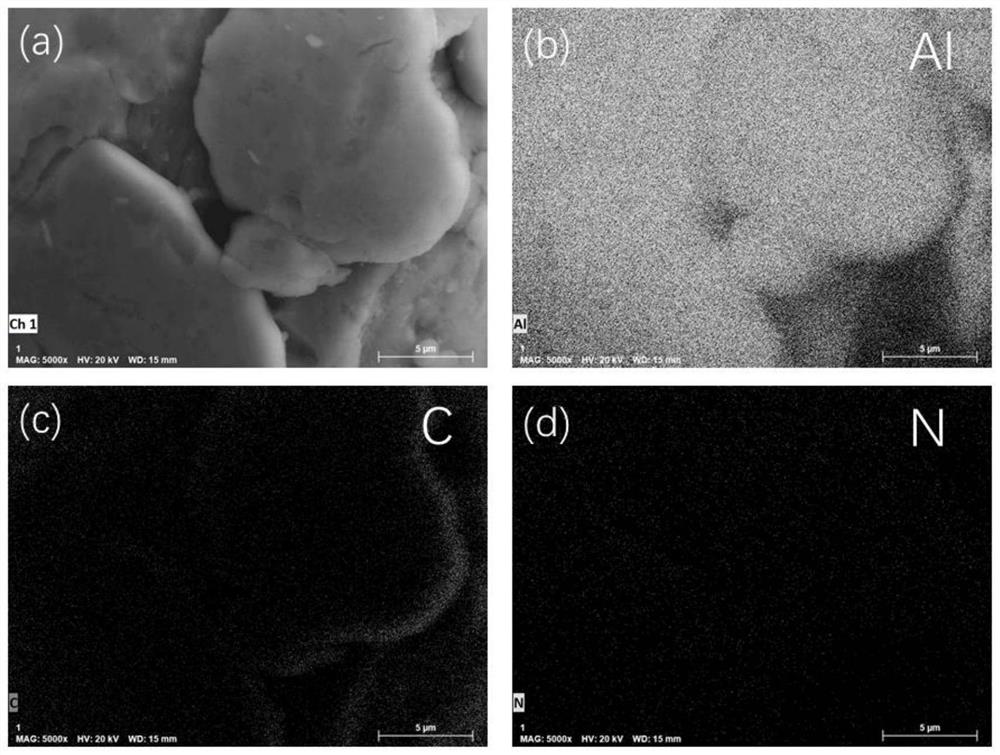
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-5
[0050] A preparation method of nitrogen-doped carbon-coated aluminum material, comprising the following steps:
[0051]1) Dissolve 60.6 mg of tris(hydroxymethylaminomethane) in 50 mL of deionized water, and adjust pH=10.0 with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solution.
[0052] 2) Dopamine is added to the solution obtained in step 1) to dissolve, and then 1 g of aluminum is added to react. The mass ratio of aluminum to dopamine, the form of aluminum and the reaction time are shown in Table 3 below.
[0053] 3) Rinse the aluminum obtained in step 2) with deionized water for 3 times, dry the moisture in an oven at 105° C., calcinate at 600° C. for 2 hours in a tube furnace under nitrogen atmosphere after drying, and cool to room temperature to obtain nitrogen-doped Miscellaneous carbon clad aluminum material.
