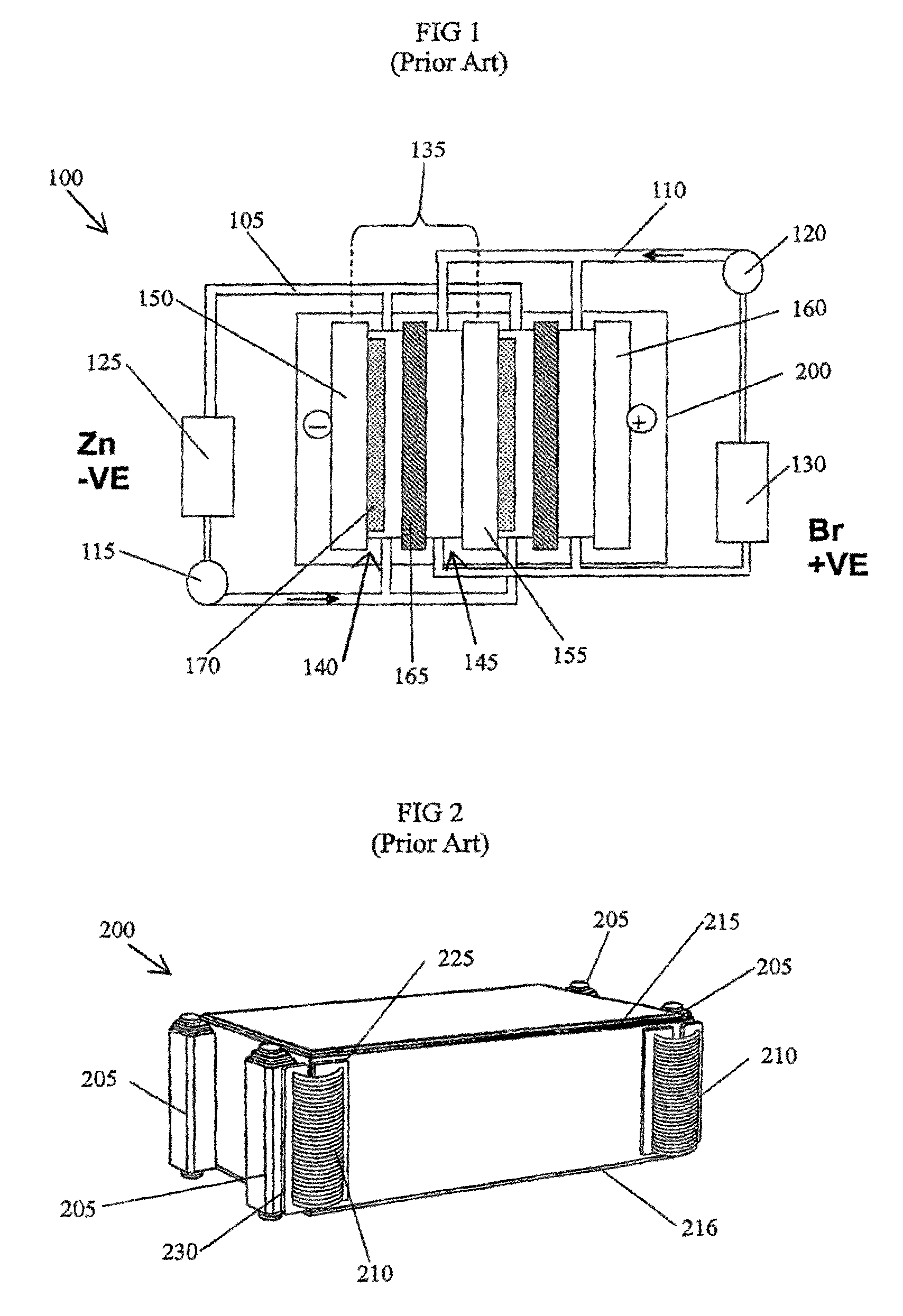
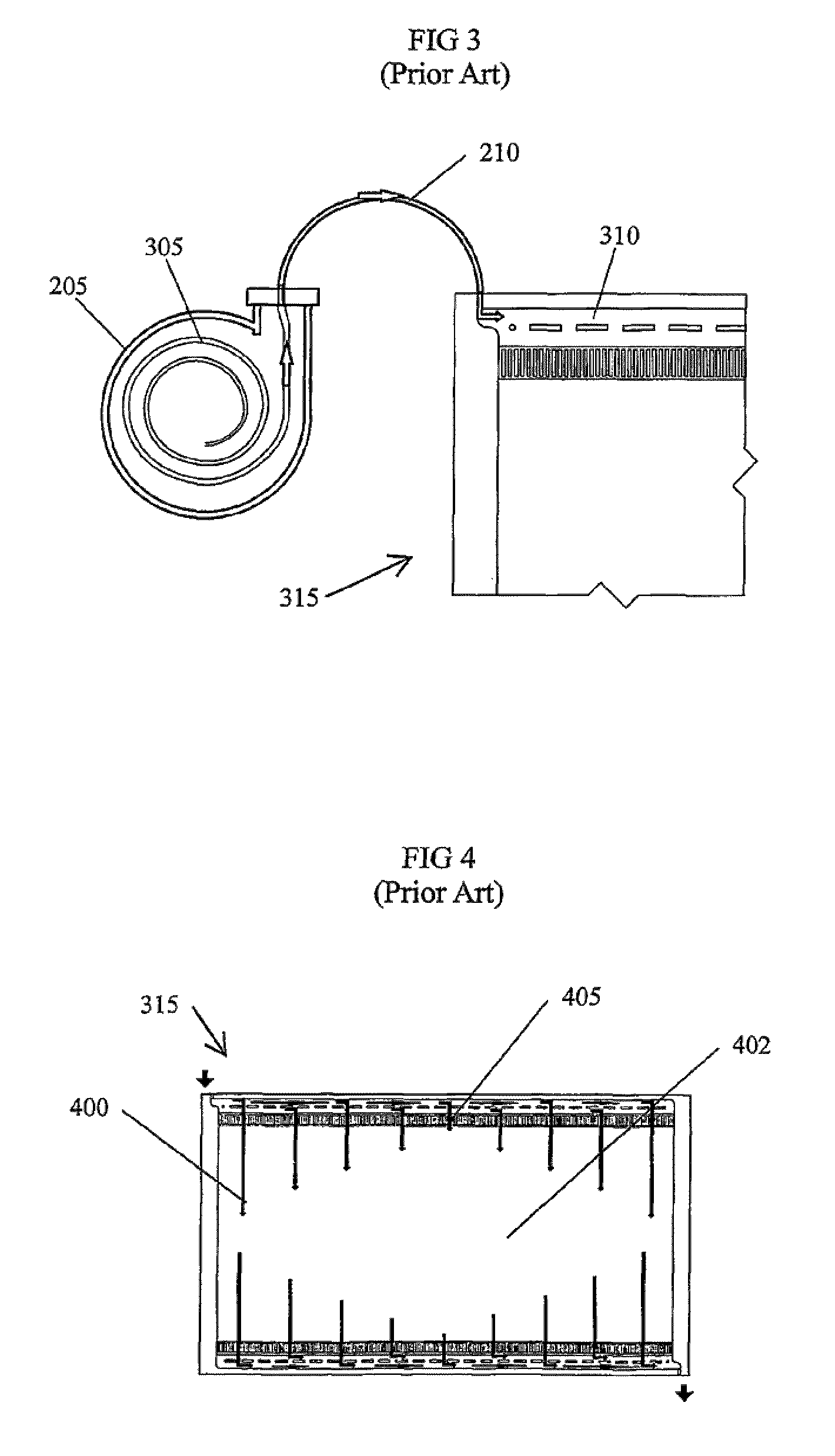
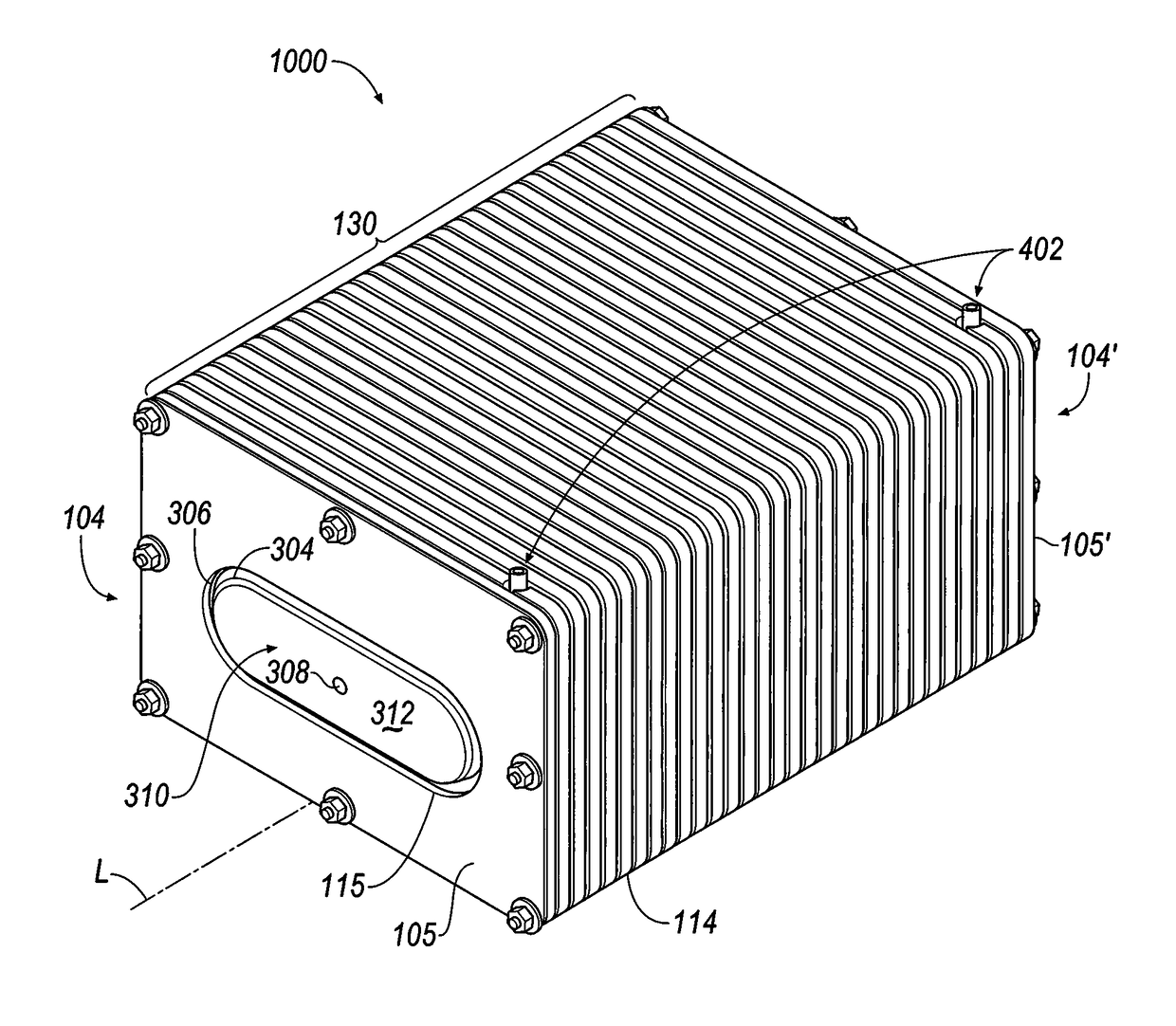
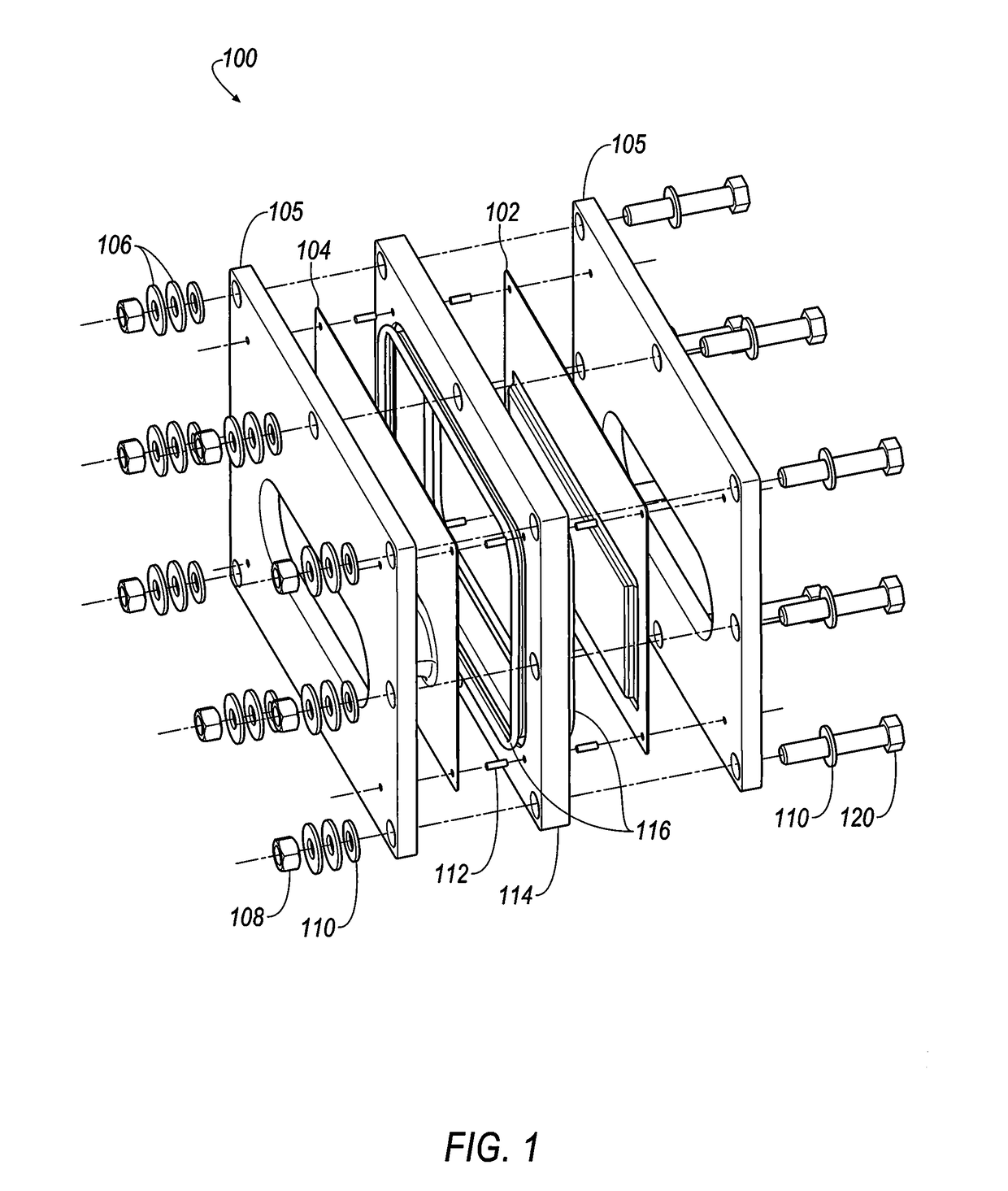
Patents
Literature
92results about "Zinc-halogen accumulators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
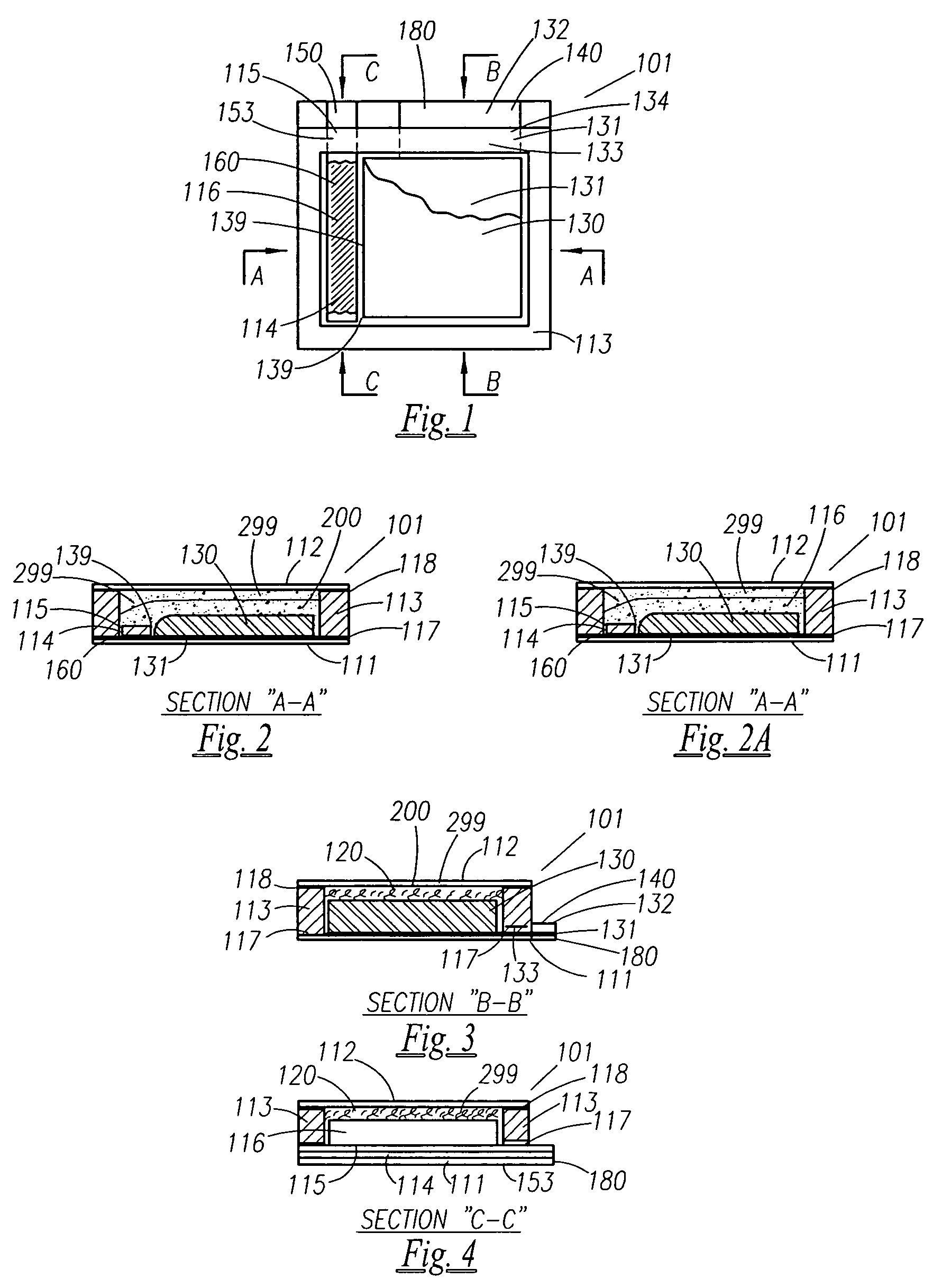
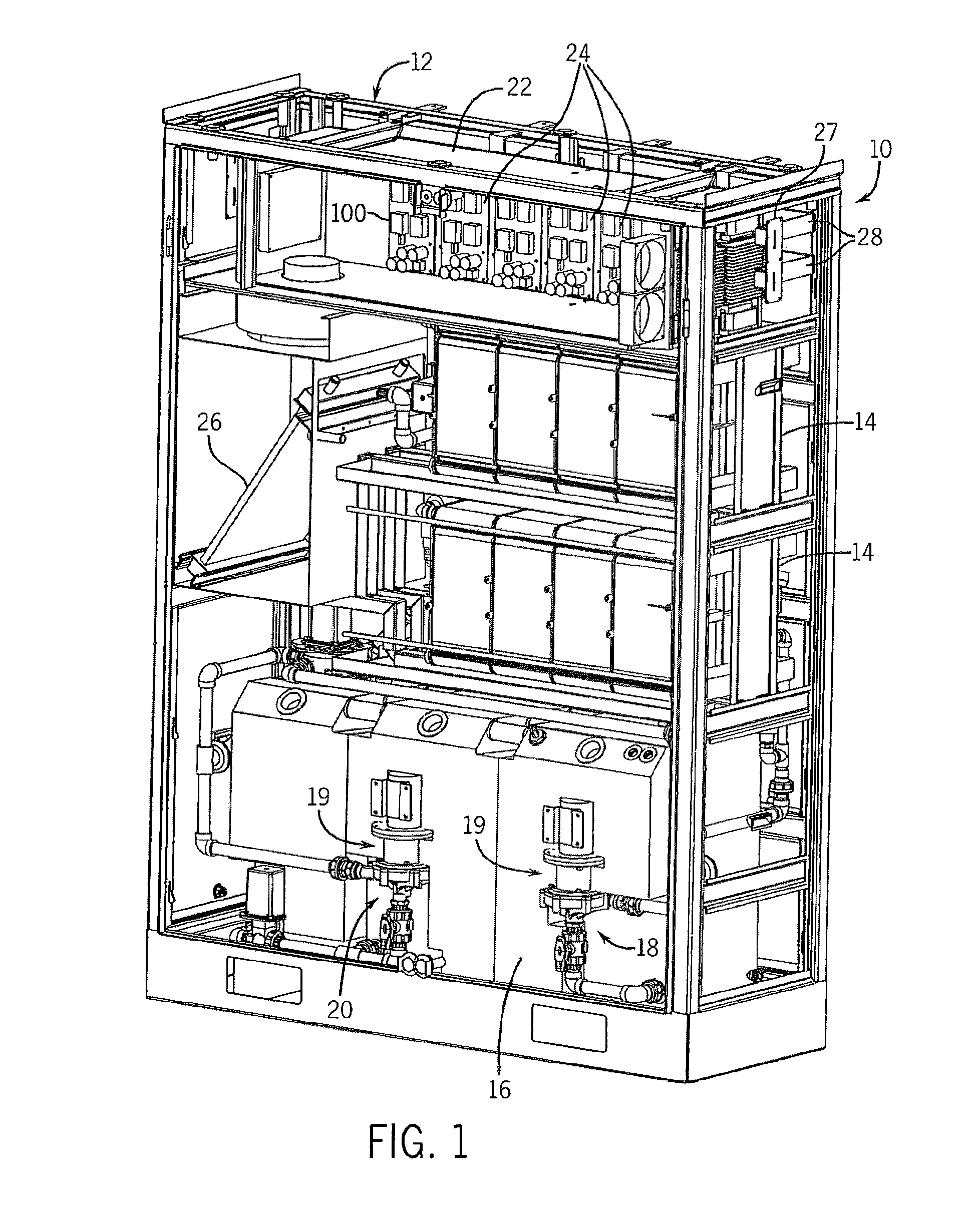
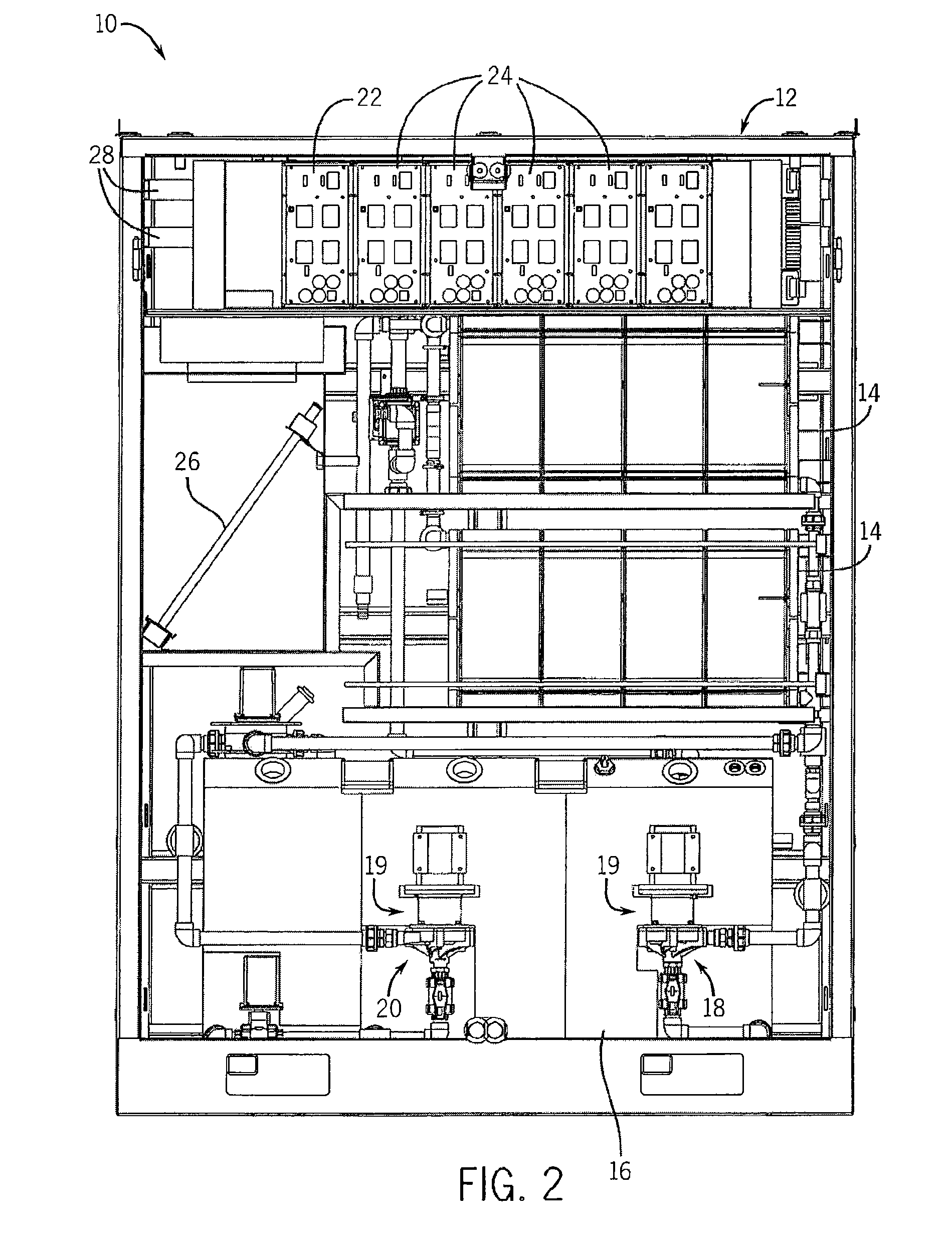
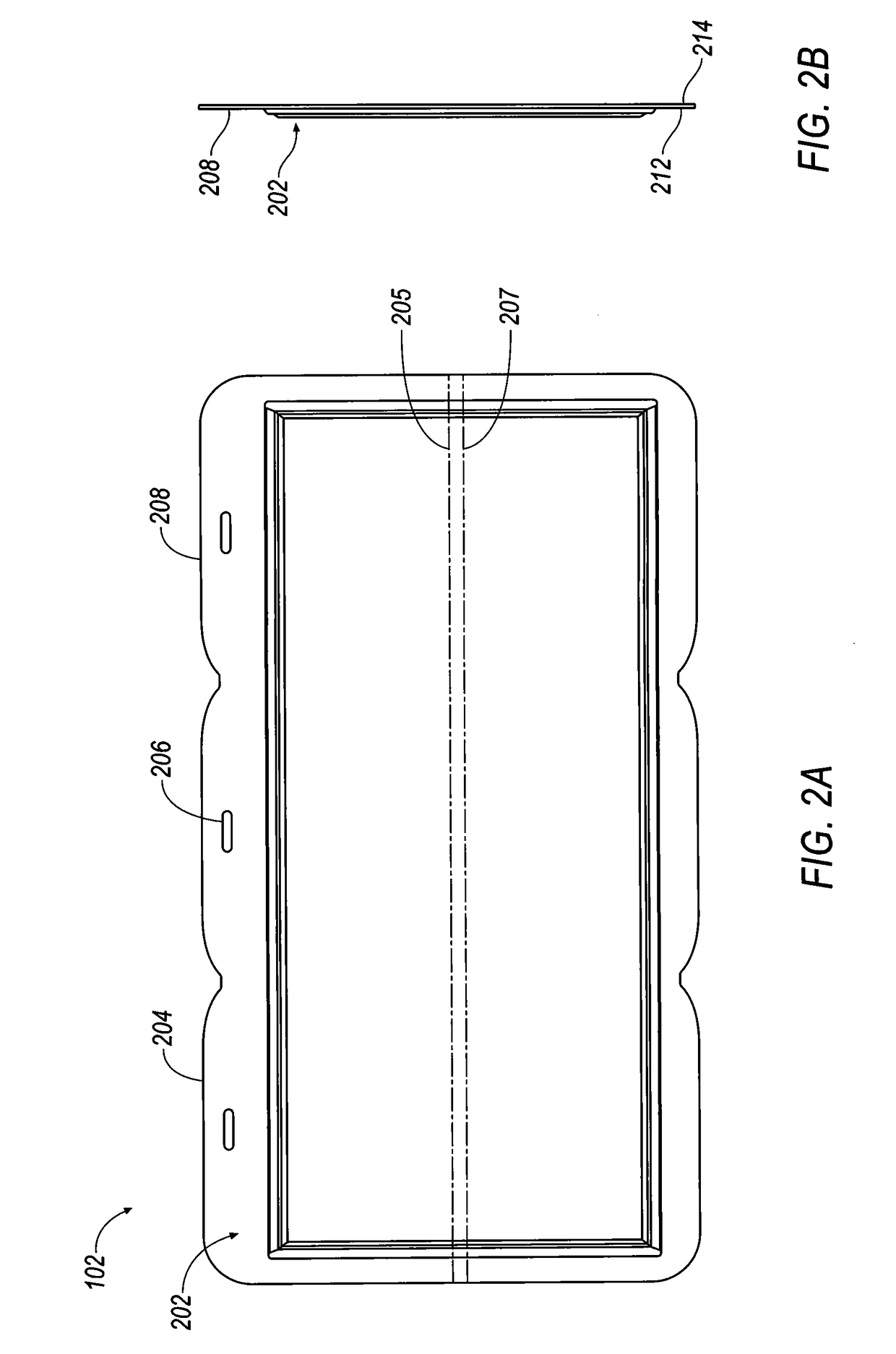
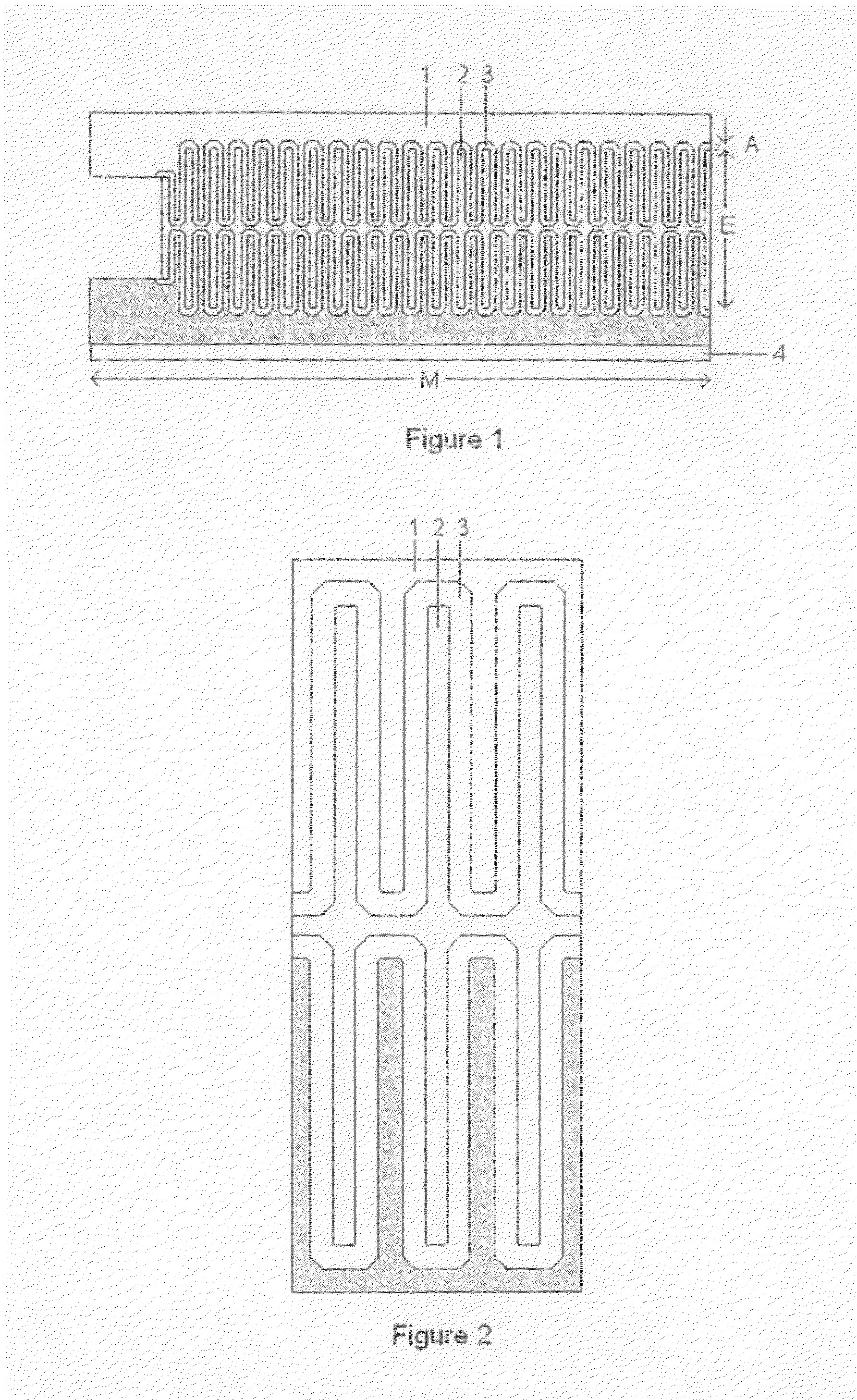
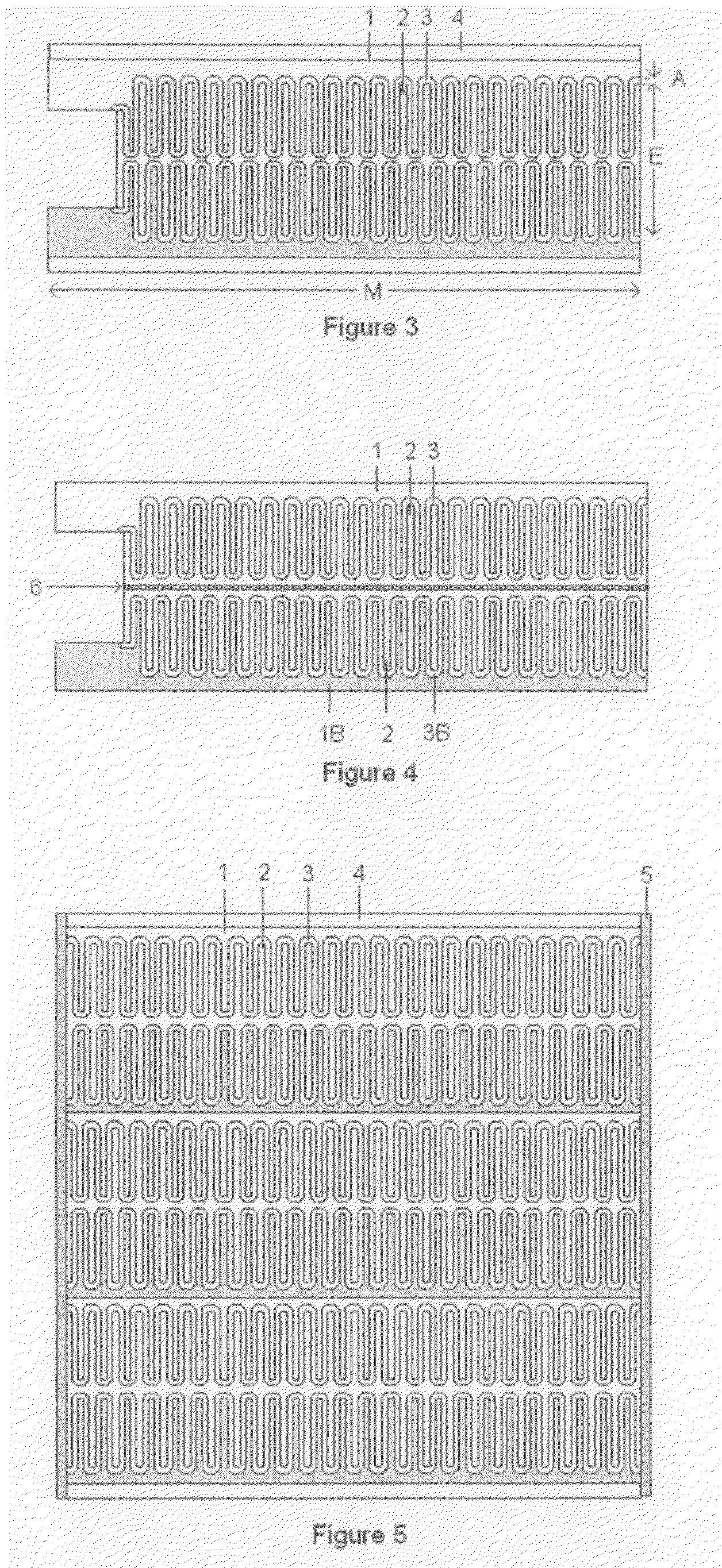
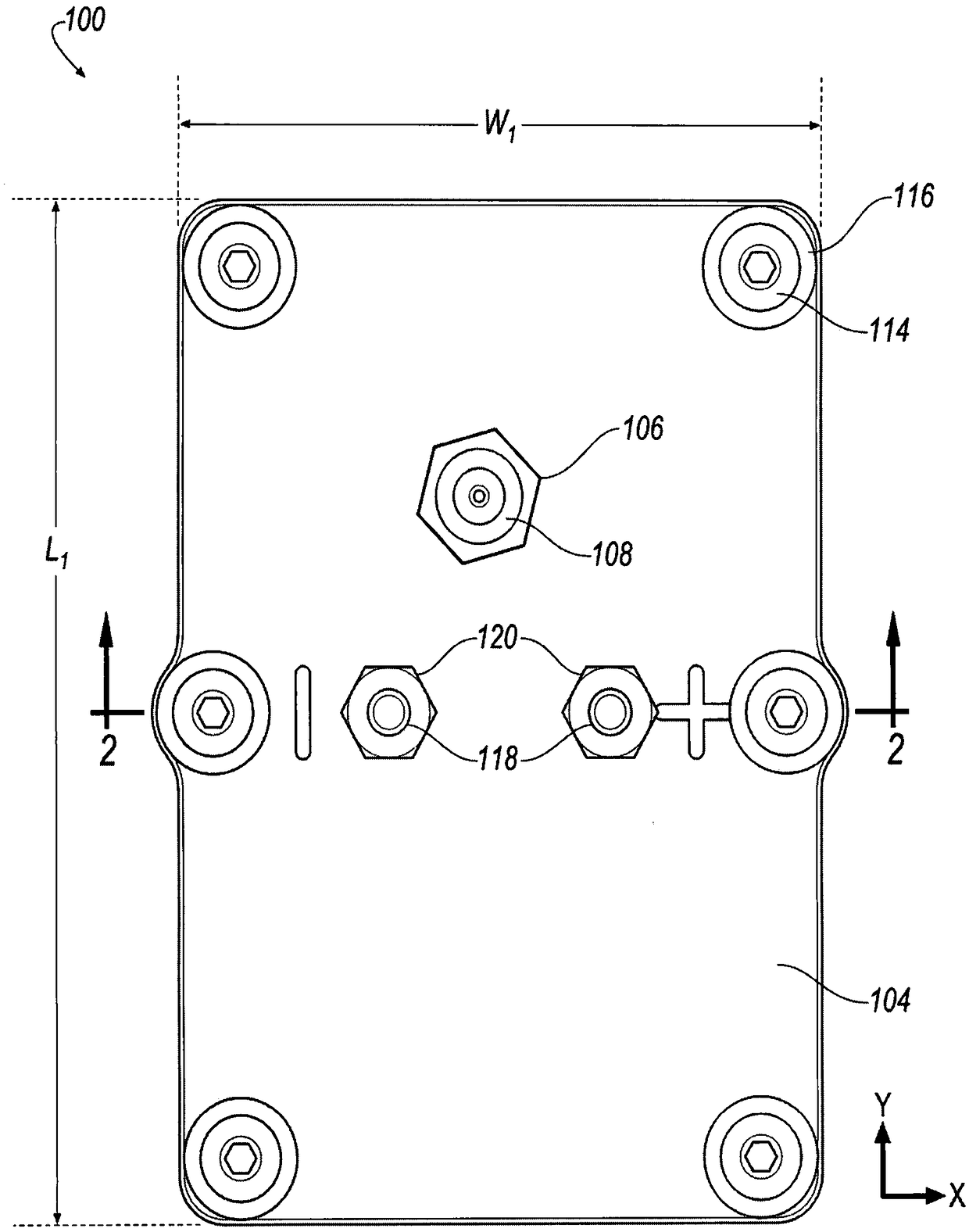
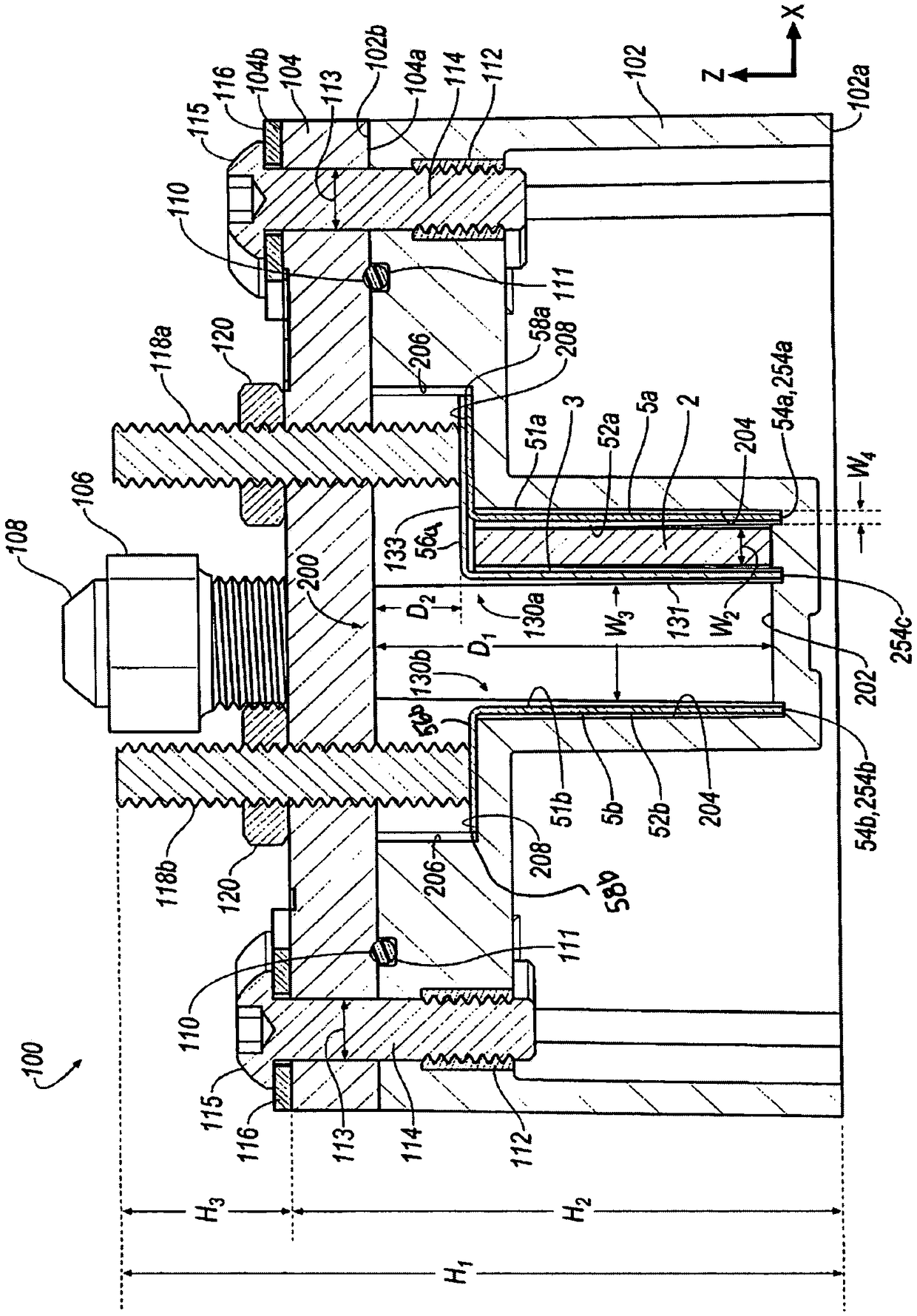
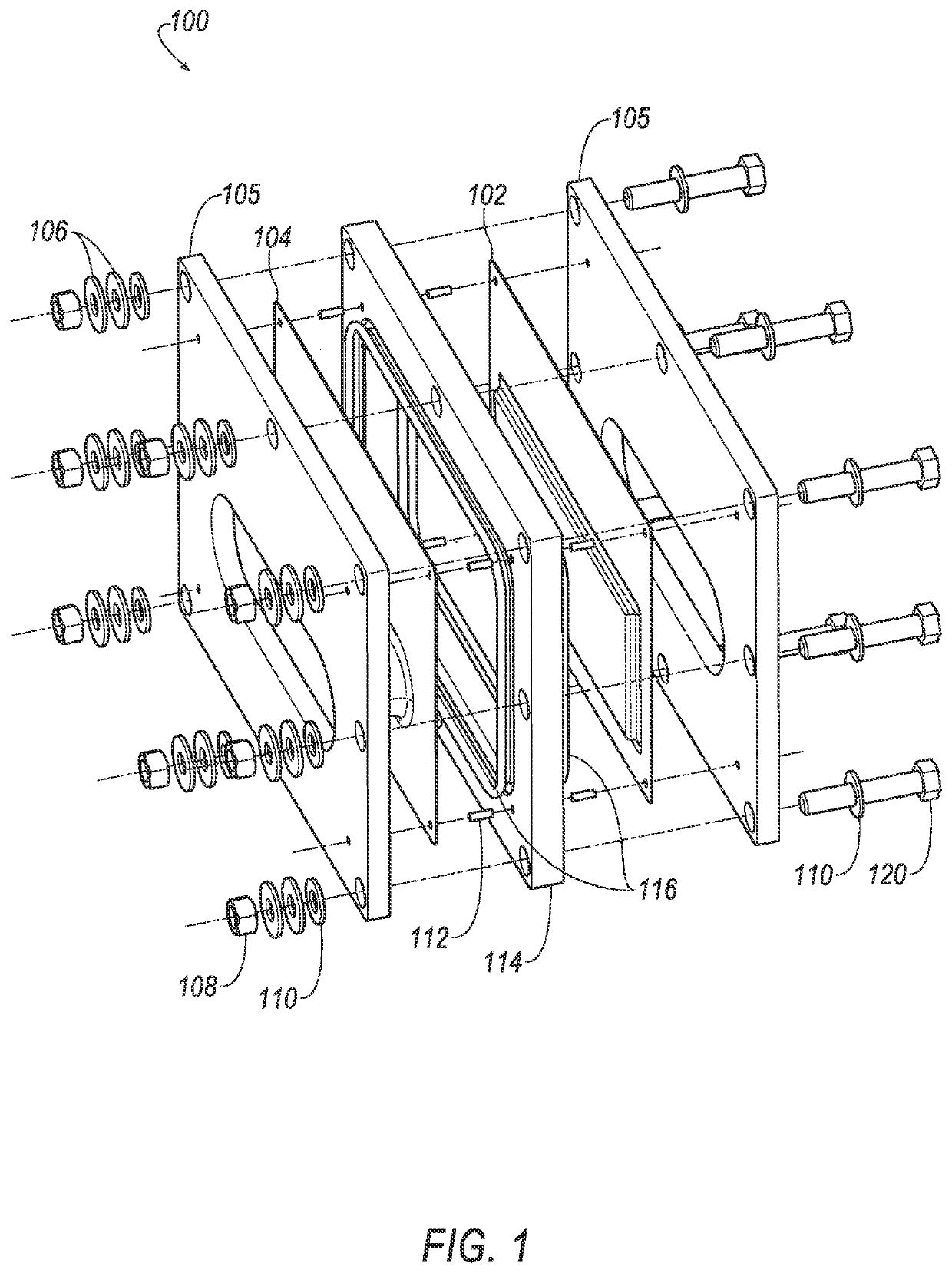
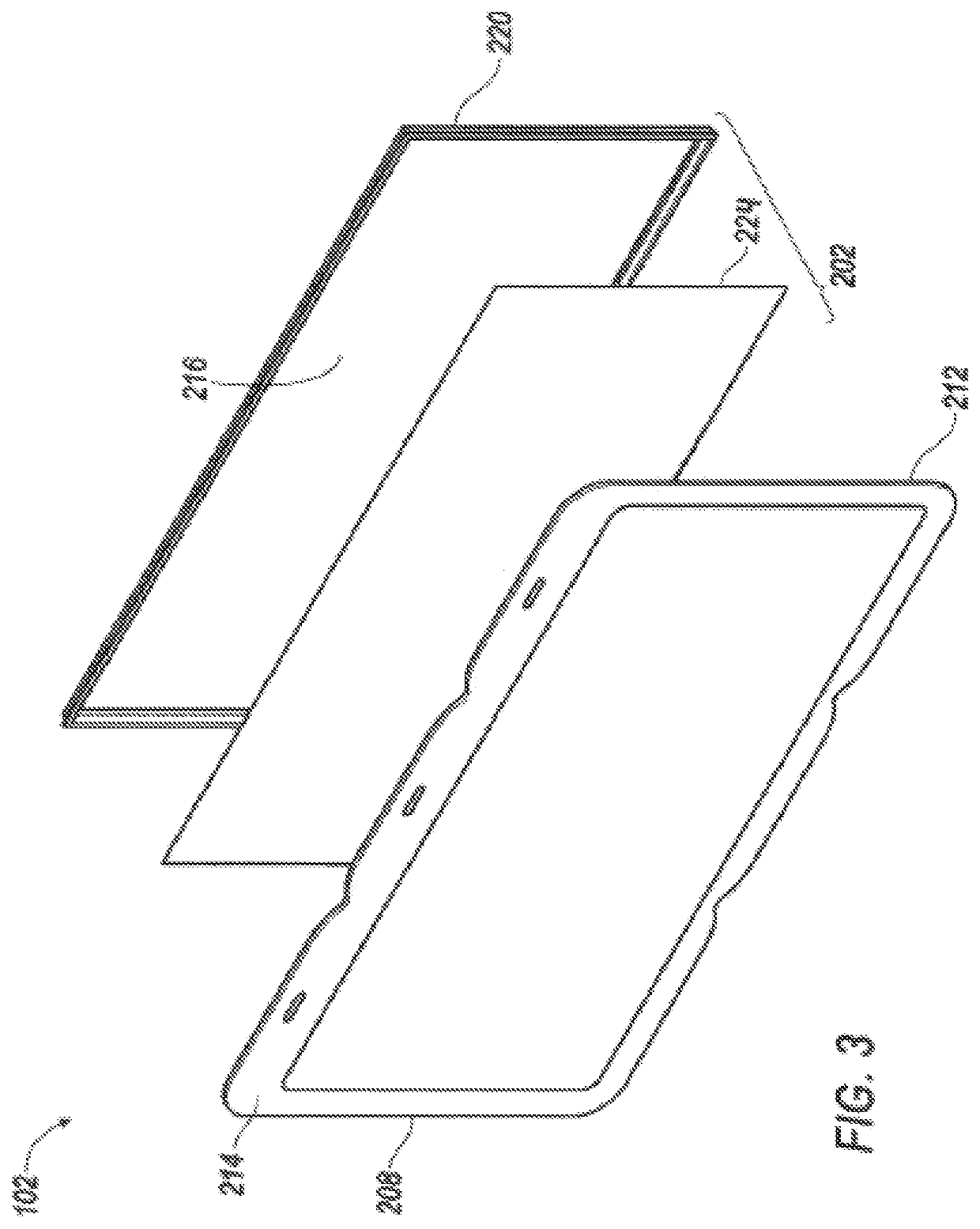
Thin printable electrochemical cell utilizing a "picture frame" and methods of making the same
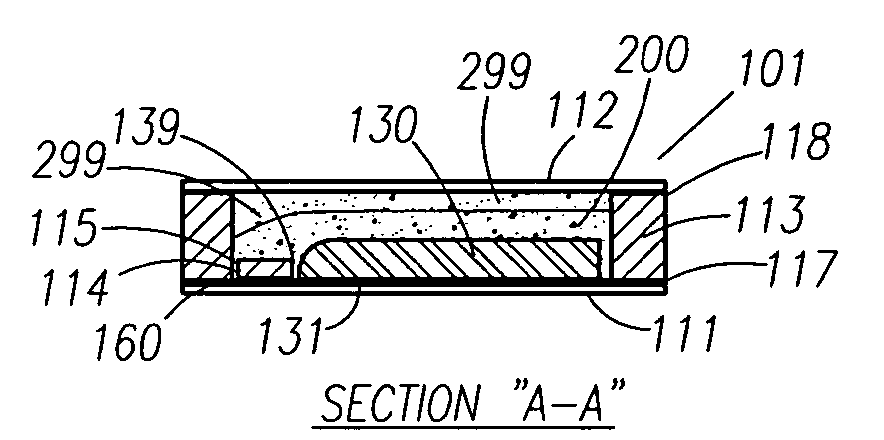