[0054] The process conditions of table 3 embodiment 1-5
[0055]
[0056]
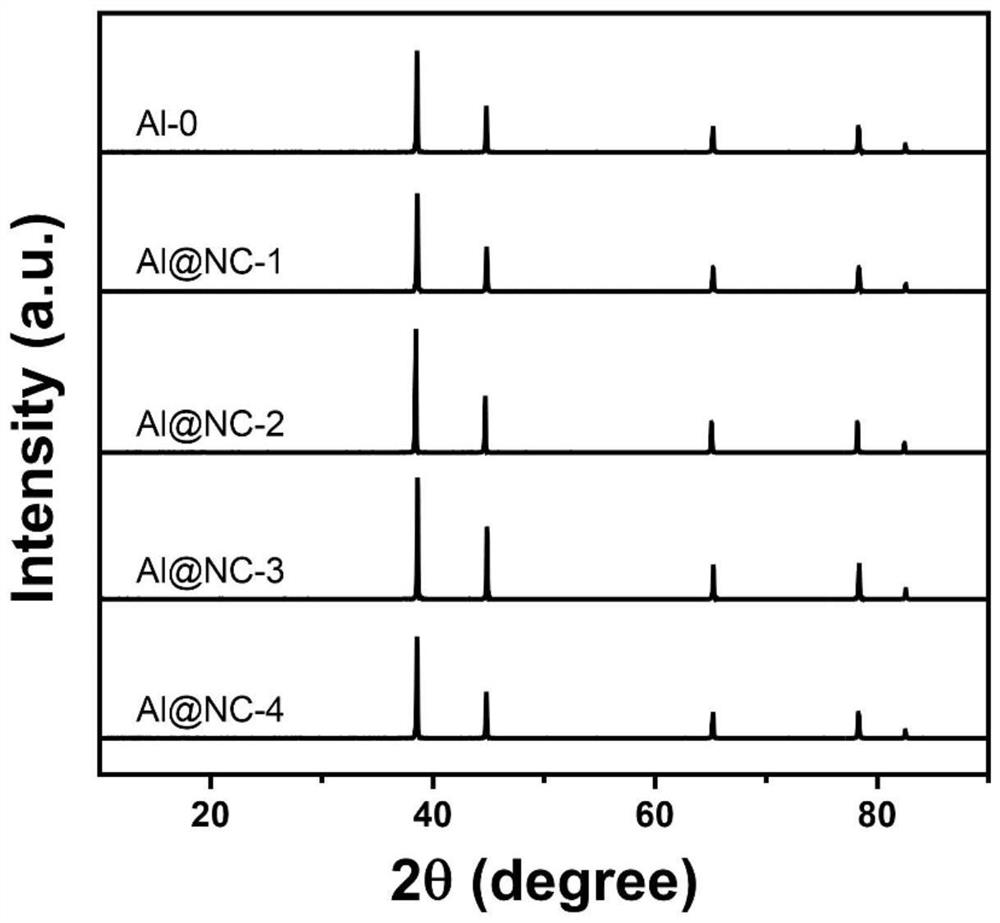
[0057] figure 1 For the XRD of the aluminum obtained in Comparative Example 1 ...
Embodiment 6
[0064] The uncoated aluminum obtained in Comparative Example 1, the carbon-coated aluminum obtained in Comparative Example 3, and the nitrogen-doped carbon-coated aluminum materials obtained in Examples 1-4 were respectively put into an aqueous solution of potassium bromate with an initial concentration of bromate of 10 μM, After mixing, the aluminum concentration was 2 g / L, and the reaction was magnetically stirred for 1 hour, and the concentration of the remaining bromate in the solution was measured by ion chromatography. Figure 5 It is the degradation rate of bromate by the methods in Examples 1-4, Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2.
[0065] Take 1 g each of the uncoated aluminum foam obtained in Comparative Example 2 and the bulk nitrogen-doped carbon-coated aluminum foam obtained in Example 5, and put them into 100 mL of potassium bromate aqueous solution with an initial concentration of bromate of 0.1 mM, respectively, and react for 1 hour. , the concentr...
Embodiment 7
[0068] The nitrogen-doped carbon-coated aluminum material obtained in Example 2 was put into an aqueous solution of potassium bromate with an initial concentration of 10 μM, the concentration of the nitrogen-doped carbon-coated aluminum material after mixing was 2 g / L, and the magnetic stirring reaction was performed for 1 hour. Then, the nitrogen-doped carbon-coated aluminum material was filtered, washed and dried, and then reacted again under the same conditions for 5 cycles. The concentration of bromate remaining in the solution was determined by ion chromatography.
[0069] Image 6 It shows the effect of recycling the nitrogen-doped carbon-coated aluminum material prepared in Example 2 to reduce bromate. After 5 times of recycling, the complete reduction and degradation of 10 μM potassium bromate can still be achieved within 1 hour. Nitrogen-doped carbon-coated aluminum materials have good stability.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com