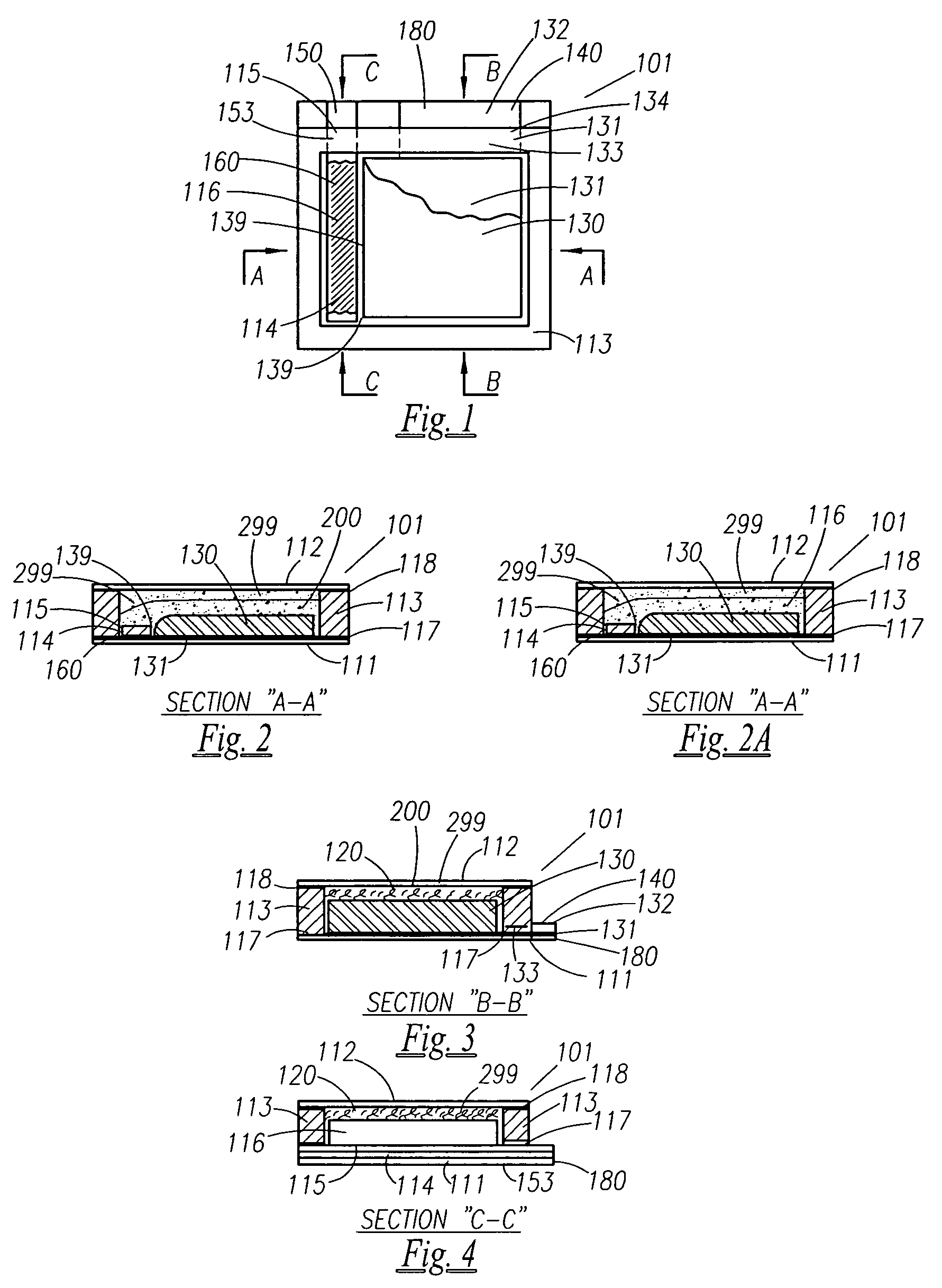
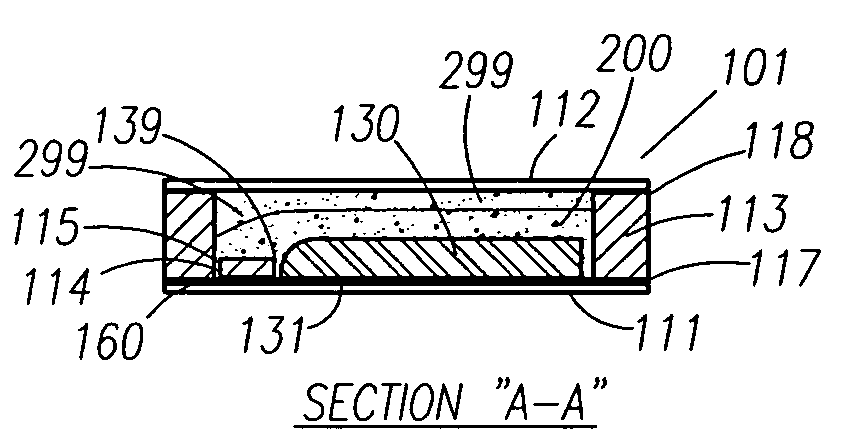
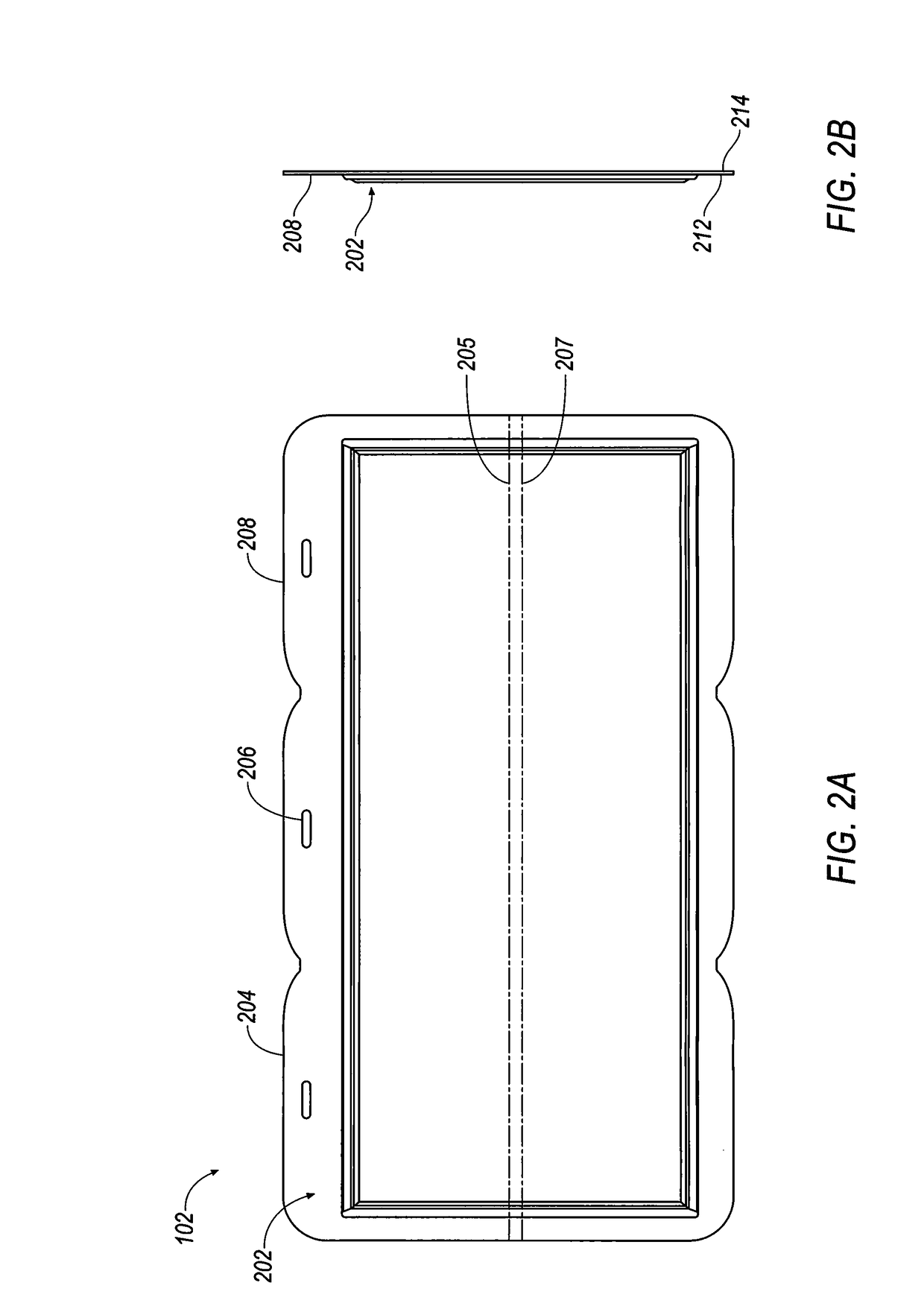
A thin printed flexible electrochemical cell, and its method of manufacture, using a “picture frame” structure sealed, for example, with a high moisture and oxygen barrier polymer film and featuring, for example, a printed cathode deposited on an optional, highly conductive carbon printed cathode collector with a printed or a foil strip anode placed adjacent to the cathode. A viscous or gelled electrolyte is dispensed and / or printed in the cell, and a top laminate can then be sealed onto the picture frame. Such a construction could allow the entire cell to be made on a printing press, for example, as well as gives the opportunity to integrate the battery directly with an electronic application, for example.
Owner:BLUE SPARK INNOVATIONS LLC
Thin printable electrochemical cell utilizing a “picture frame” and methods of making the same
Owner:BLUE SPARK INNOVATIONS LLC
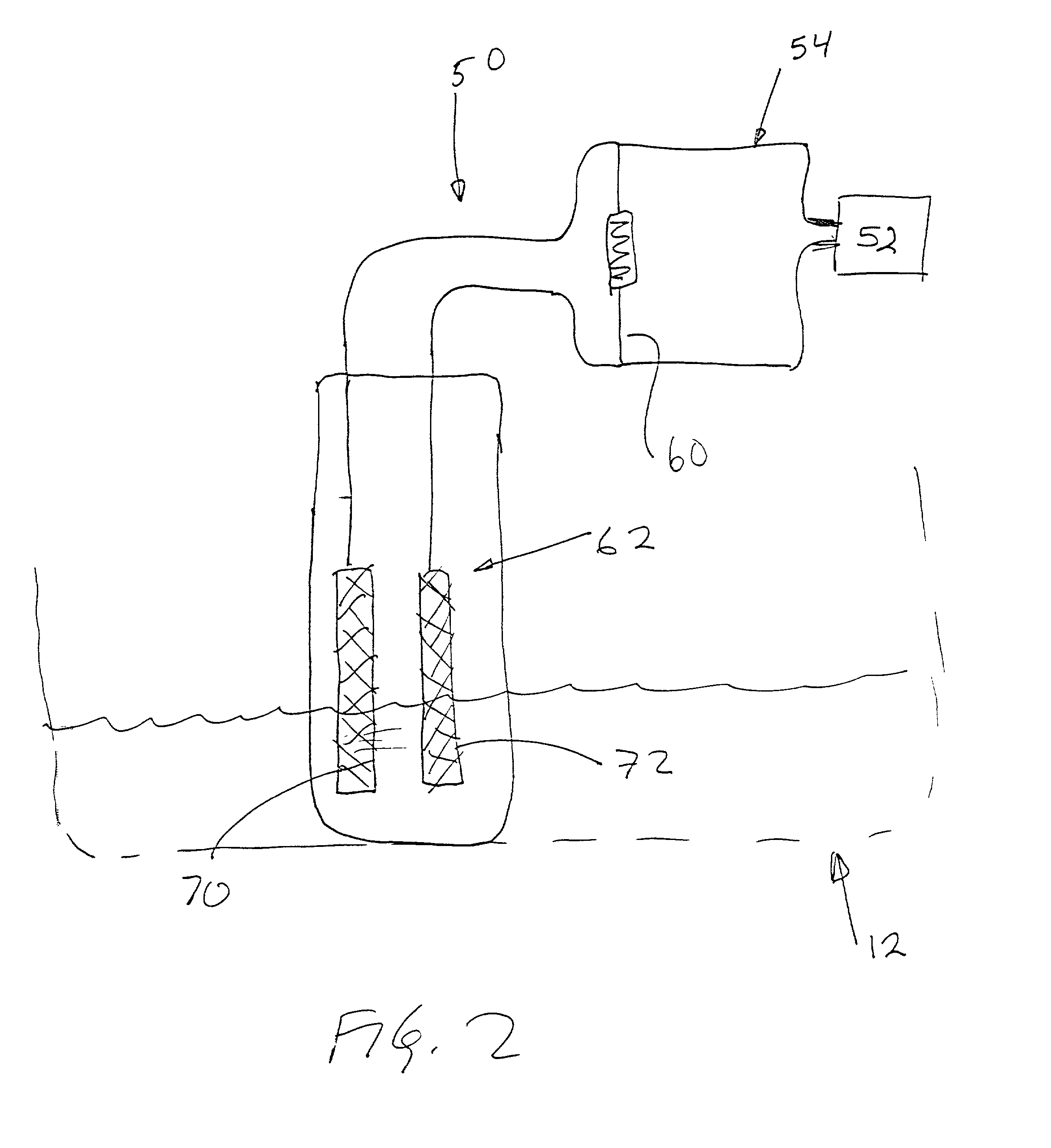
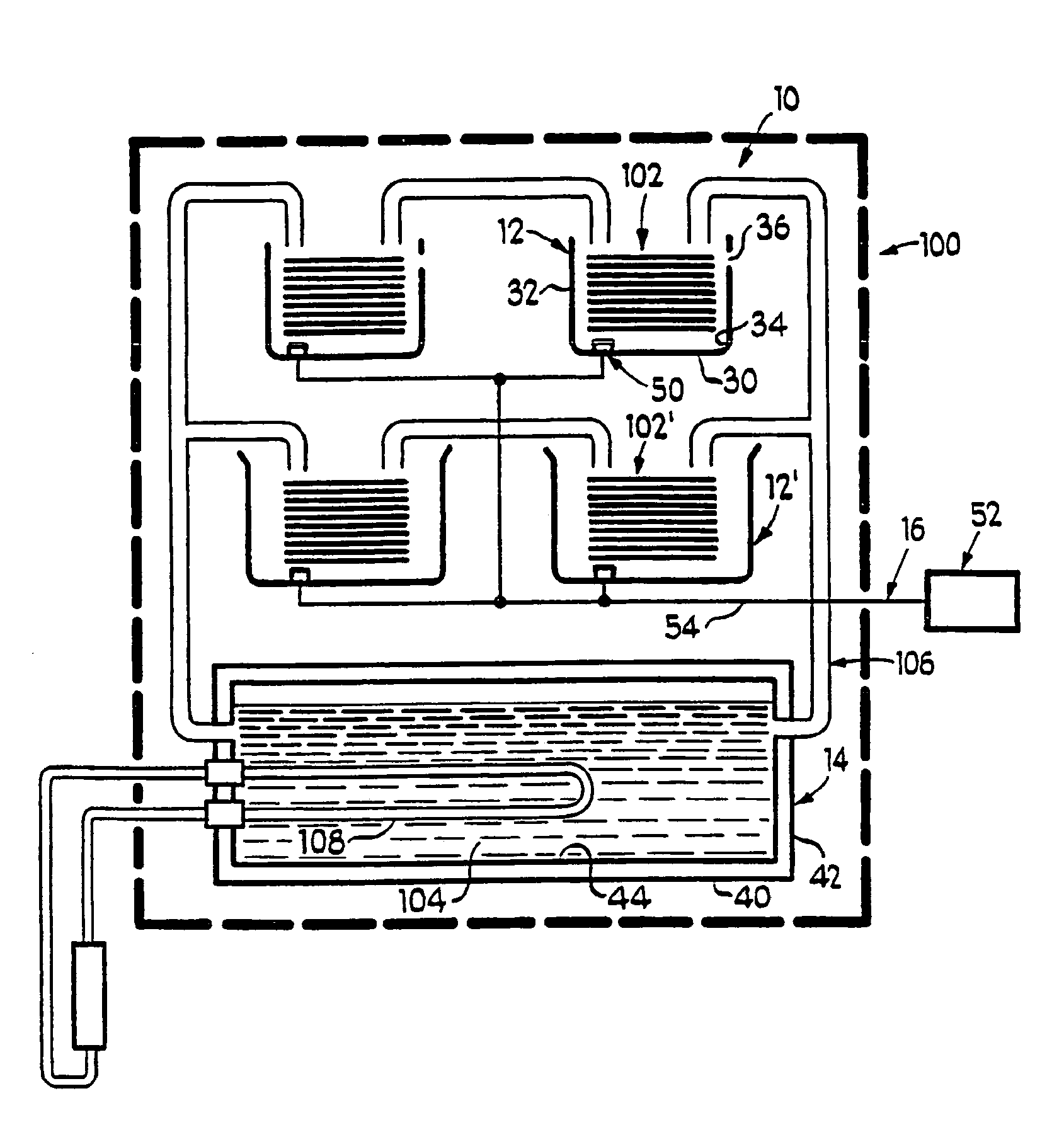
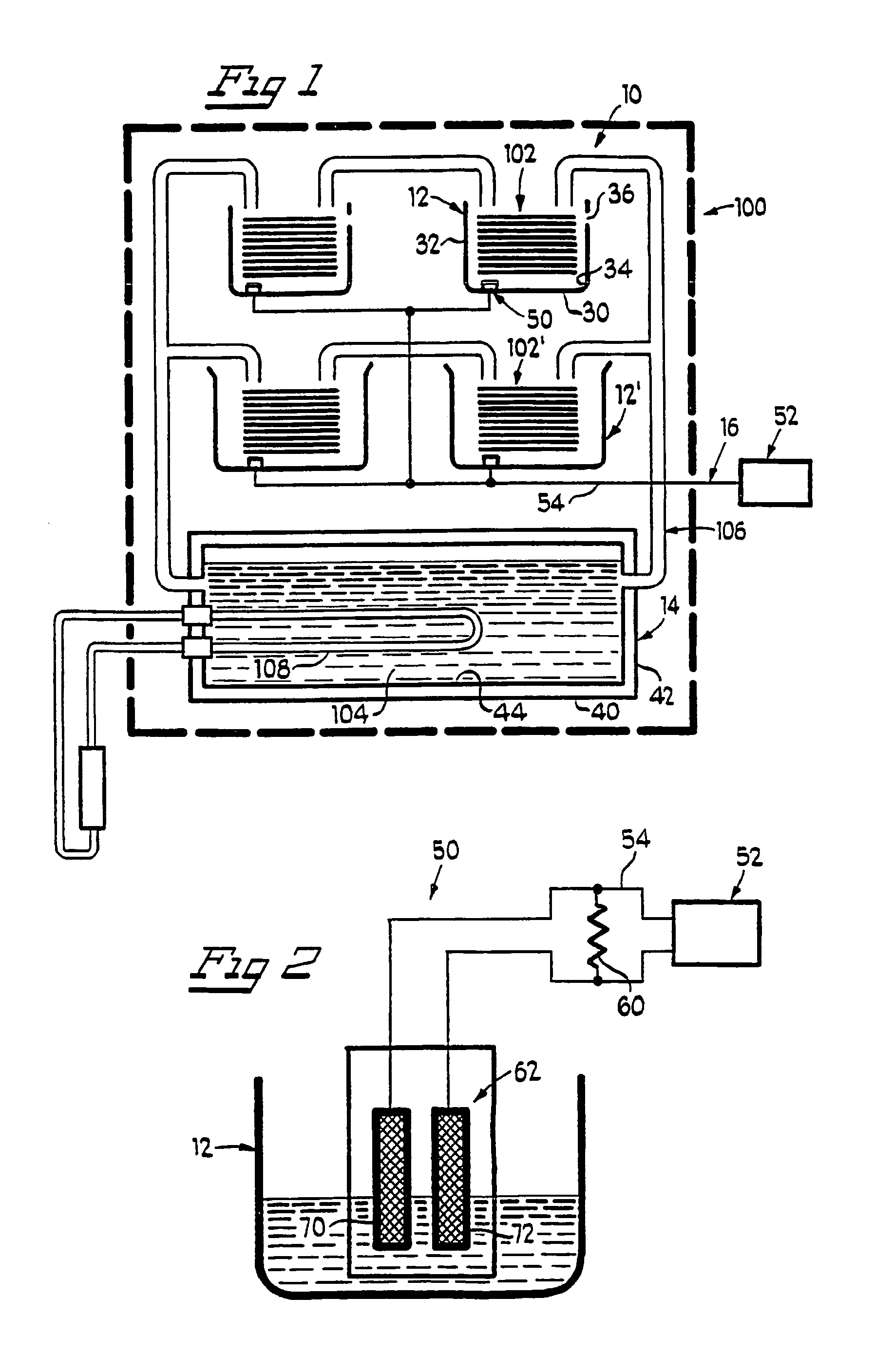
Leak sensor for flowing electrolyte batteries
InactiveUS20030008203A1Primary cell to battery groupingPrimary cell maintainance/servicingEngineeringLeak detection
A leak detection system for a flowing electrolyte battery comprising a containment member associated with at least one of a stack of a flowing electrolyte battery and an electrolyte reservoir of a flowing electrolyte battery and a sensing member for sensing a fluid leak within the containment member.
Owner:LARGO CLEAN ENERGY CORP
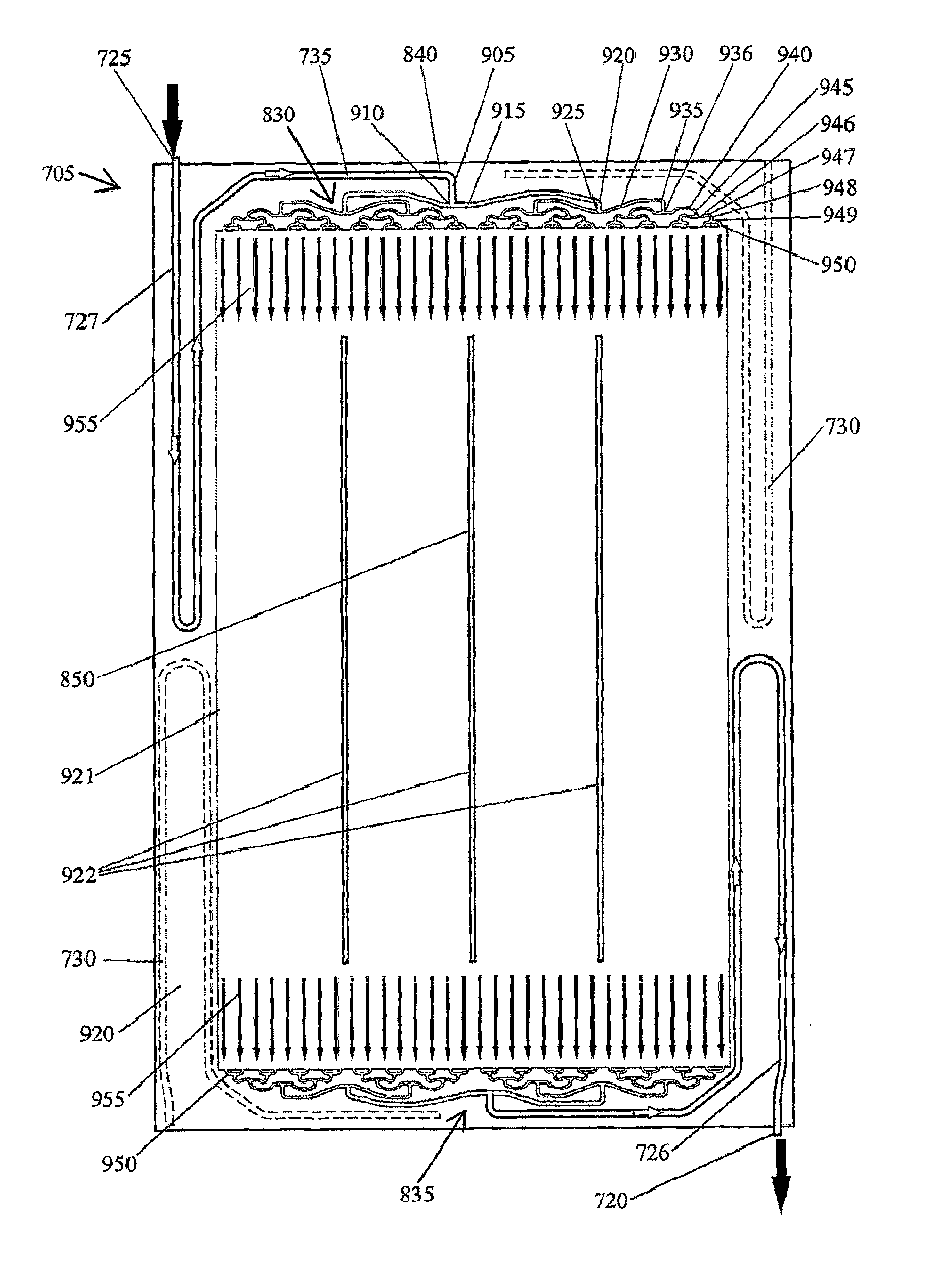
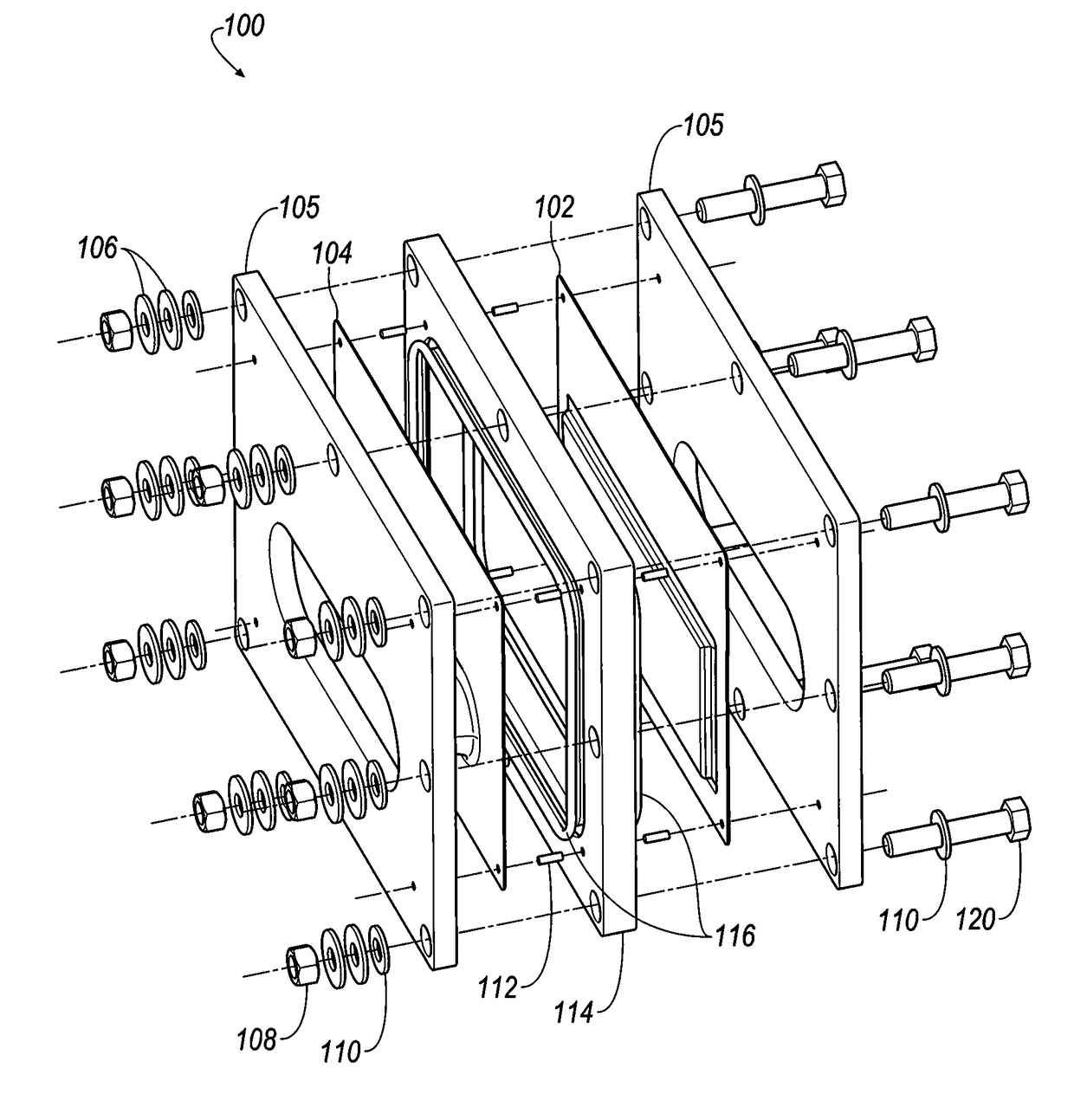
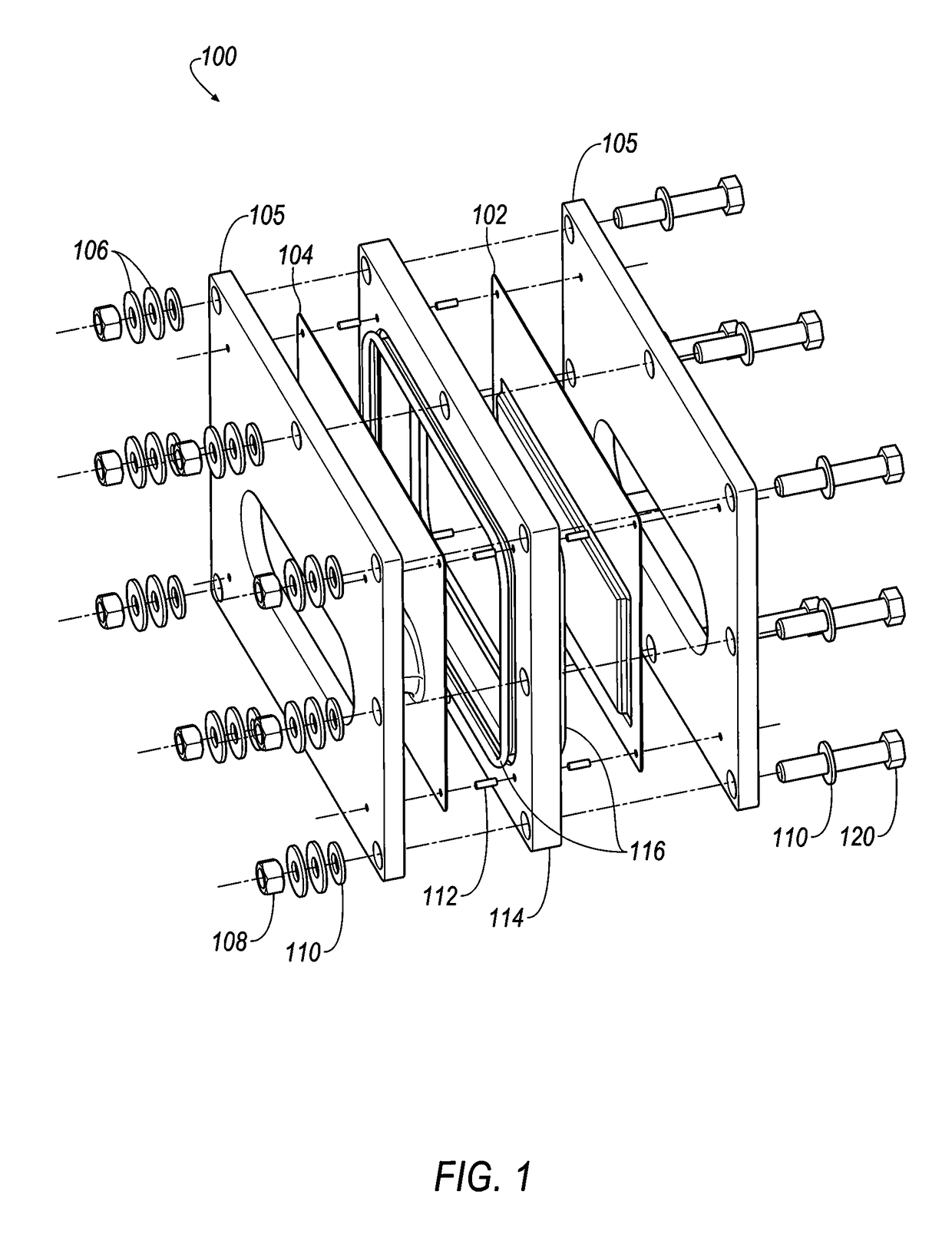
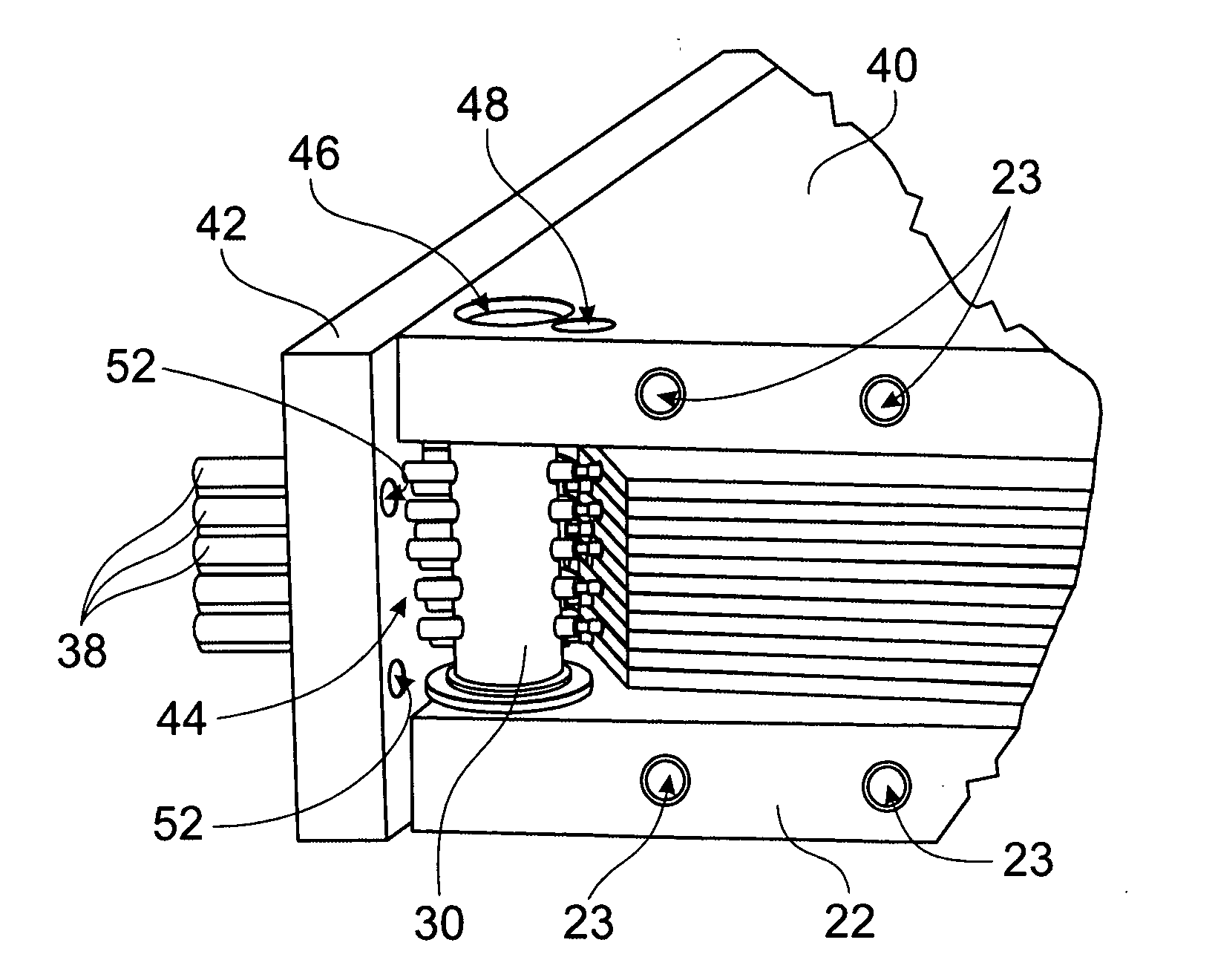
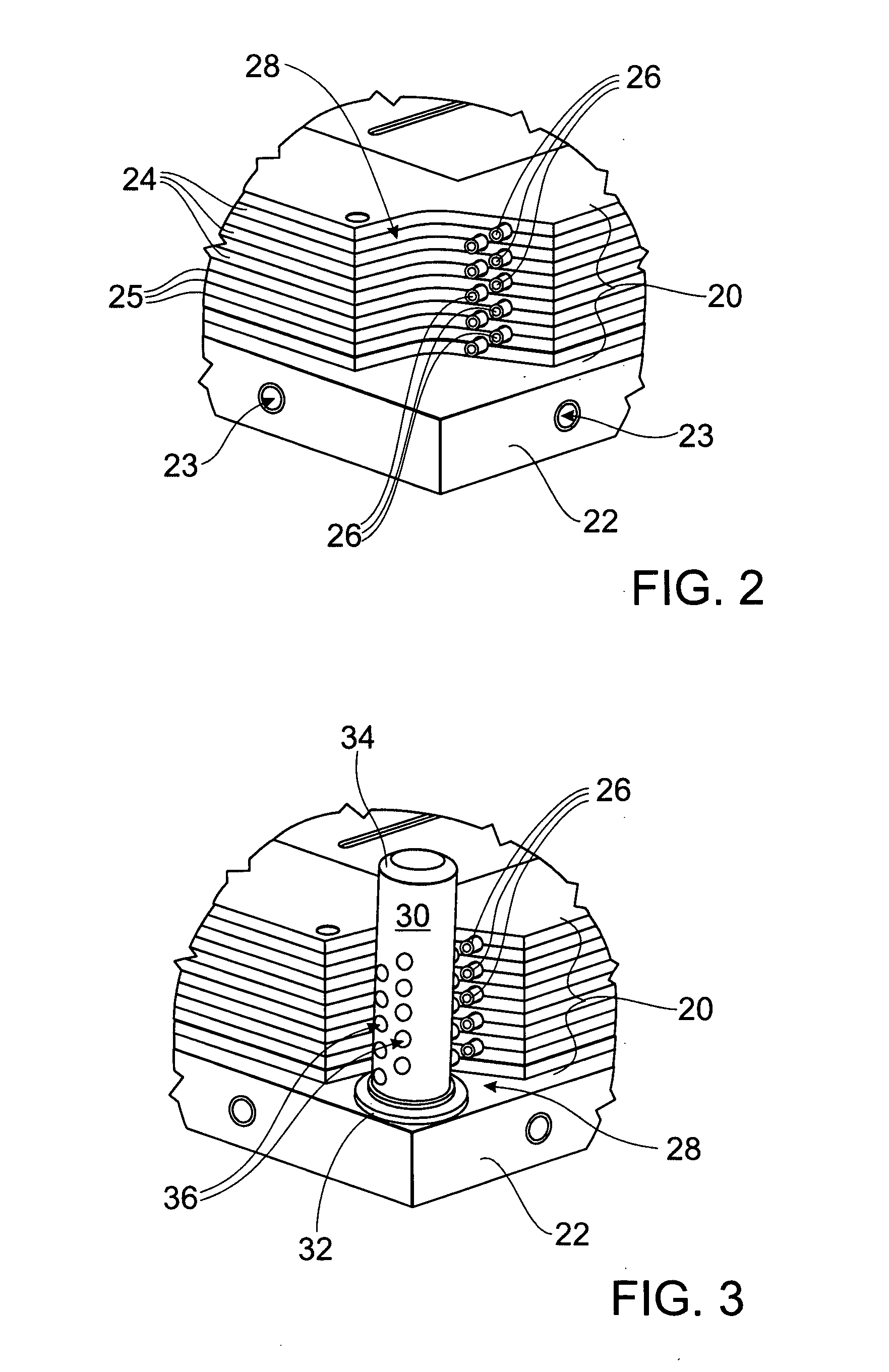
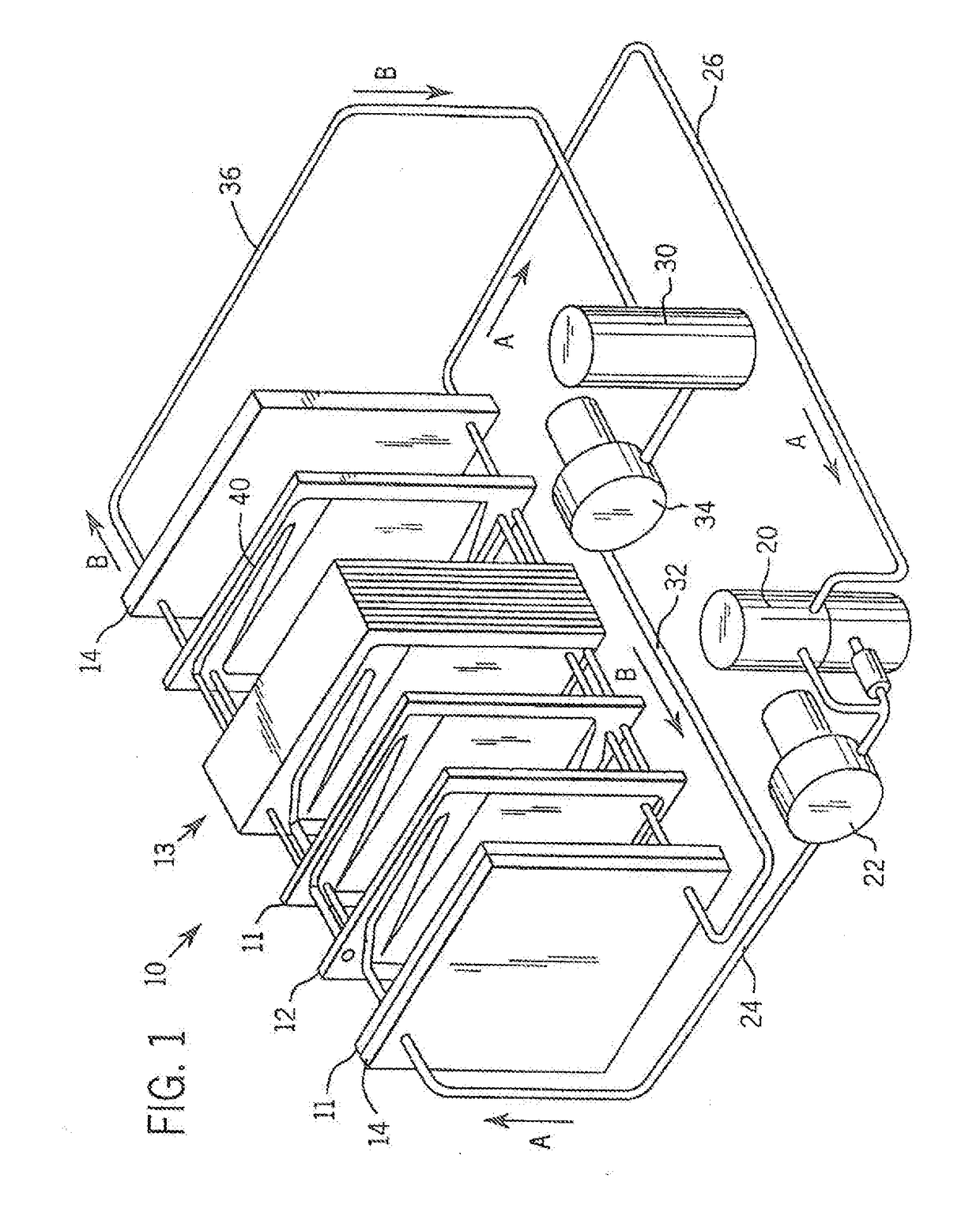
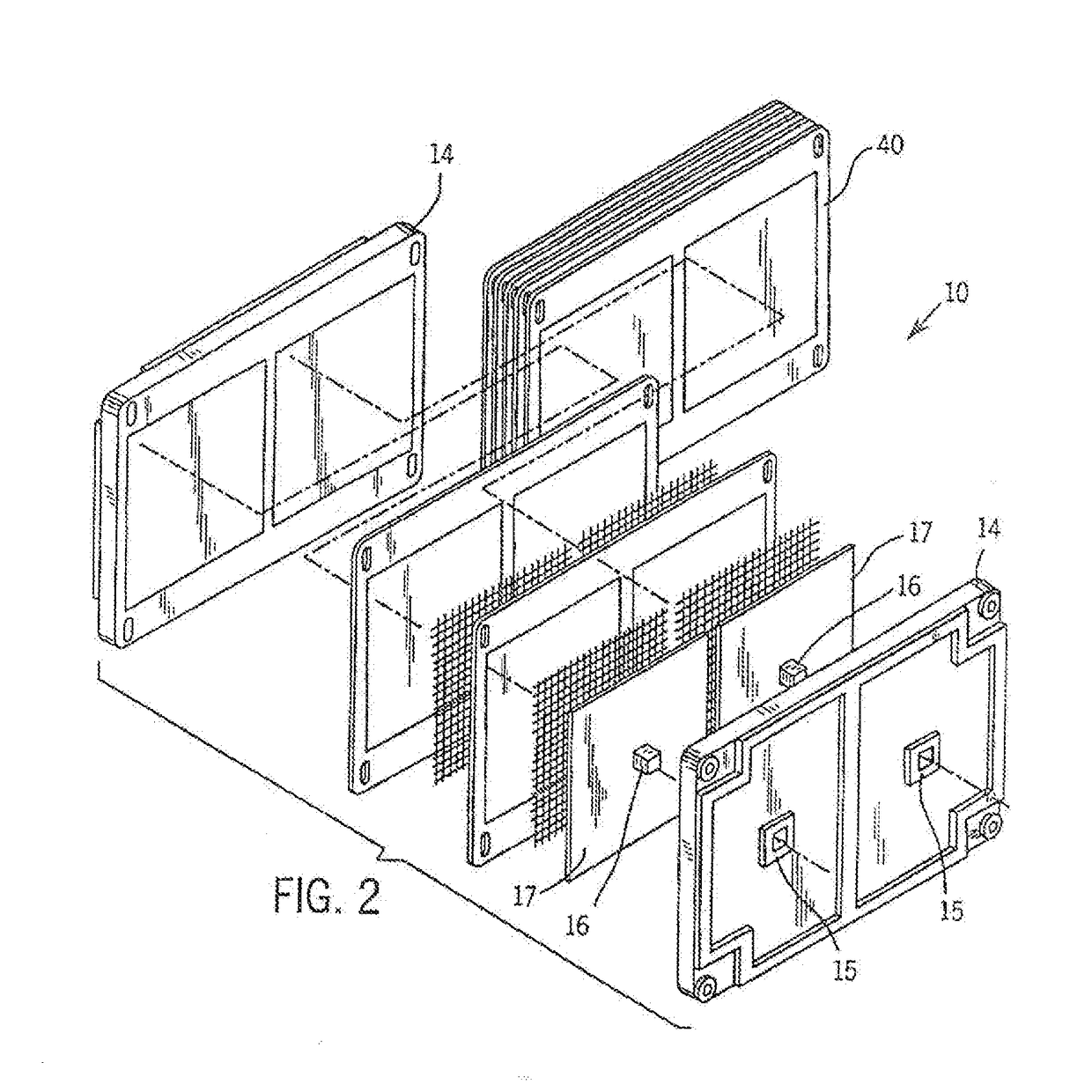
Cell stack for a flowing electrolyte battery
ActiveUS20100119937A1Increase in sizeReduce manufacturing costElectrolyte moving arrangementsAlkaline accumulatorsReduced sizeEngineering
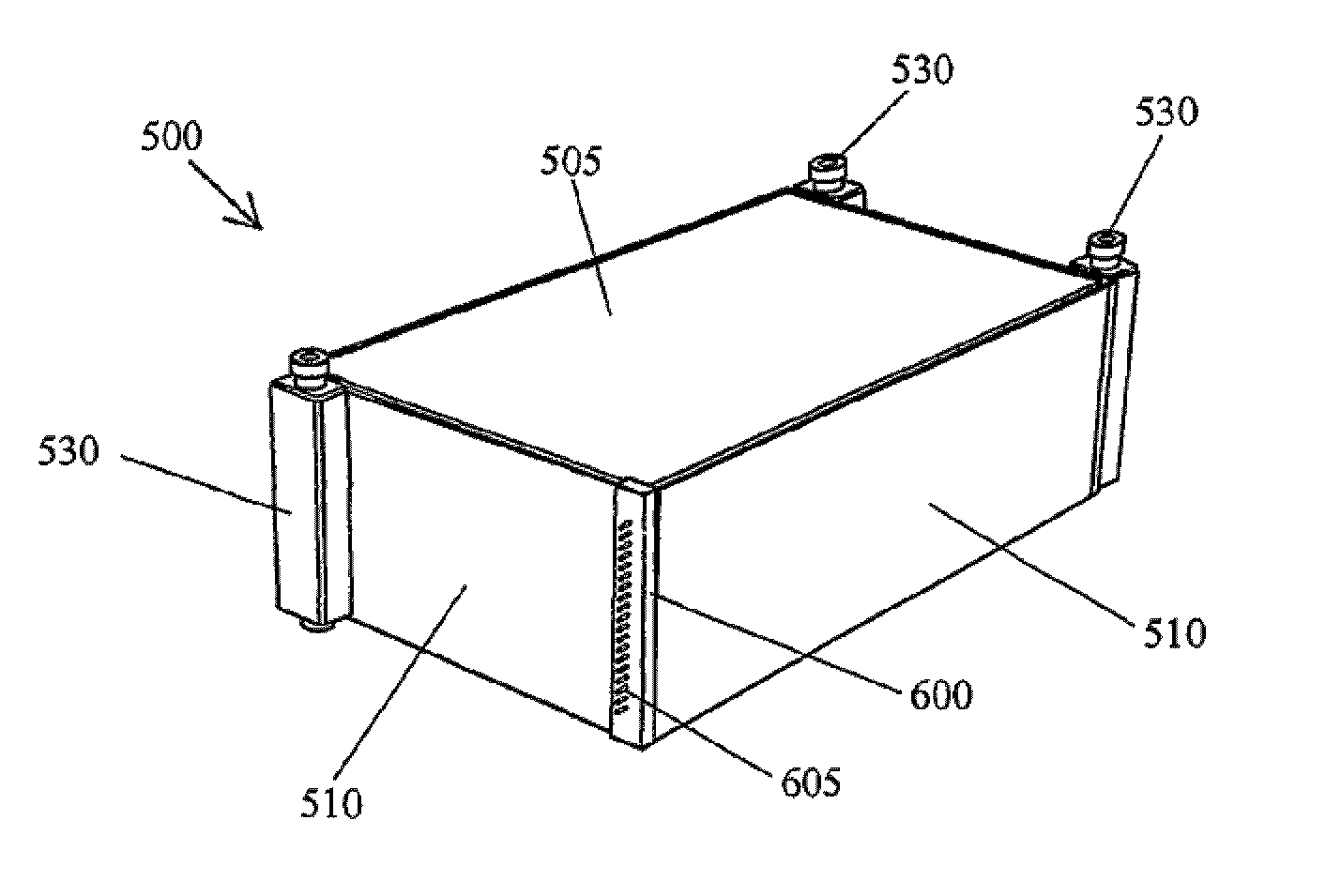
A cell stack (700) as provided enables a flowing electrolyte battery to have a reduced size and weight. The cell stack (700) includes a casing having a positive polarity end and a negative polarity end. A plurality of half cells (805) are inside the casing, and each half cell (805) includes an electrode plate (705), an adjacent separator plate (715), and at least one capillary tube (727) positioned between the electrode plate (705) and the adjacent separator plate (715). The capillary tube (727) has a first end extending outside of the half cell (805) and a second end located inside the half cell (805). At least one manifold (530) is in hydraulic communication with a plurality of capillary tube ends including the first end of the capillary tube (727) in each half cell (805). The capillary tube (727) in each half cell (805) enables electrolyte to circulate through the plurality of half cells (805) via the at least one manifold (530).
Owner:REDFLOW PTY LTD
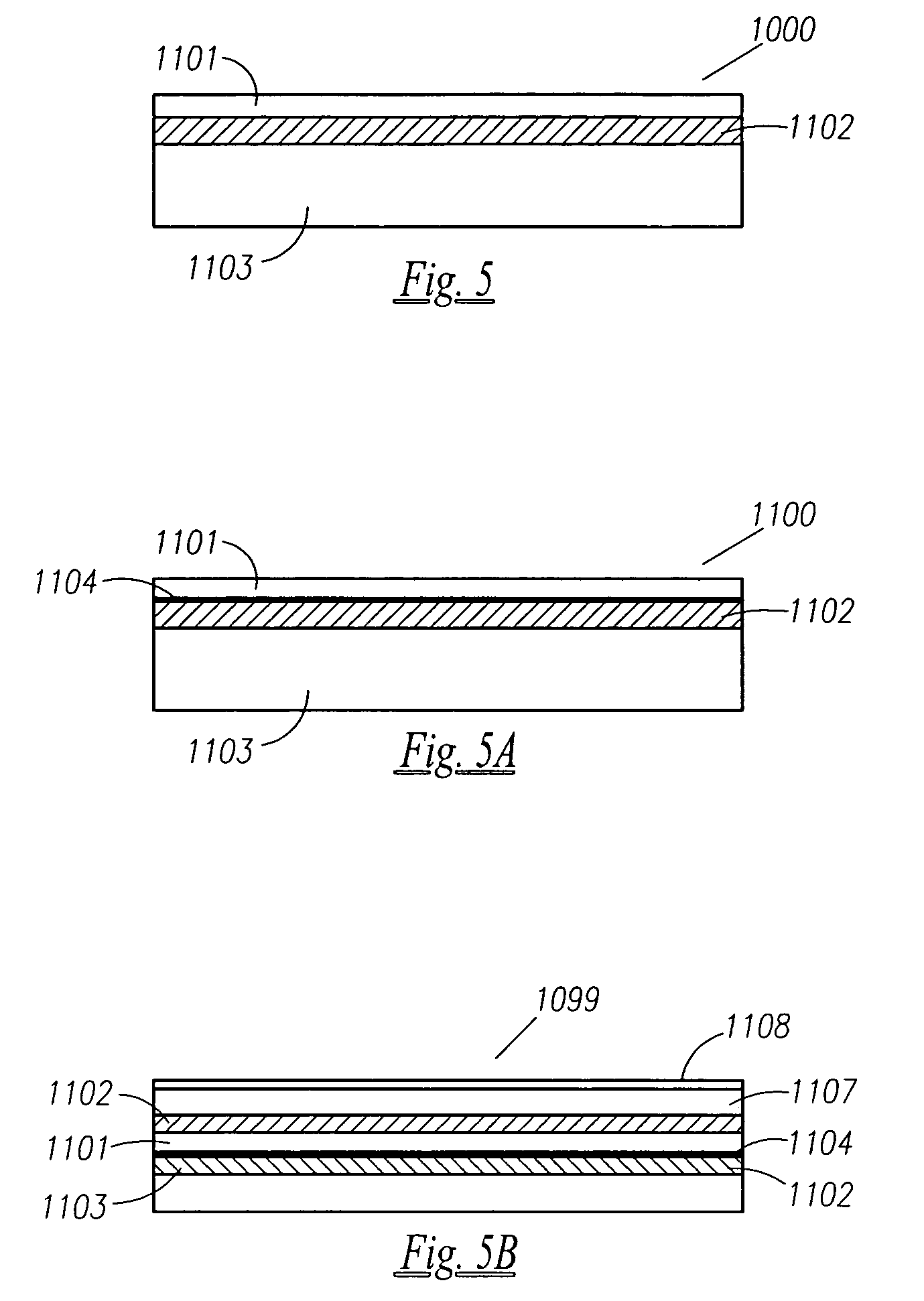
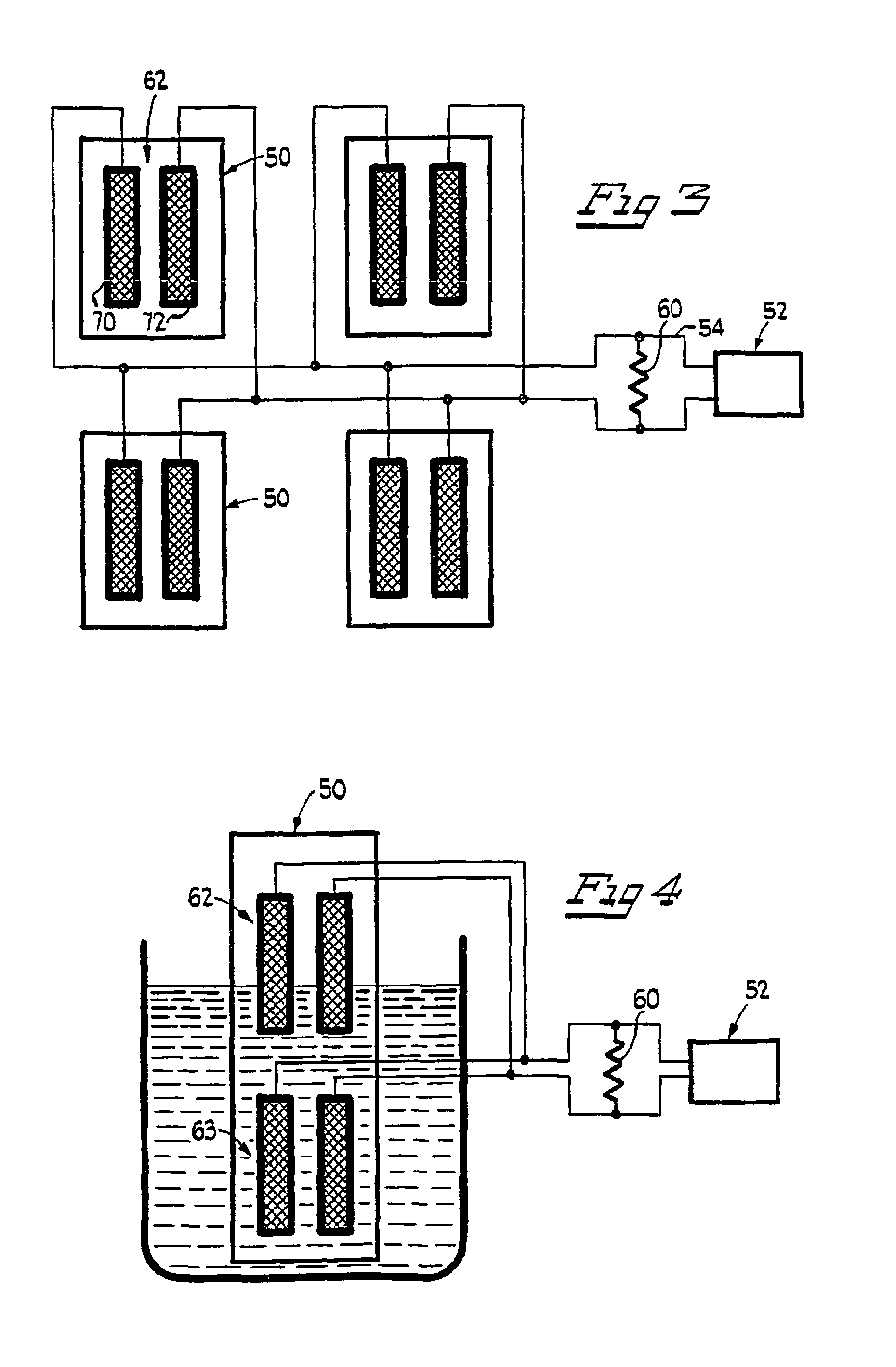
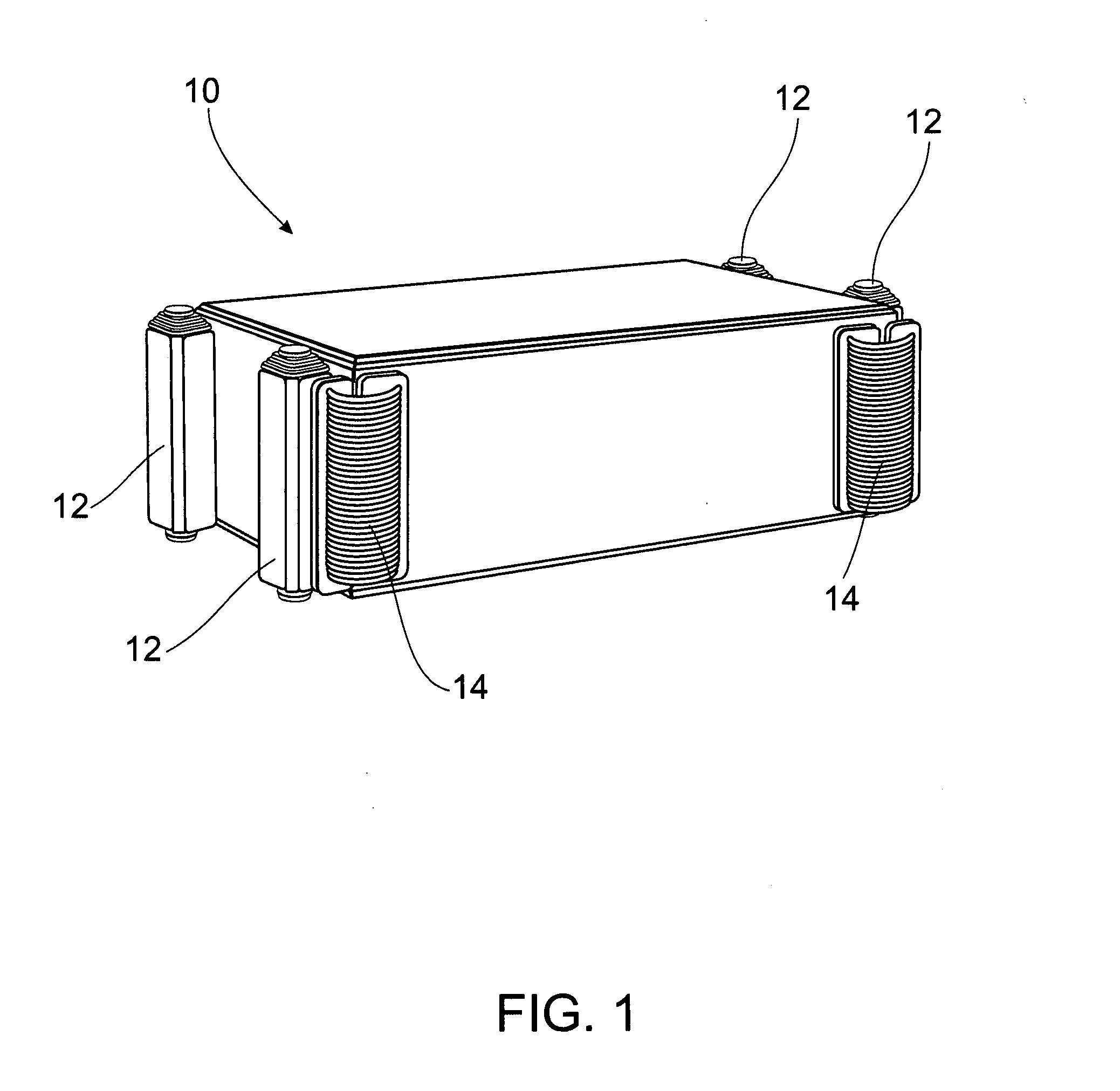
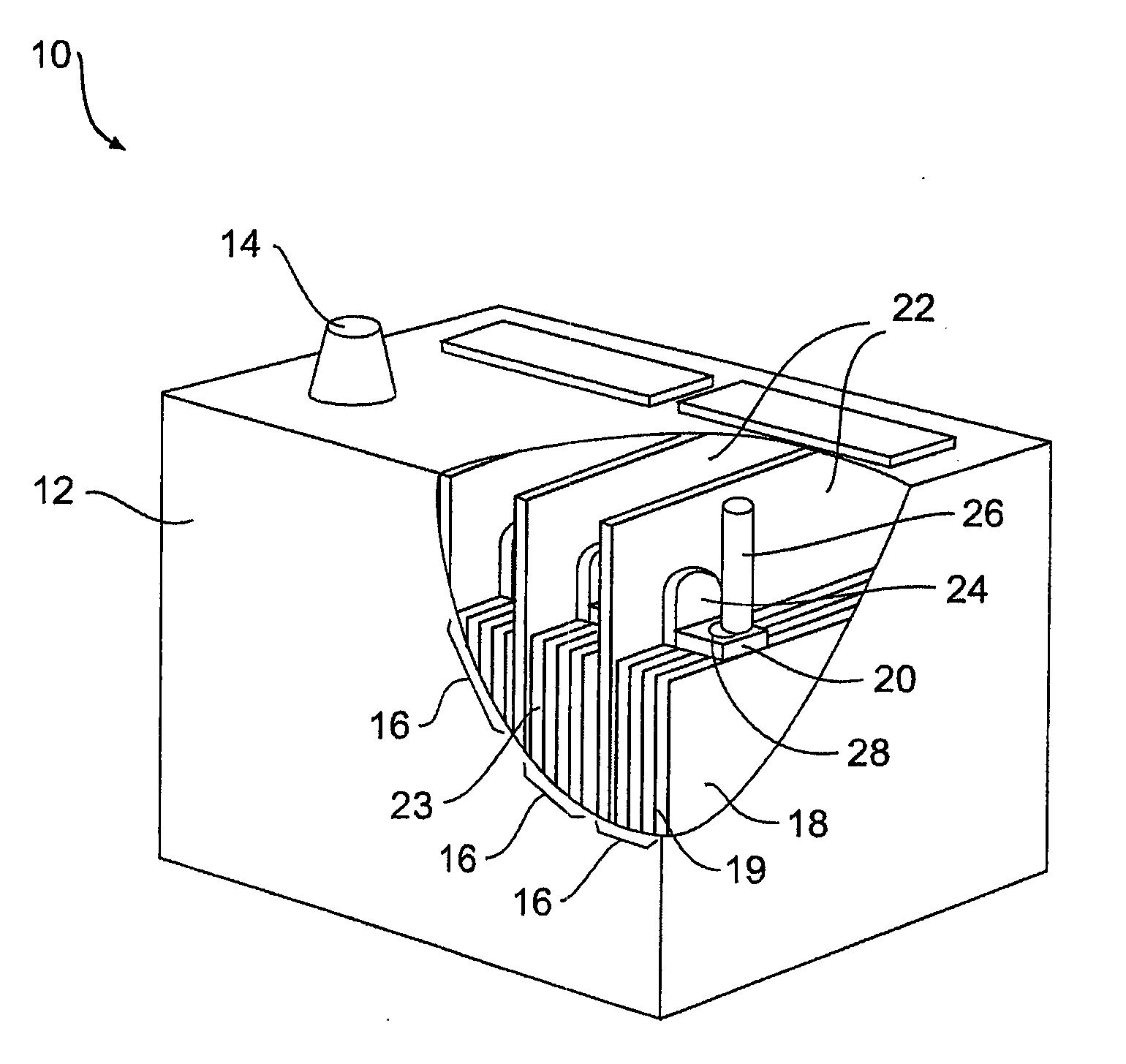
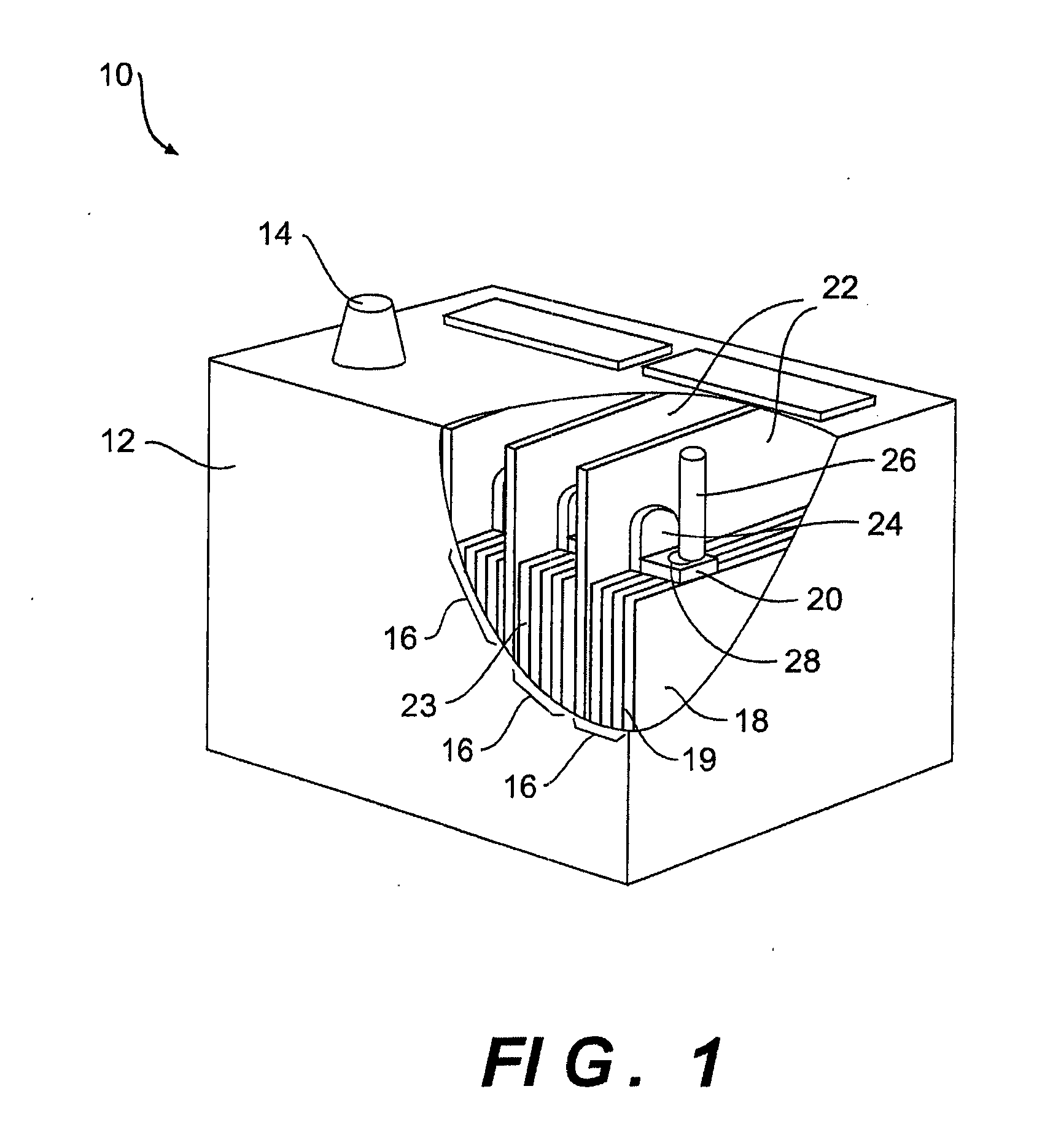
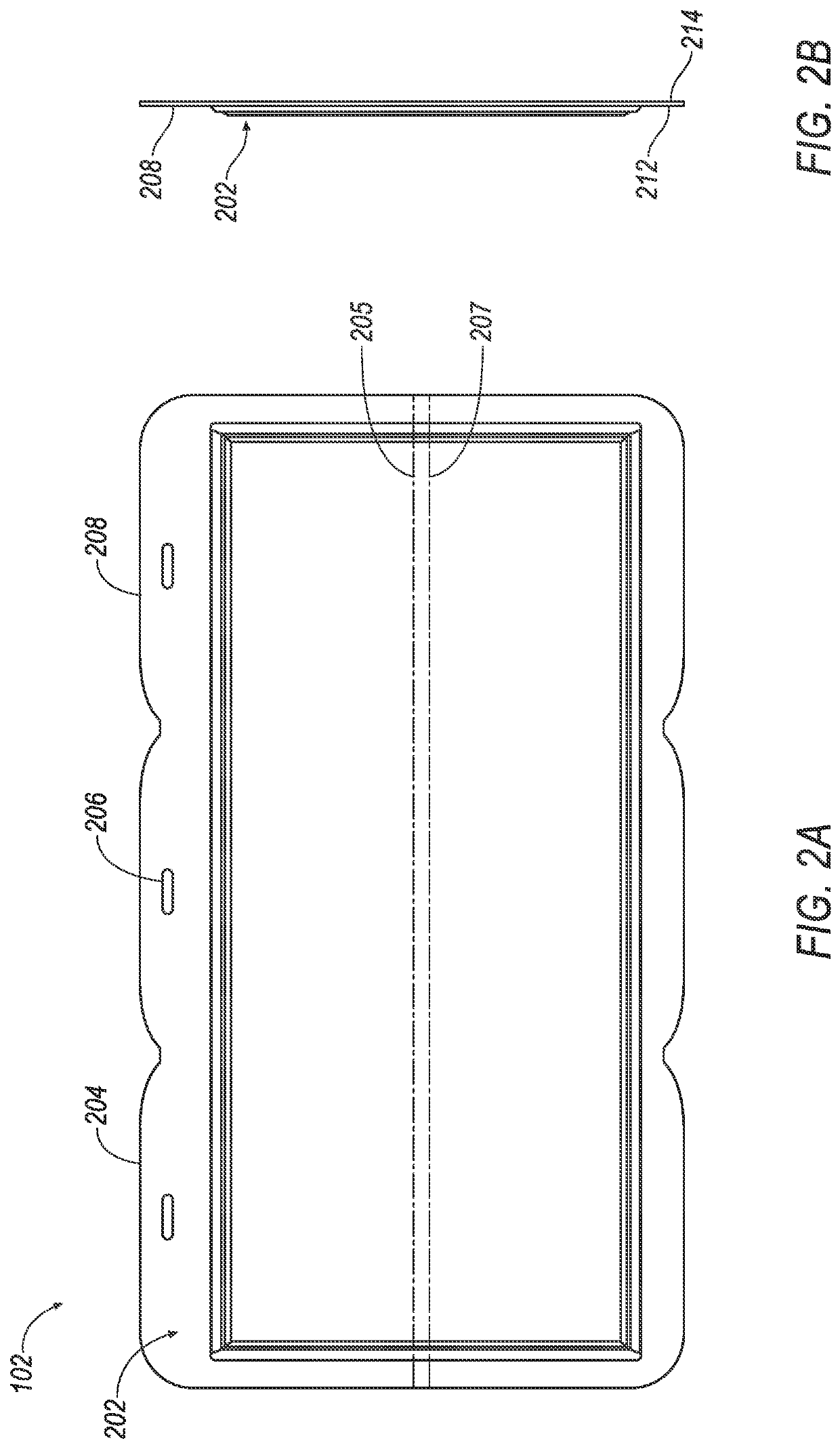
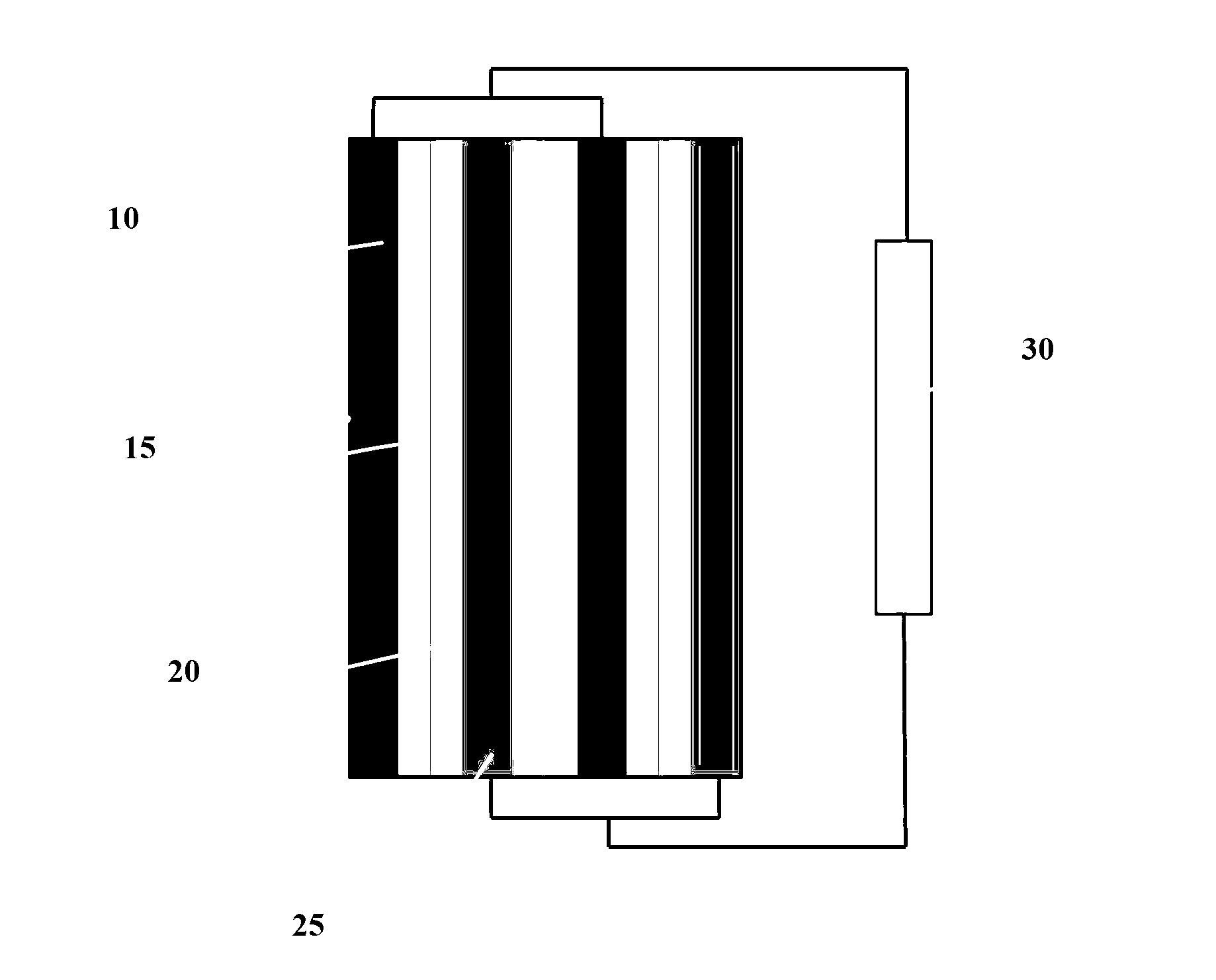
Multi-cell battery
ActiveUS20130323565A1Easy to foldPrimary cell to battery groupingCylindrical casing cells/batteryEngineeringElectrochemical cell
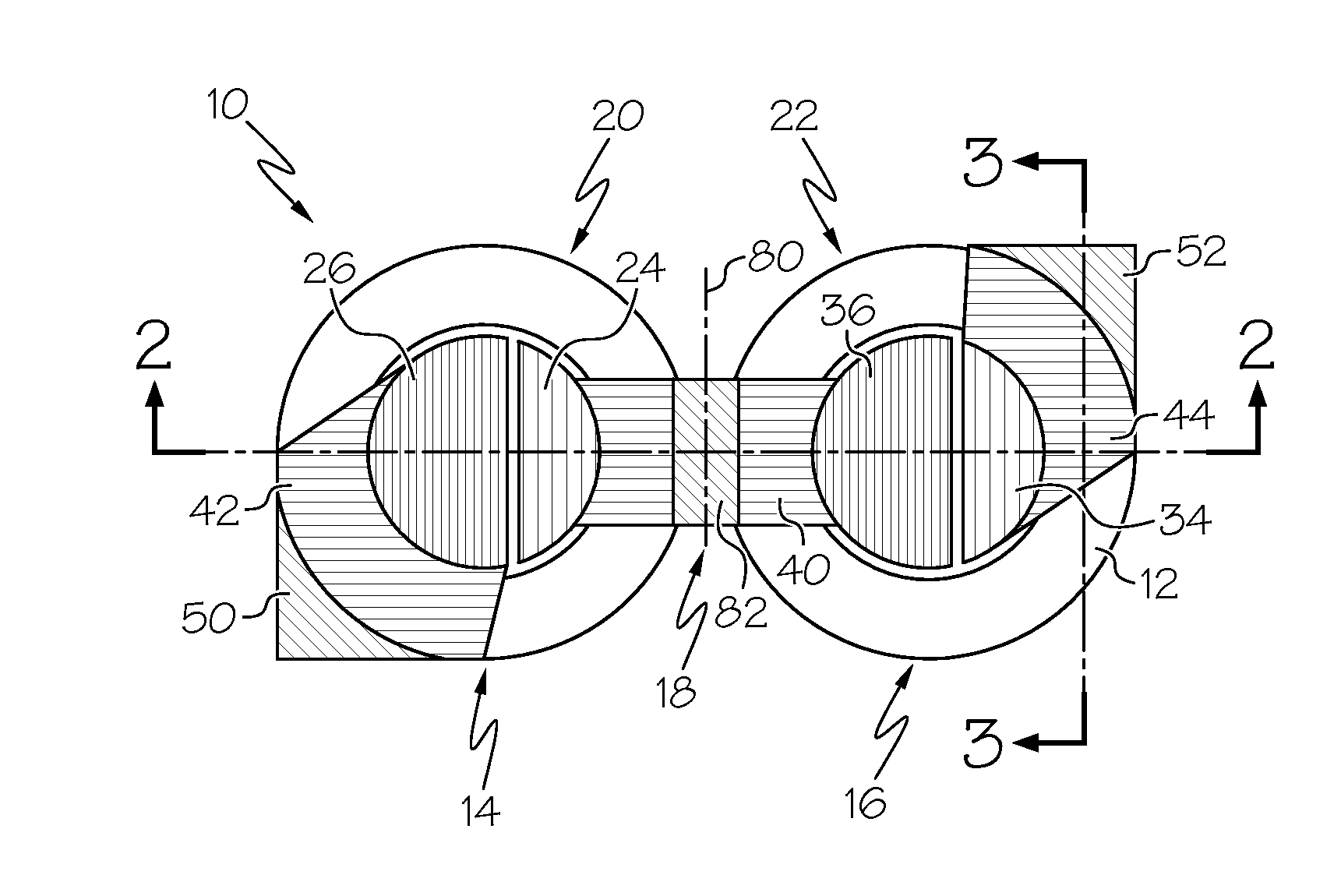
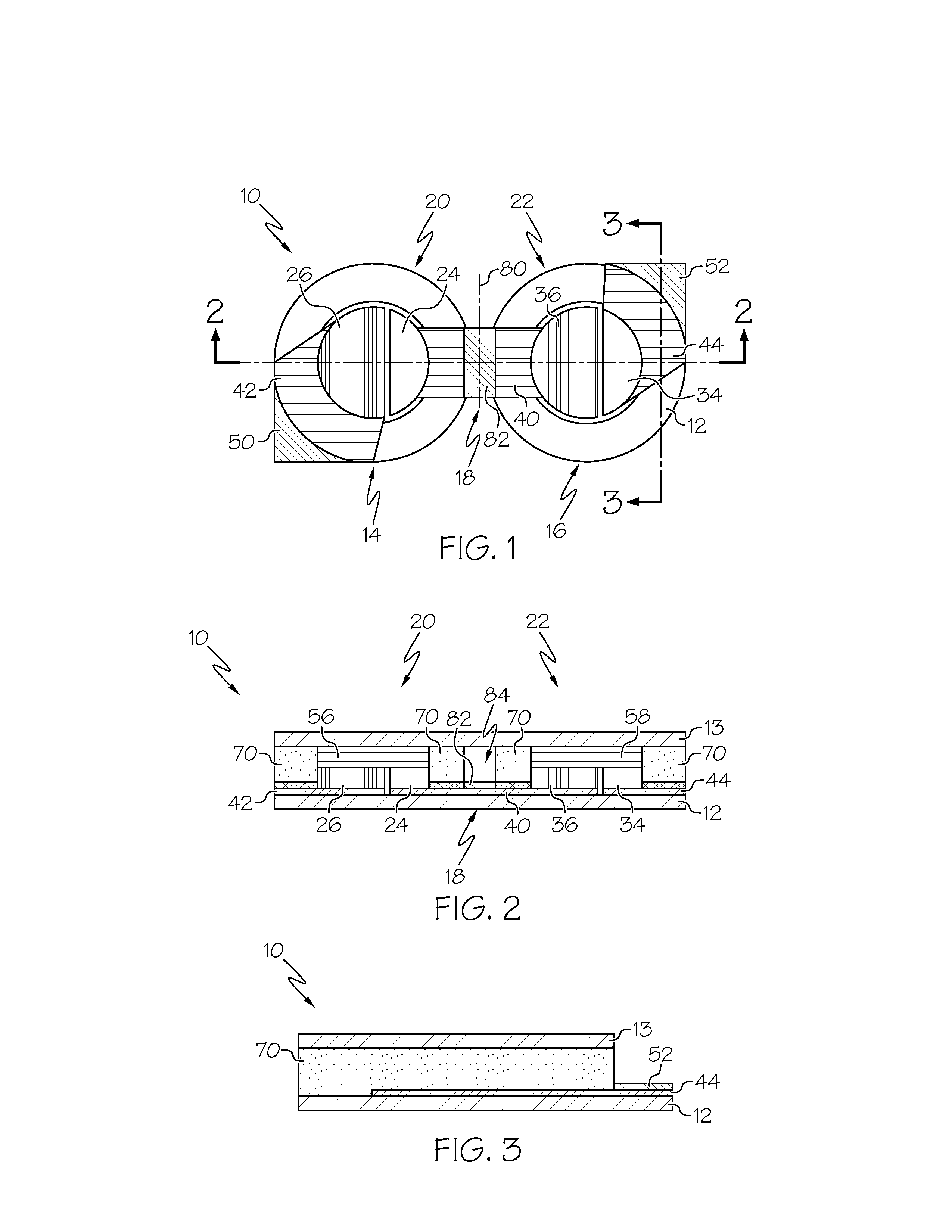
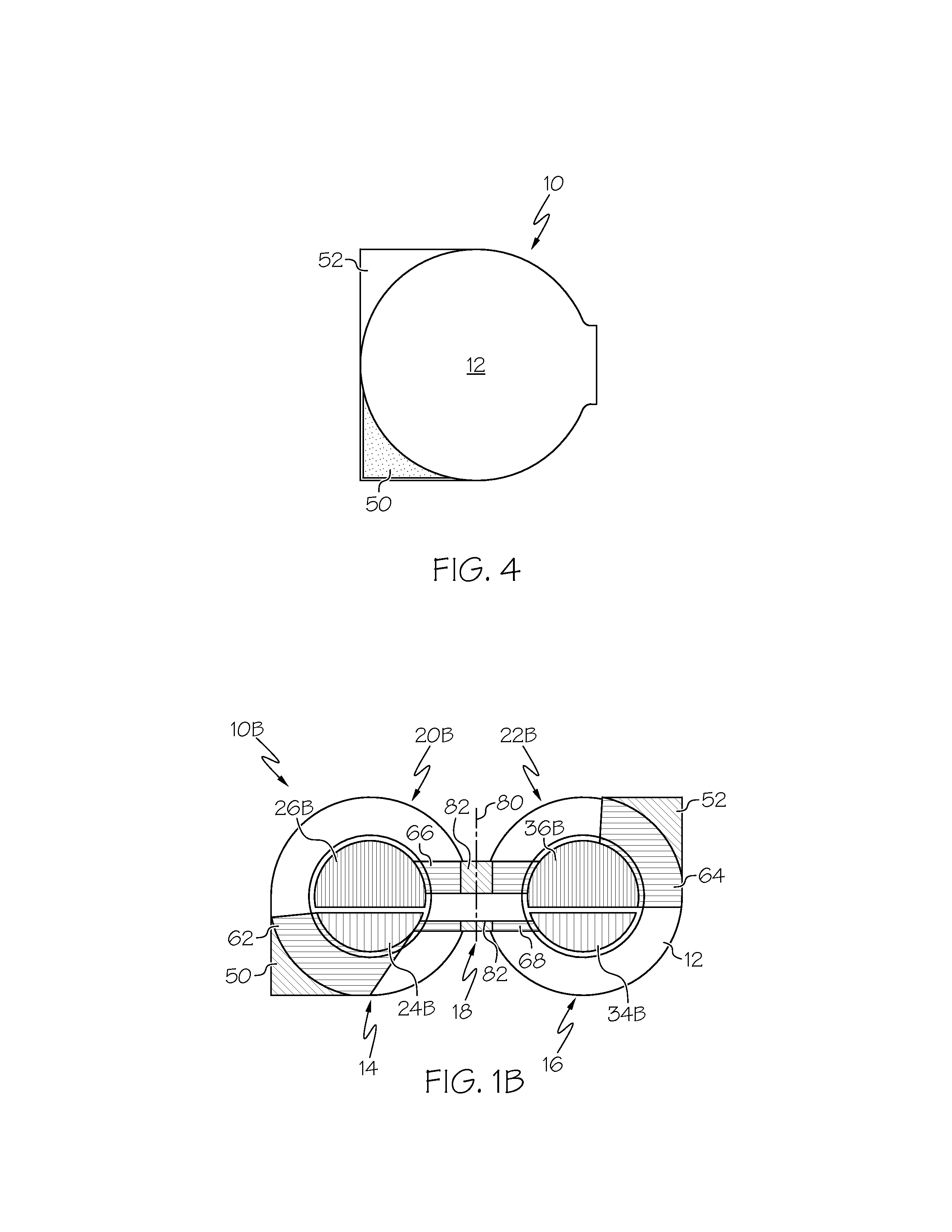
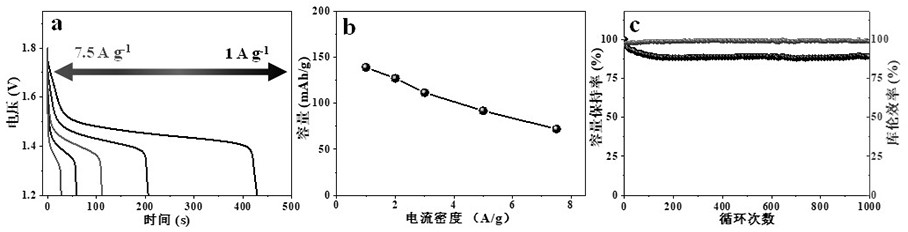
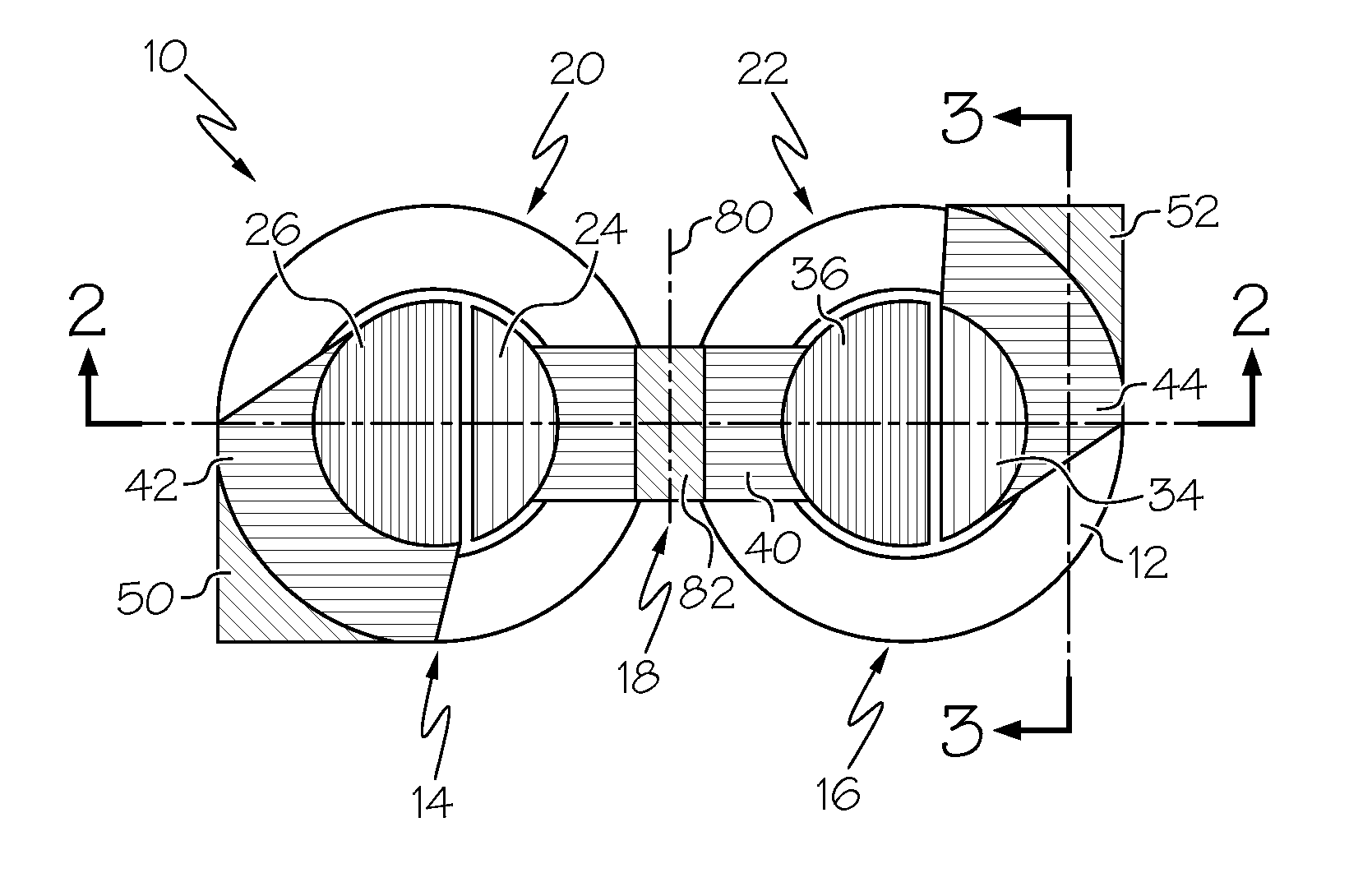
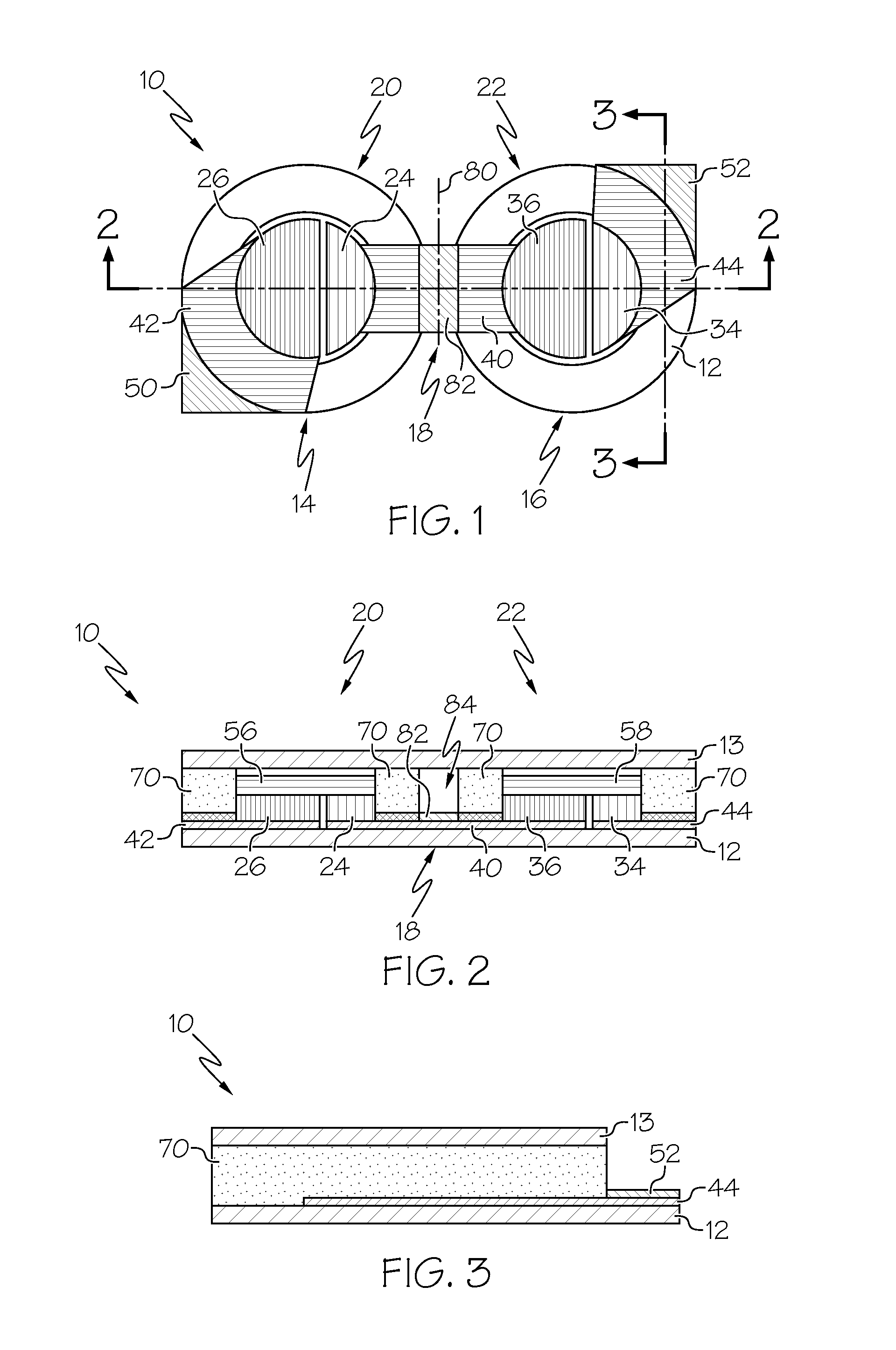
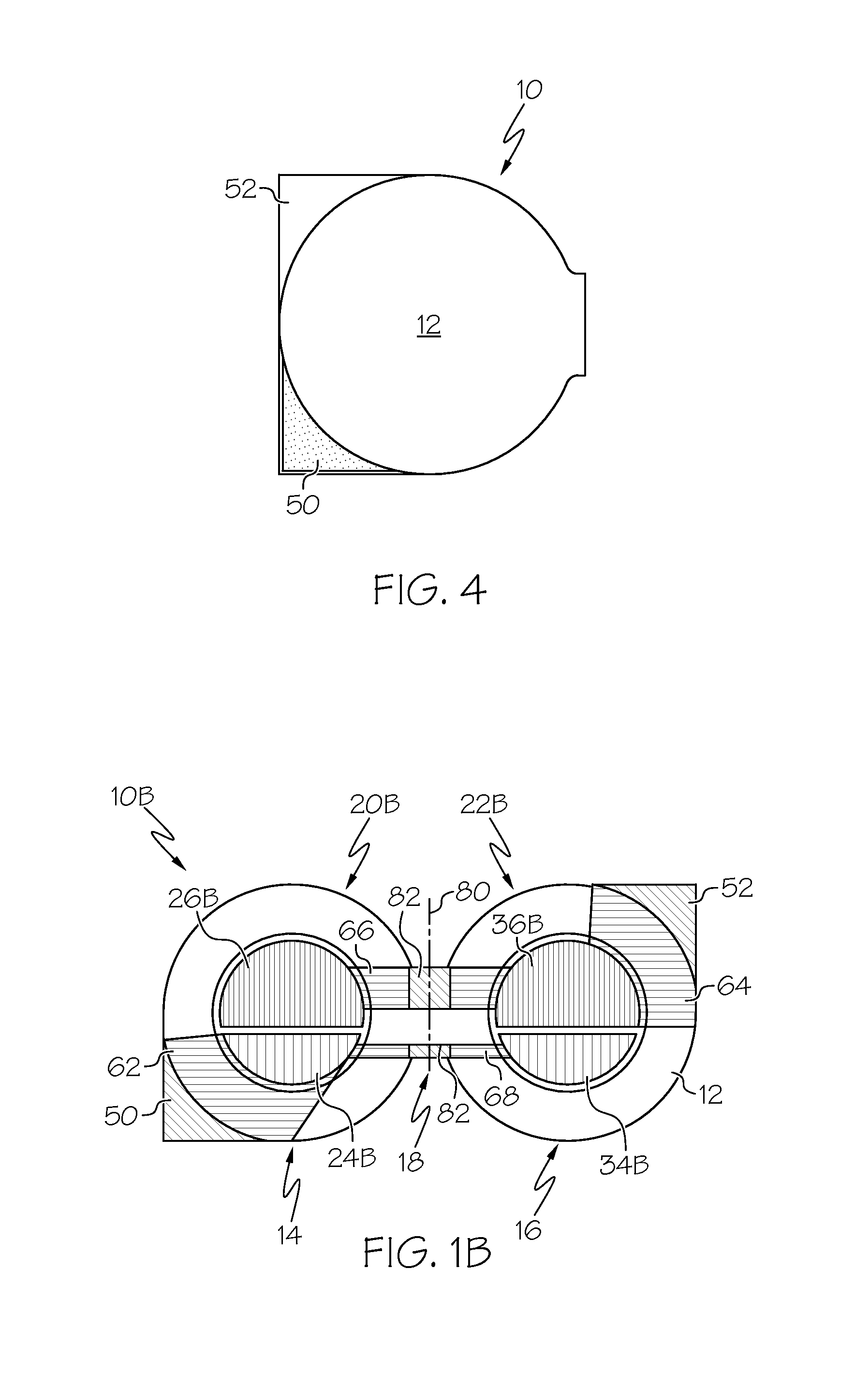
A flexible battery includes a first substrate layer with a first cell portion, a second cell portion, and a bridge portion connecting the first and second cell portions. An electrical bridge electrically couples a first electrochemical cell to a second electrochemical cell in series or parallel, and an electrical bridge is flexible and extends across the bridge portion of the first substrate layer. A second substrate layer is connected to the first substrate layer such that both of the first and second electrochemical cells are separately sealed. The flexible battery is configured to be folded over itself along the bridge portion such that the first and second electrochemical cells are arranged in a covering relationship. Optionally, an open gap area is disposed over the bridge portion of the first substrate to facilitate folding the flexible battery over itself along a line extending through the bridge portion.
Owner:BLUE SPARK INNOVATIONS LLC
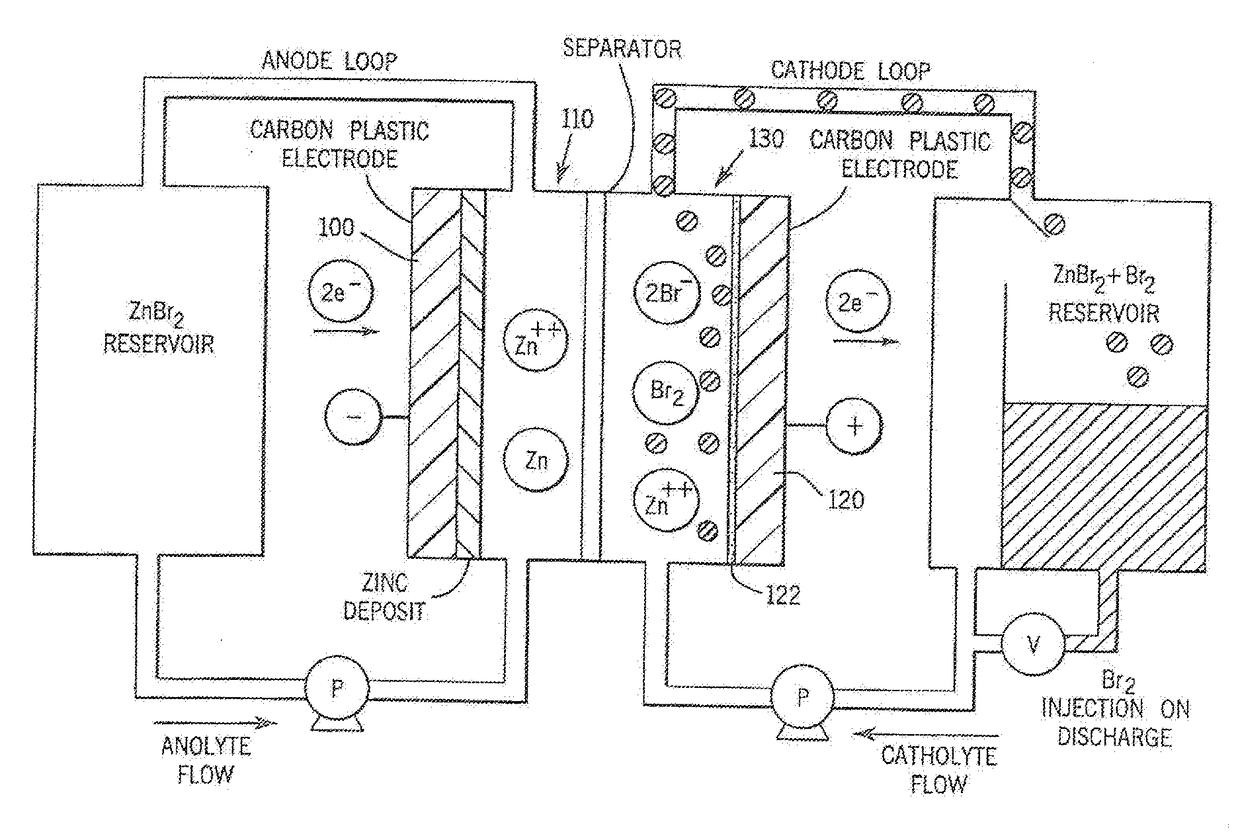
Reversible polarity operation and switching method for ZnBr flow battery when connected to common DC bus
ActiveUS20120326672A1Reduce manufacturing costSimple structureBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrode thermal treatmentElectrical polarityEngineering
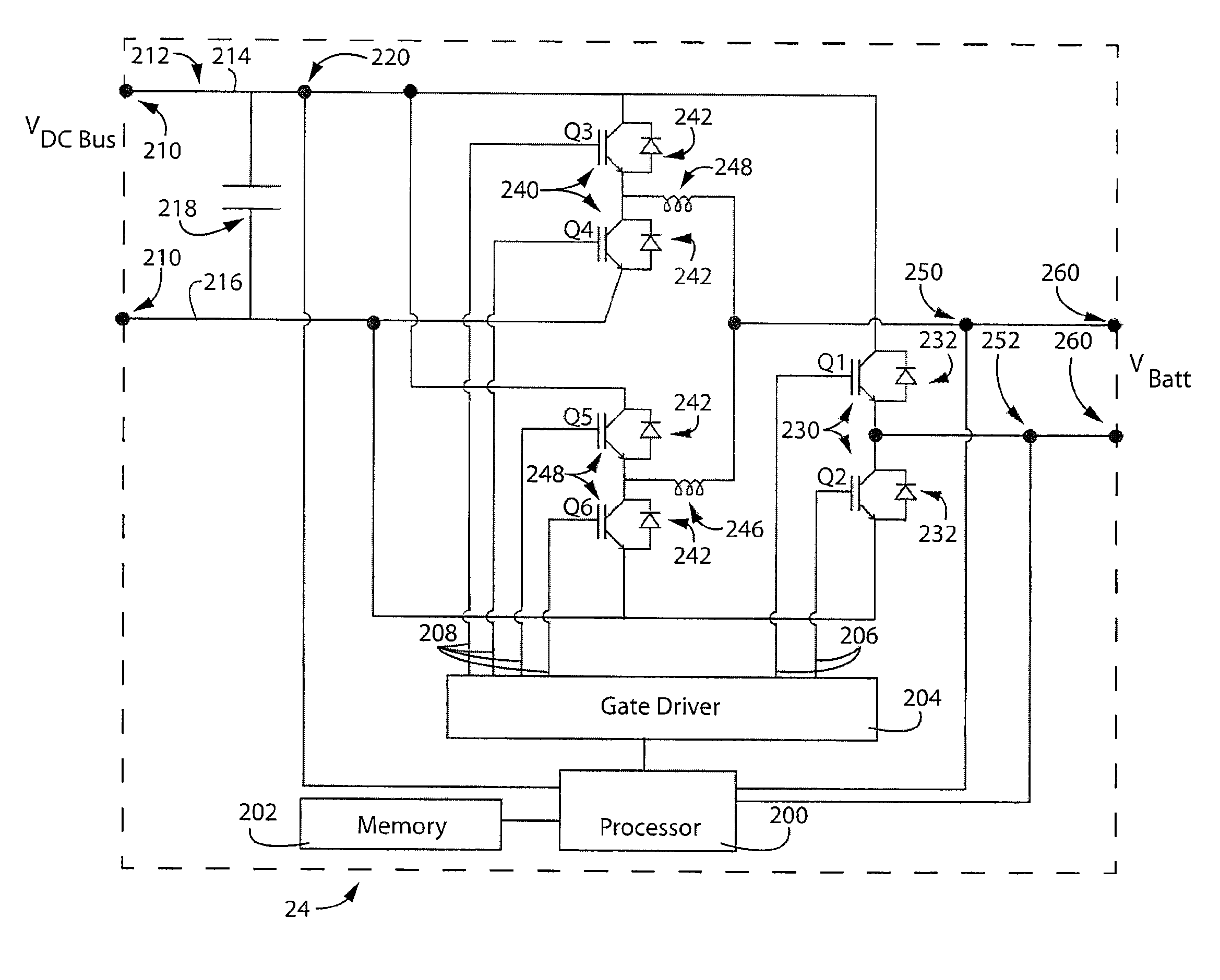
An improved electrolyte battery is provided that includes a tank assembly adapted to hold an amount of an anolyte and a catholyte, a number of cell stacks operably connected to the tank assembly, each stack formed of a number of flow frames disposed between end caps and a number of power converters operatively connected to the cell stacks. The cell stacks are formed with a number of flow frames each including individual inlets and outlets for anolyte and catholyte fluids and a separator disposed between flow frames defining anodic and cathodic half cells between each pair of flow frames. The power converter is configured to connect the battery with either forward or reverse polarity to a DC power source, such as a DC bus. The anodic and cathodic half cells switch as a function of the polarity by which the battery is connected to the Dc power source.
Owner:LOTTE CHEM CORP +1
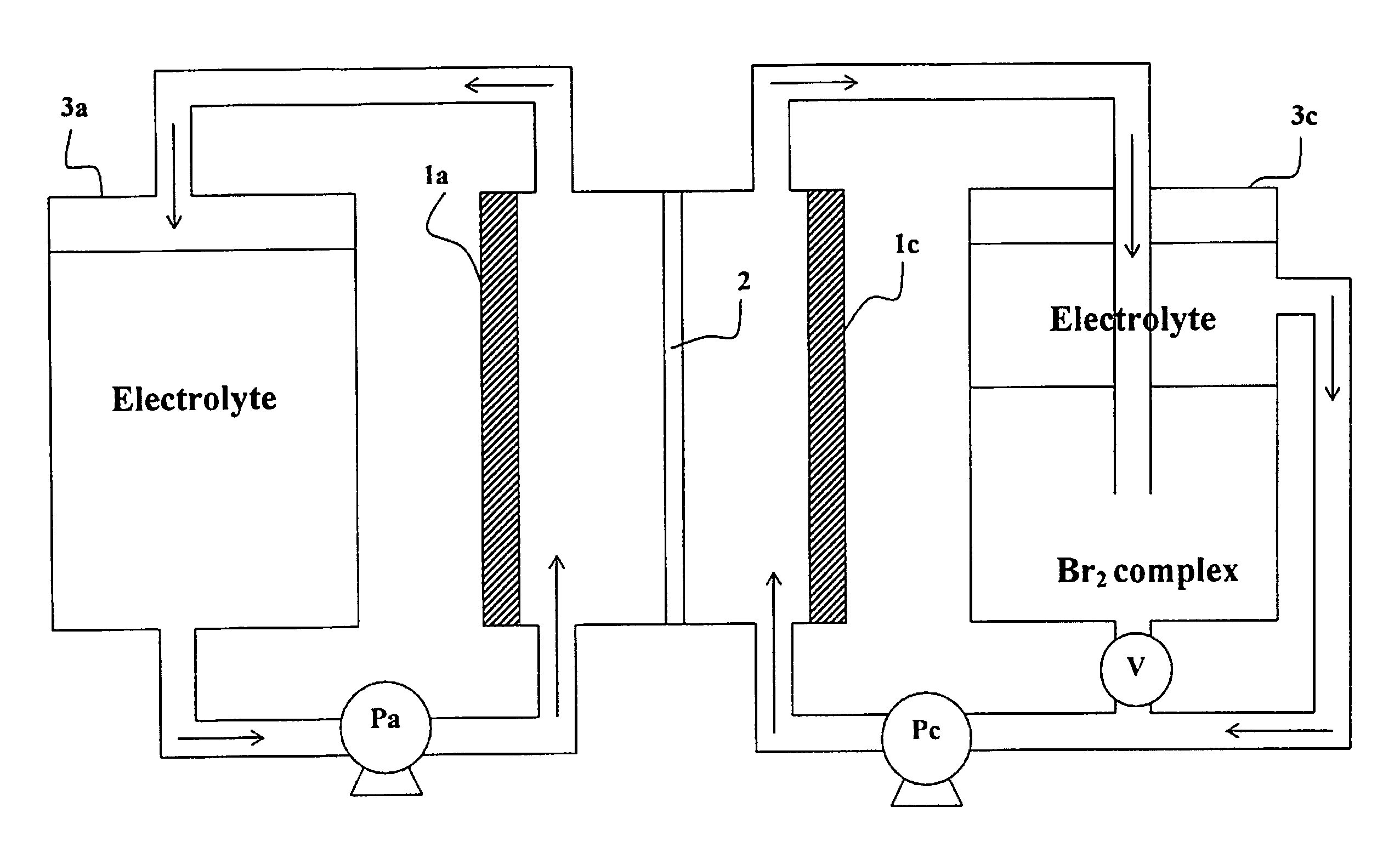
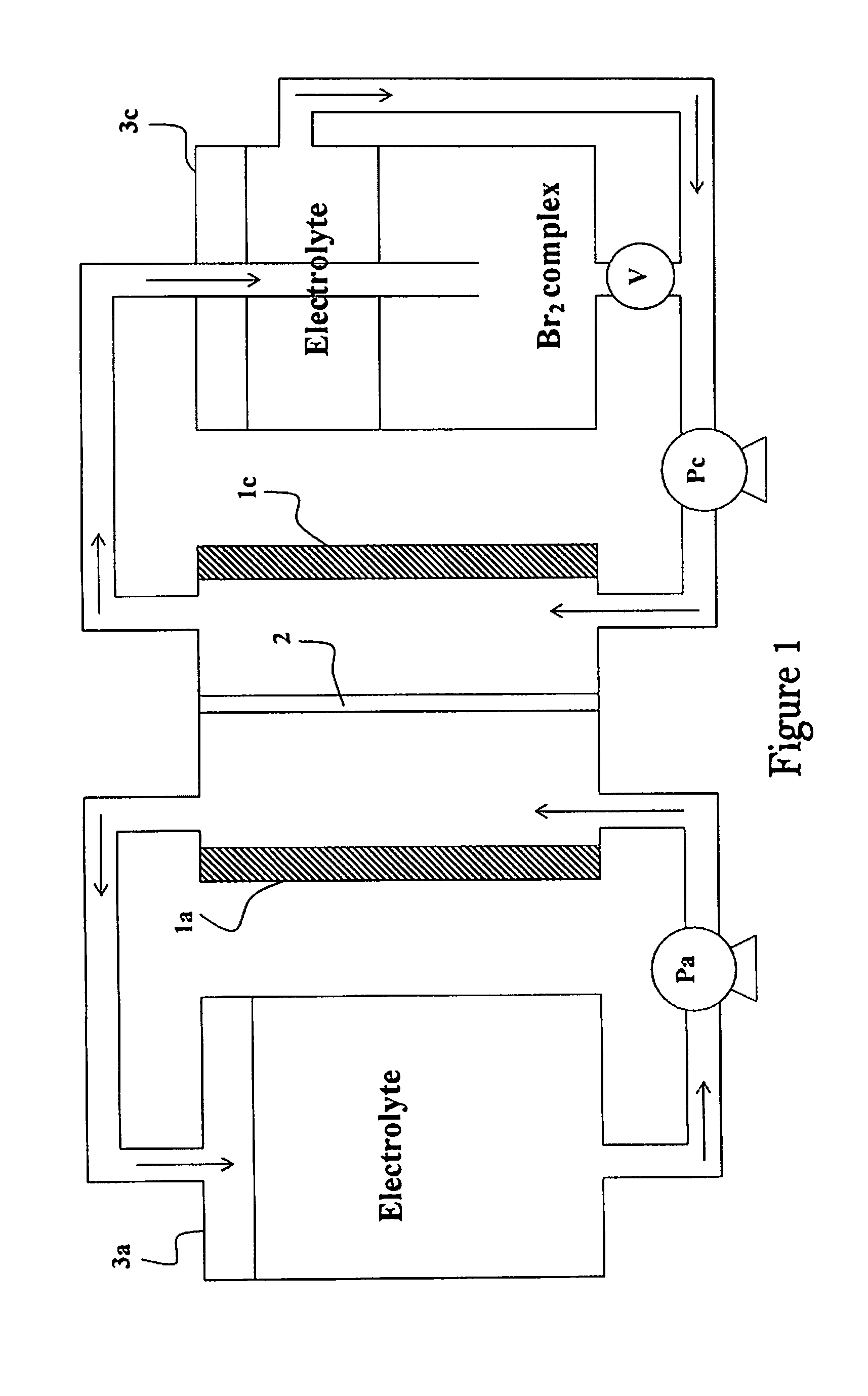
Method of Operating Metal-Bromine Cells
InactiveUS20110253553A1Easy to operateBatteries circuit arrangementsPhotography auxillary processesBromineMetal
A method for generating molecular bromine in bromide-containing electrolyte solution suitable for use in a metal bromine cell, involves chemically oxidizing bromide (Br−) in the electrolyte solution in an acidic environment, to produce the molecular bromine.
Owner:BROMINE COMPOUNDS
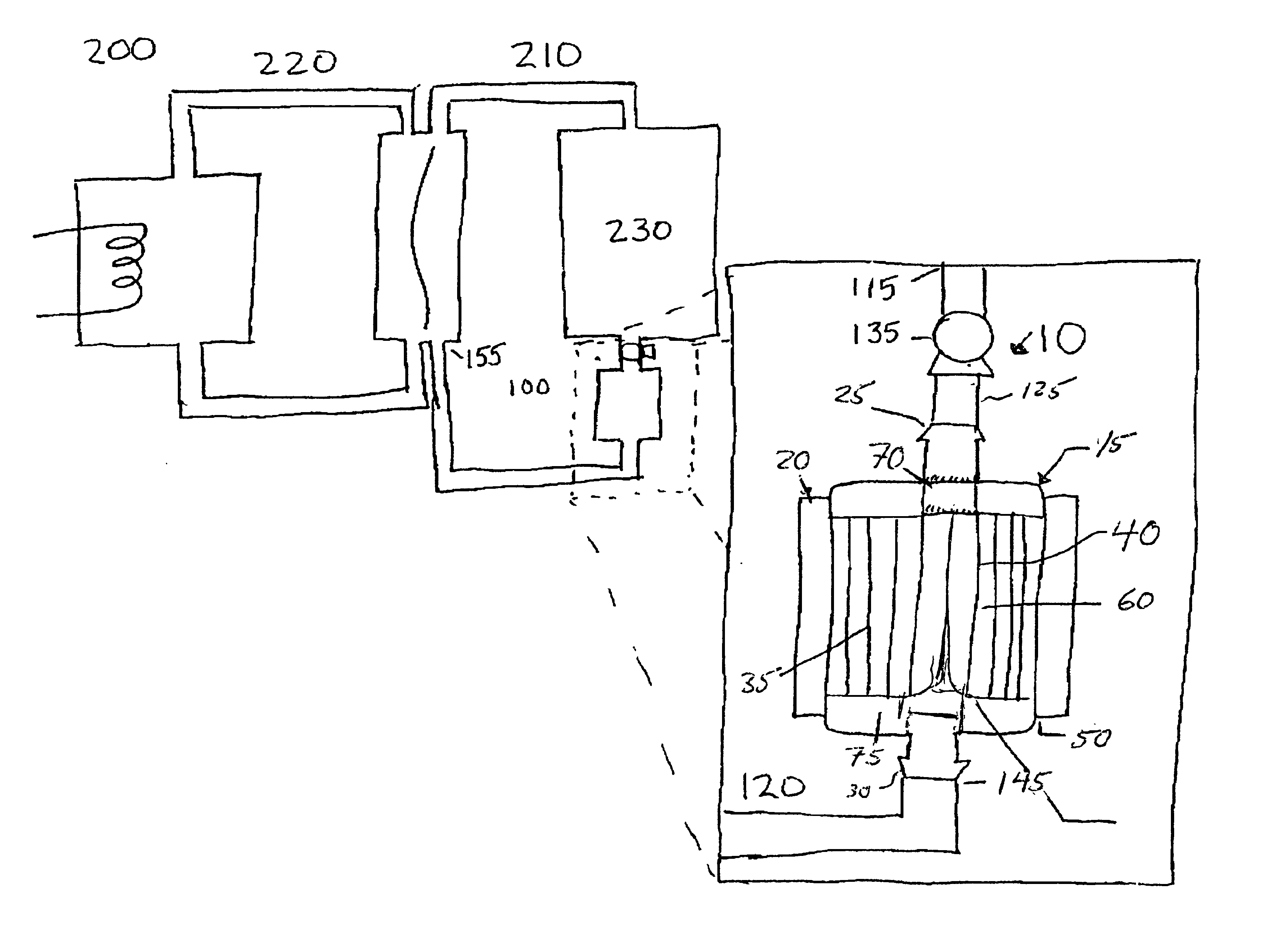
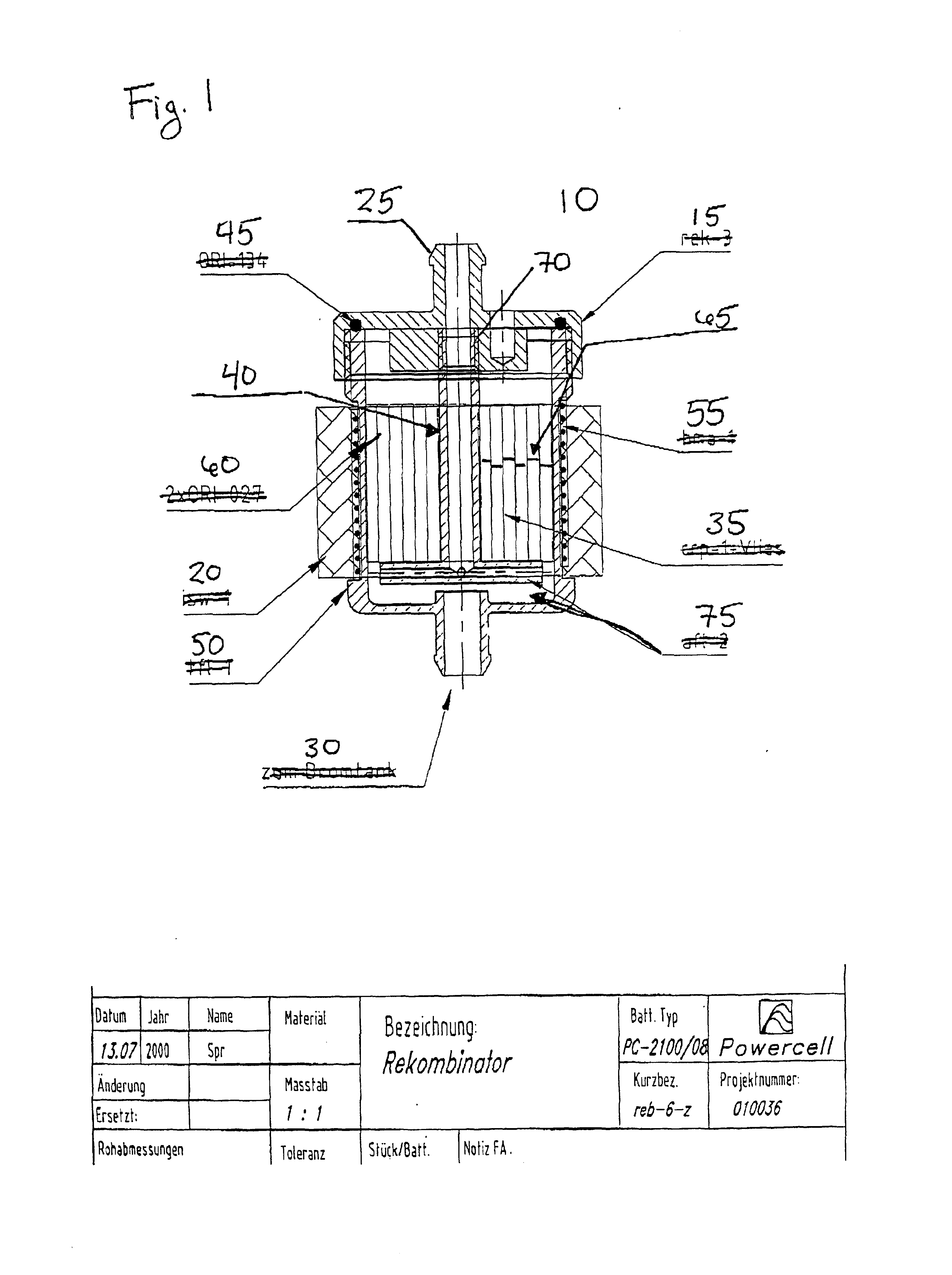
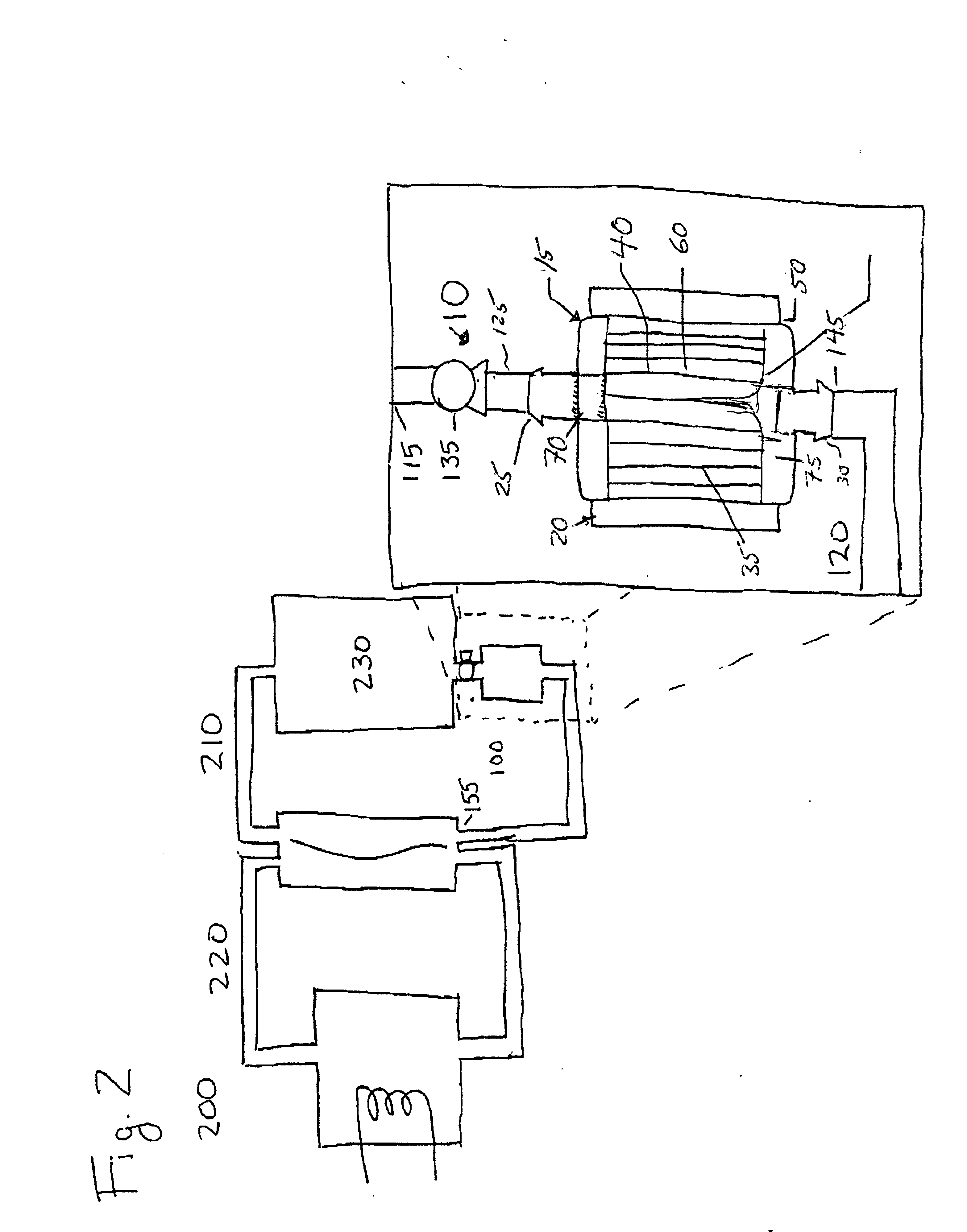
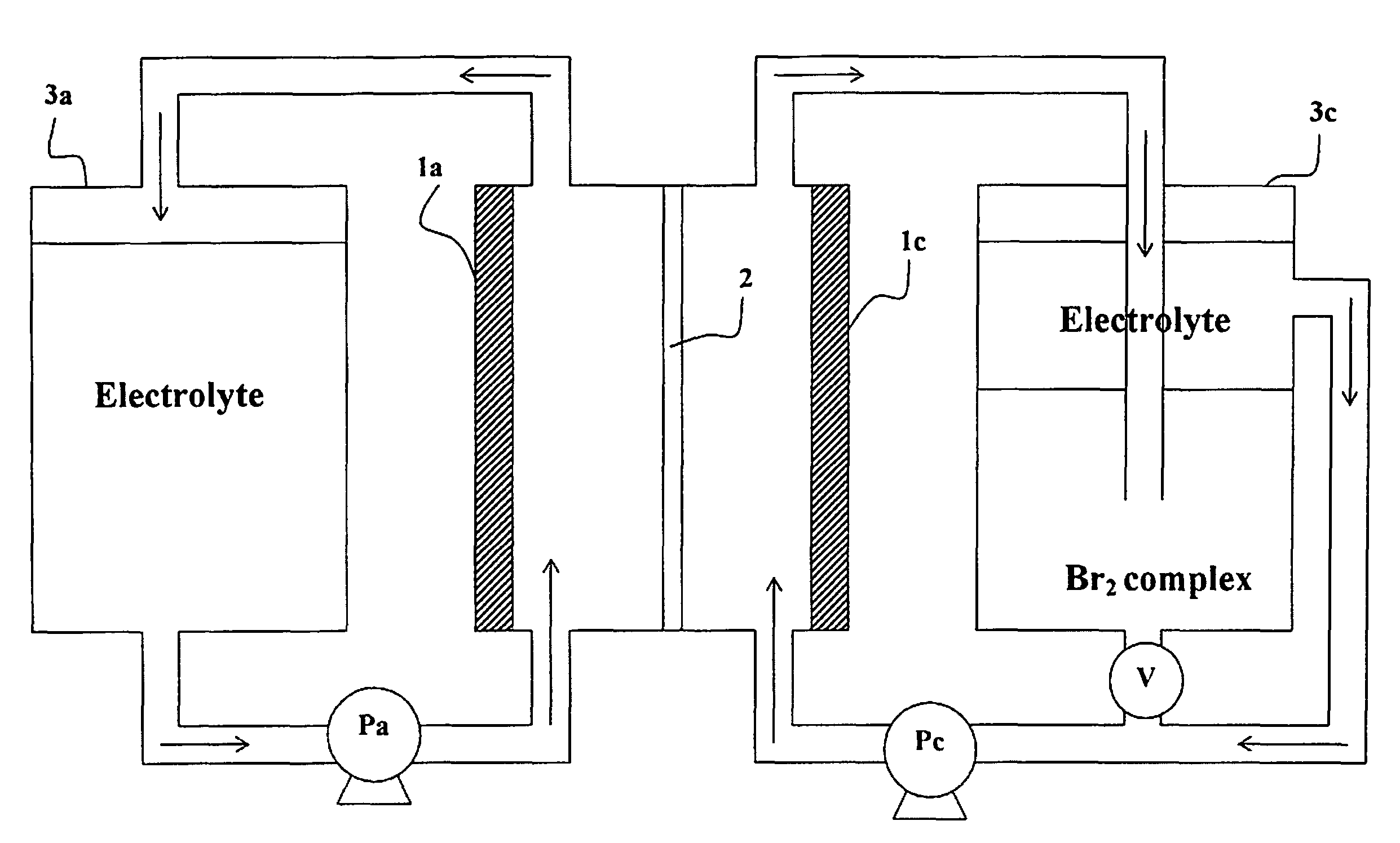
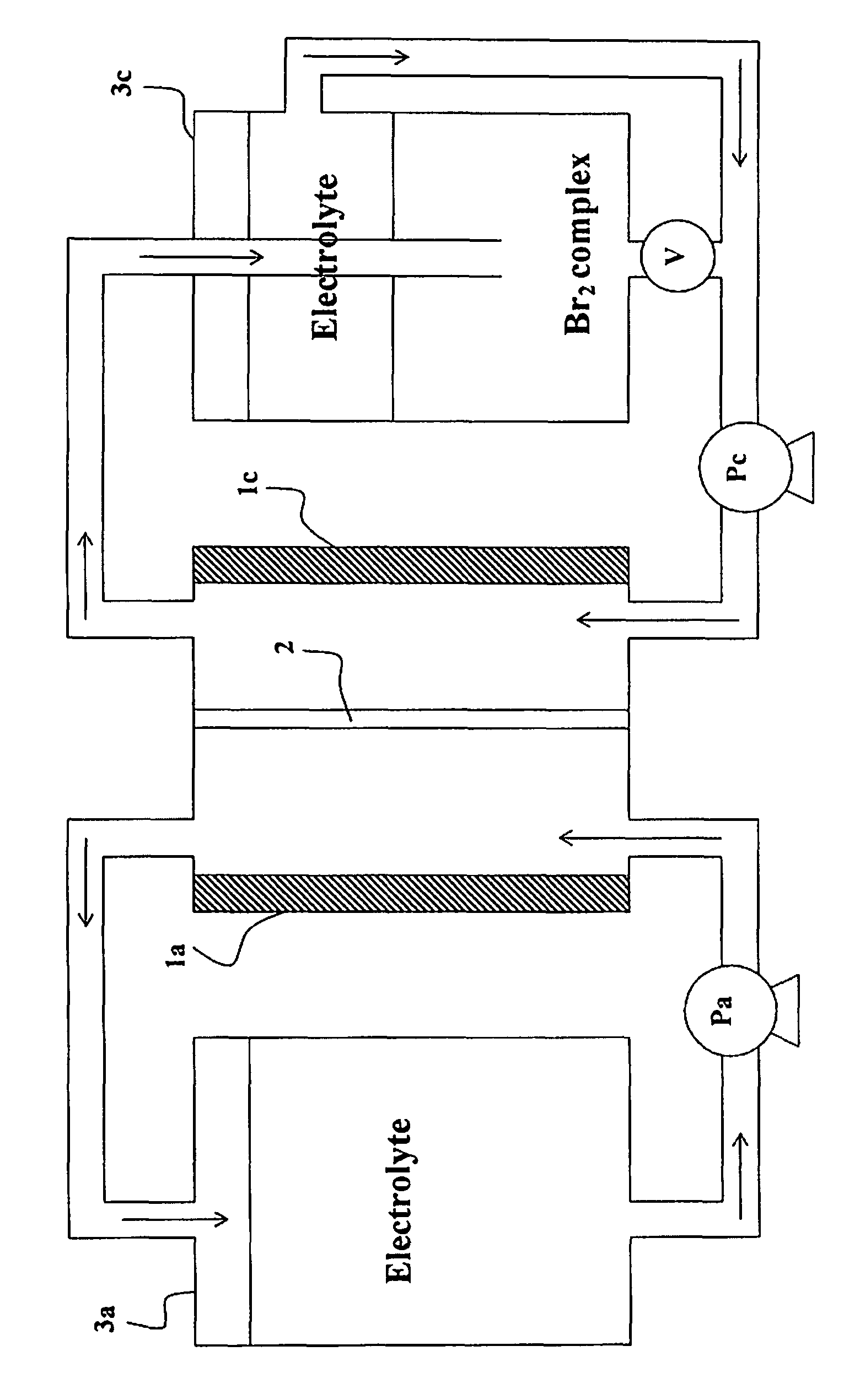
Recombinator for the re-acidification of an electrolyte stream in a flowing electrolyte zinc-bromine battery
A recombinator device and associated method for re-acidification of an electrolyte in a flowing electrolyte zinc-bromine battery. The recombinator device receives hydrogen, formed as a result of electrolysis within cell stacks of the zinc-bromine battery, as well as aqueous bromine from the zinc-bromine battery. Upon receipt, the hydrogen and bromine are introduced into a reaction chamber in the recombinator device so as to form hydrobromic acid. The hydrobromic acid is then reintroduced back into the electrolyte of the zinc-bromine battery for re-acidification of same.
Owner:PREMIUM POWER ACQUISITION
Leak sensor for flowing electrolyte batteries
InactiveUS7314761B2Primary cell to battery groupingPrimary cell maintainance/servicingEngineeringLeak detection
A leak detection system for a flowing electrolyte battery comprising a containment member associated with at least one of a stack of a flowing electrolyte battery and an electrolyte reservoir of a flowing electrolyte battery and a sensing member for sensing a fluid leak within the containment member.
Owner:LARGO CLEAN ENERGY CORP
Electrolyte for rechargeable electrochemical cell
ActiveUS20170194666A1Increased durabilityImprove stabilityLarge-sized flat cells/batteriesFinal product manufacturePolymer chemistryElectrolytic agent
The present invention provides an aqueous electrolyte for use in rechargeable zinc-halide storage batteries that possesses improved stability and durability and improves zinc-halide battery performance. One aspect of the present invention provides an electrolyte for use in a secondary zinc bromine electrochemical cell comprising from about 30 wt % to about 40 wt % of ZnBr2 by weight of the electrolyte; from about 5 wt % to about 15 wt % of KBr; from about 5 wt % to about 15 wt % of KCl; and one or more quaternary ammonium agents, wherein the electrolyte comprises from about 0.5 wt % to about 10 wt % of the one or more quaternary ammonium agents.
Owner:EOS ENERGY TECH HLDG LLC
Integral manifold
A method of forming passages of an integral manifold adjacent a cell stack of a flowing electrolyte battery provides enhanced sealing between the manifold and capillary tubes of the cell stack. The method includes forming a mould cavity adjacent the cell stack, with the mould cavity open to capillary openings of cells of the cell stack. A plurality of pins are then located in the mould cavity, with end regions of the pins being contiguous with the capillary openings. The mould cavity is then filled with material and the material is allowed to solidify into a moulded section. The pins are then removed from the moulded section, thereby forming passages in the moulded section which are in fluid communication with the capillary openings.
Owner:REDFLOW PTY LTD
Blend membranes based on sulfonated poly (phenylene ether) for enbanced polymer electrochemical cells
InactiveCN1312839AImprove conductivityImprove flexibilitySolid electrolytesSemi-permeable membranesPolymer sciencePolyphenylene oxide
Solid polymer membranes comprised of a high charge density sulfonated poly (phenylene oxide) blended with poly(vinylidene fluoride) in varied ratios have improved membrane characteristics. These membranes are inexpensive and possess very high ionic conductivity, and thus are suitable for solid polymer electrolytes in electrochemical applications, especially for the polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cell, the electrolyte double-layer capacitor, and the rechargeable zinc-halide cell. These membranes enhance the performance of these devices.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
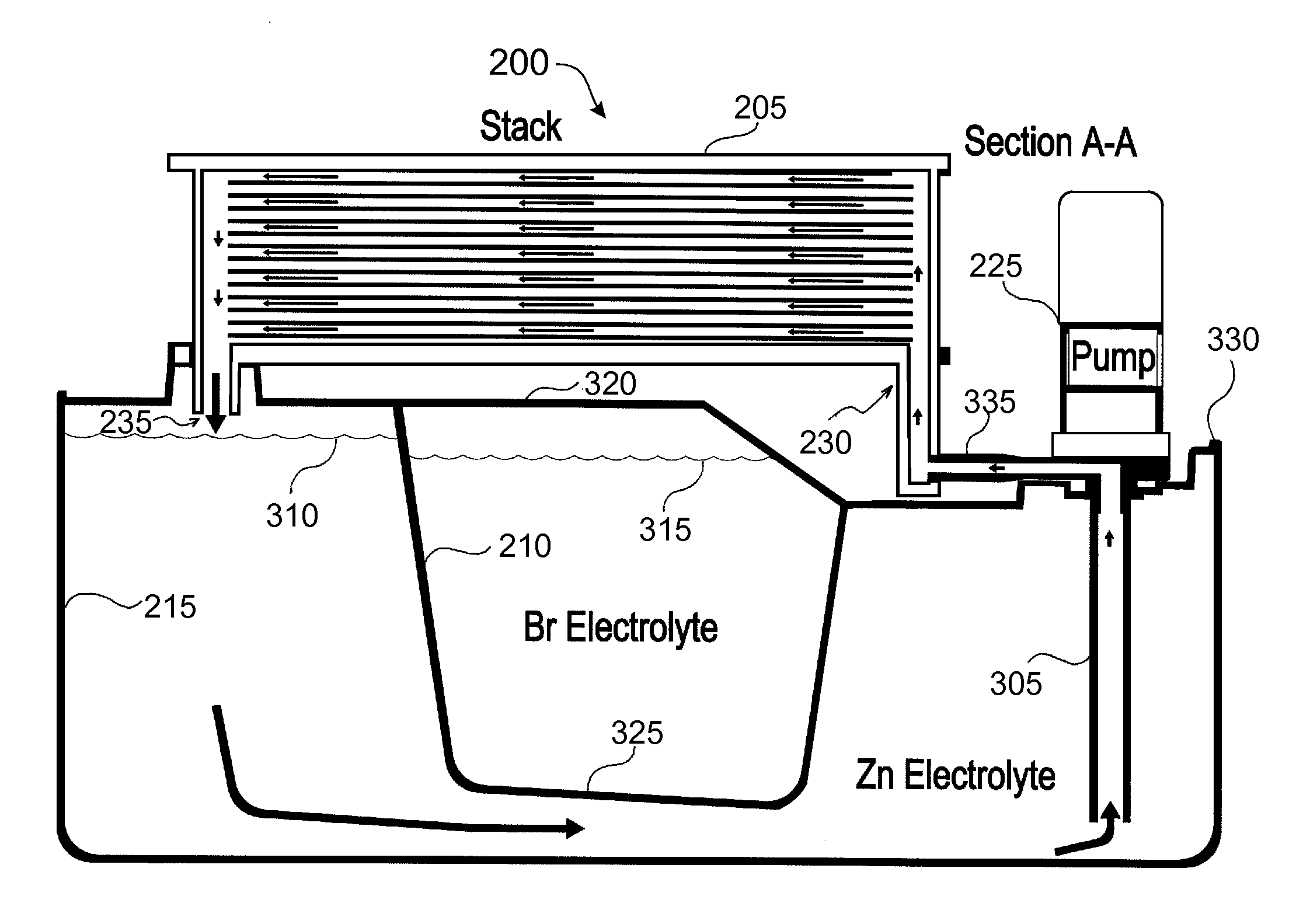
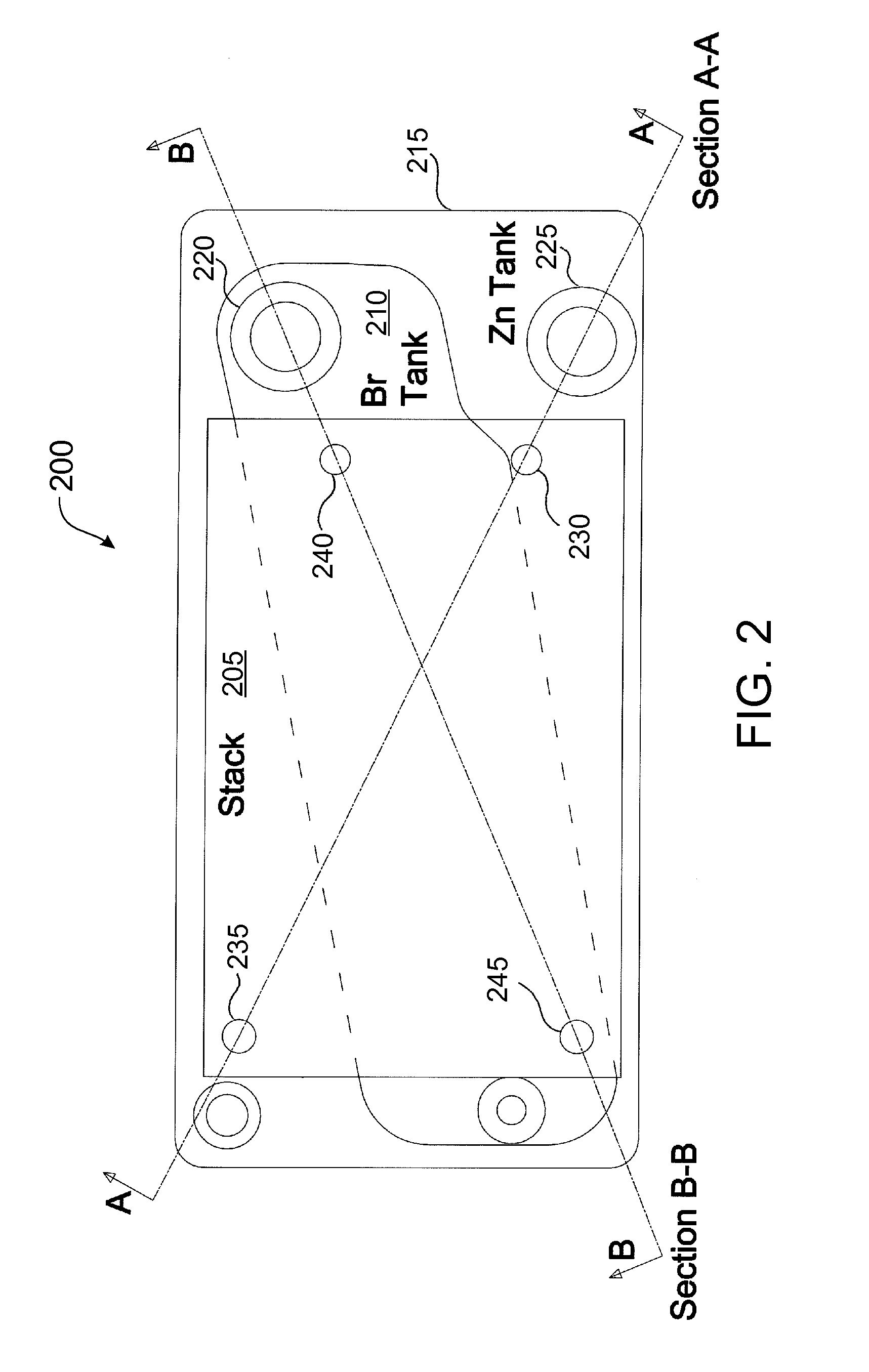
Flowing electrolyte reservoir system
InactiveUS20120308867A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove securityPrimary cell to battery groupingElectrolyte moving arrangementsEngineeringReservoir system
A flowing electrolyte reservoir system for a flowing electrolyte battery. The system comprises an outer electrolyte tank and an inner electrolyte tank placed under a battery cell stack. The inner tank is transversely positioned between opposite corners of the outer electrolyte tank, and beneath opposite corners of the battery cell stack.
Owner:REDFLOW PTY LTD
High-Power Battery
InactiveUS20090042101A1Low electrolyte resistanceHigh resistivityElectrochemical processing of electrodesLead-acid accumulatorsElectrical resistance and conductanceThin layer
A method of forming battery electrodes with high specific surface and thin layers of active material is disclosed. The method enables low series resistance and high battery power.
Owner:MCGERVEY DONALD L +2
Battery including electrically conductive phosphate glass components
InactiveUS20100167117A1Lead-acid accumulatorsElectrode carriers/collectorsPhosphate glassEnergy storage
An electrode plate for an energy storage device includes a current collector fabricated at least partially from an electrically conductive phosphate glass. A chemically active material may be disposed on the current collector.
Owner:FIREFLY ENERGY INC
Electrolyte System For Rechargeable Flow Battery
InactiveUS20170214077A1Improve stabilityManufacturing EaseRegenerative fuel cellsAqueous electrolyte fuel cellsHalogenElectrical battery
An electrolyte system is provided for a rechargeable electrode zinc-halogen flow battery that utilizes a highly similar or identical electrolyte positioned on both sides of an ion-conducting membrane. The electrolyte system containing zinc salts, electrolyte conductivity enhancer, and an appropriate amount of bromine complexing agent achieves significant improvements on battery energy efficiency, self-discharge rate, and electrolyte level cycle stability over the prior art electrolyte systems.
Owner:FAITH TECH INC
Diaphragm-free static zinc-bromine battery
ActiveCN108134141ALow costSimple structureFinal product manufactureZinc-halogen accumulatorsEngineeringPositive current
The invention discloses a diaphragm-free static zinc-bromine battery. The battery mainly comprises a positive terminal plate with a liquid storage box, a positive current collector, a positive pole, apad frame, a negative current collector and a negative terminal plate with a liquid feeding box. On the one hand, the cost of the zinc-bromine battery can be reduced because a diaphragm is not used;on the other hand, devices such as a circulation pump and an electric valve required by an electrolyte circulation system are not used, so that system loss is reduced, and the system structure of thebattery is simpler.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Cell stack for a flowing electrolyte battery
ActiveUS8293390B2Increase in sizeReduce manufacturing costElectrolyte moving arrangementsAlkaline accumulatorsReduced sizeEngineering
A cell stack (700) as provided enables a flowing electrolyte battery to have a reduced size and weight. The cell stack (700) includes a casing having a positive polarity end and a negative polarity end. A plurality of half cells (805) are inside the casing, and each half cell (805) includes an electrode plate (705), an adjacent separator plate (715), and at least one capillary tube (727) positioned between the electrode plate (705) and the adjacent separator plate (715). The capillary tube (727) has a first end extending outside of the half cell (805) and a second end located inside the half cell (805). At least one manifold (530) is in hydraulic communication with a plurality of capillary tube ends including the first end of the capillary tube (727) in each half cell (805). The capillary tube (727) in each half cell (805) enables electrolyte to circulate through the plurality of half cells (805) via the at least one manifold (530).
Owner:REDFLOW PTY LTD
Electrolyte for rechargeable electrochemical cell
InactiveUS20180013185A1Increased durabilityImprove stabilityFuel and secondary cellsLarge-sized flat cells/batteriesElectrolytic agentZinc bromide
The present invention provides an aqueous electrolyte for use in rechargeable zinc-halide storage batteries that possesses improved stability and durability and improves zinc-halide battery performance. One aspect of the present invention provides an electrolyte for use in a secondary zinc bromine electrochemical cell comprising from about 30 wt % to about 40 wt % of ZnBr2 by weight of the electrolyte; from about 5 wt % to about 15 wt % of KBr; from about 5 wt % to about 15 wt % of KCl; and one or more quaternary ammonium agents, wherein the electrolyte comprises from about 0.5 wt % to about 10 wt % of the one or more quaternary ammonium agents.
Owner:EOS ENERGY TECH HLDG LLC
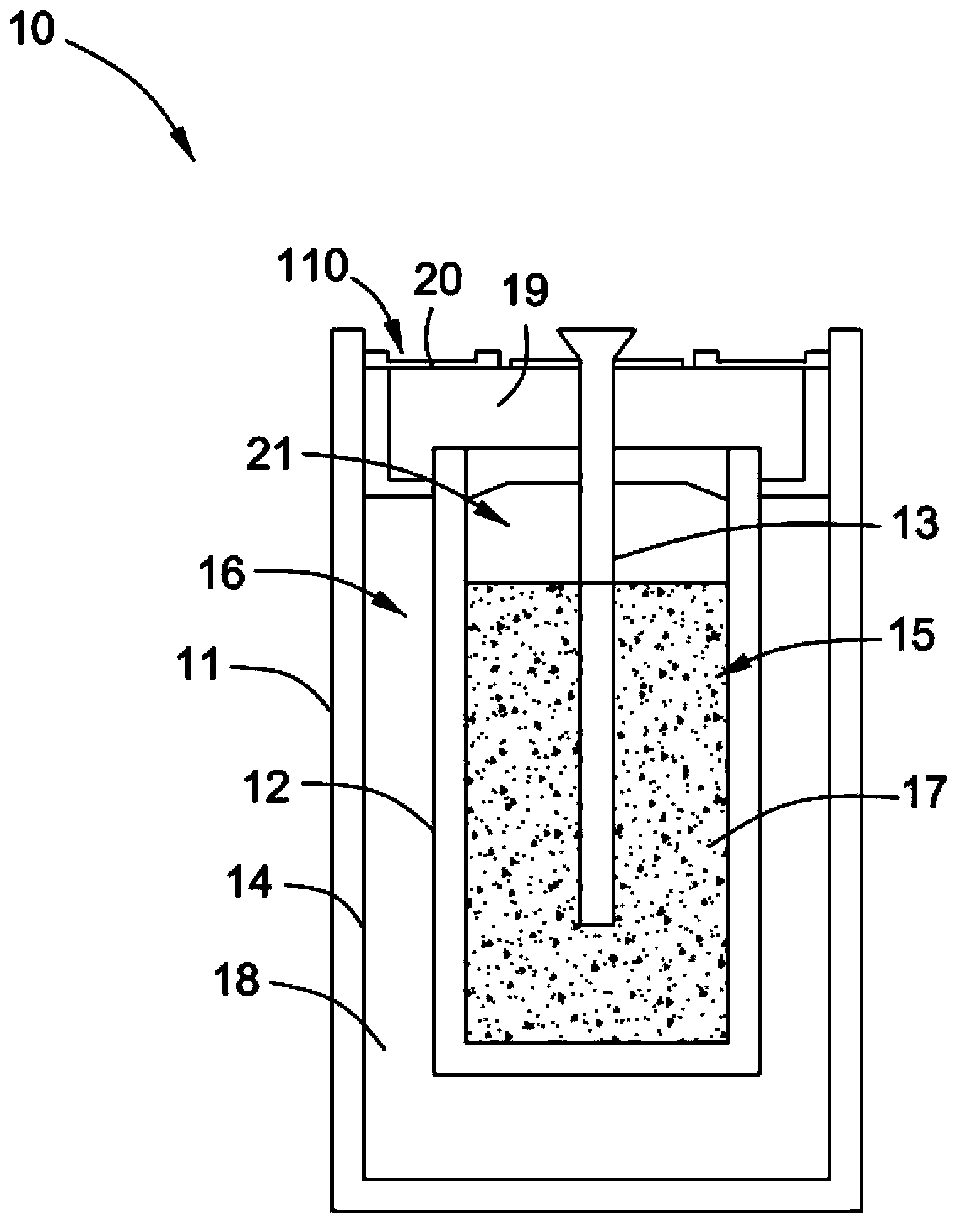
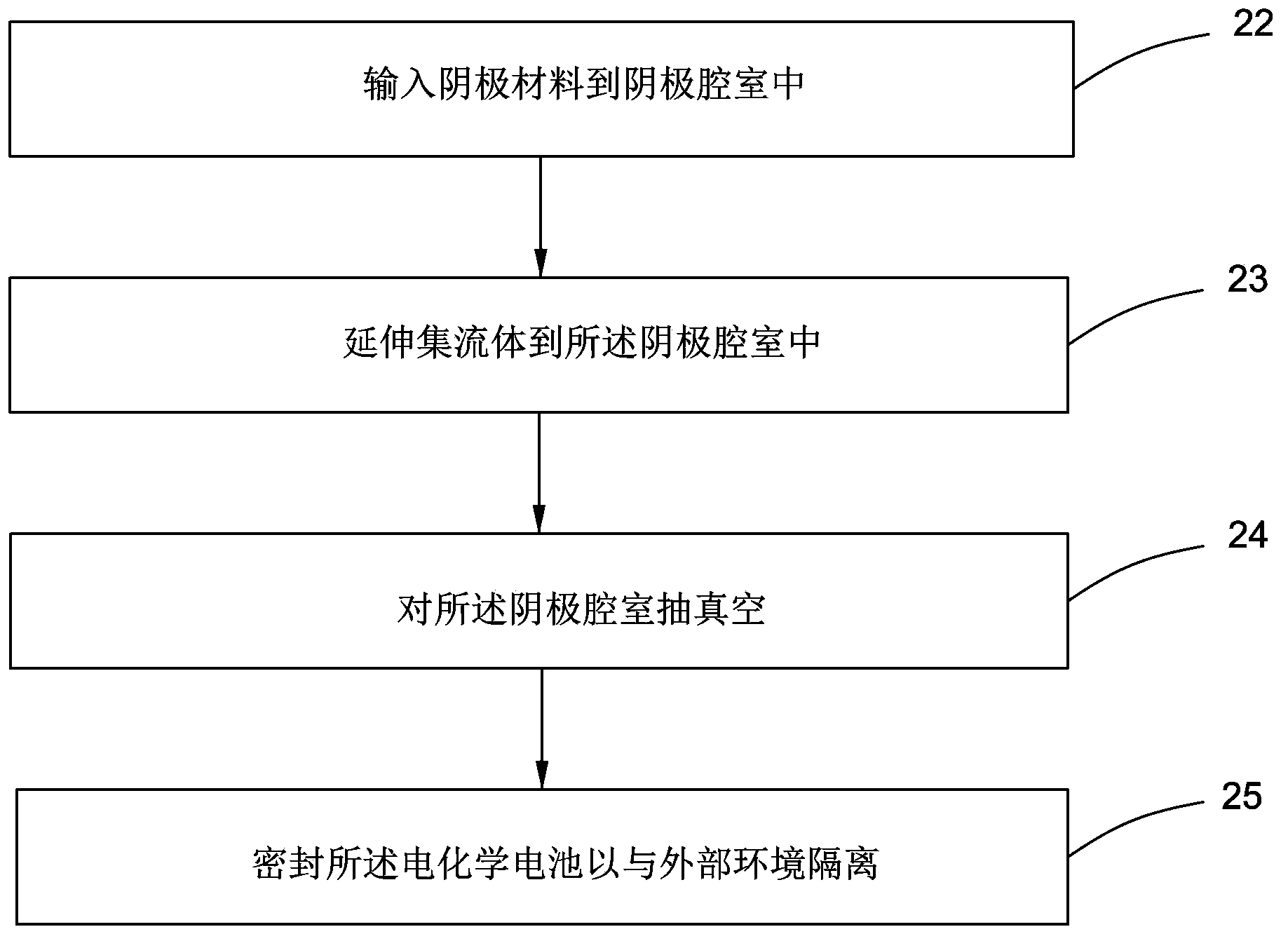
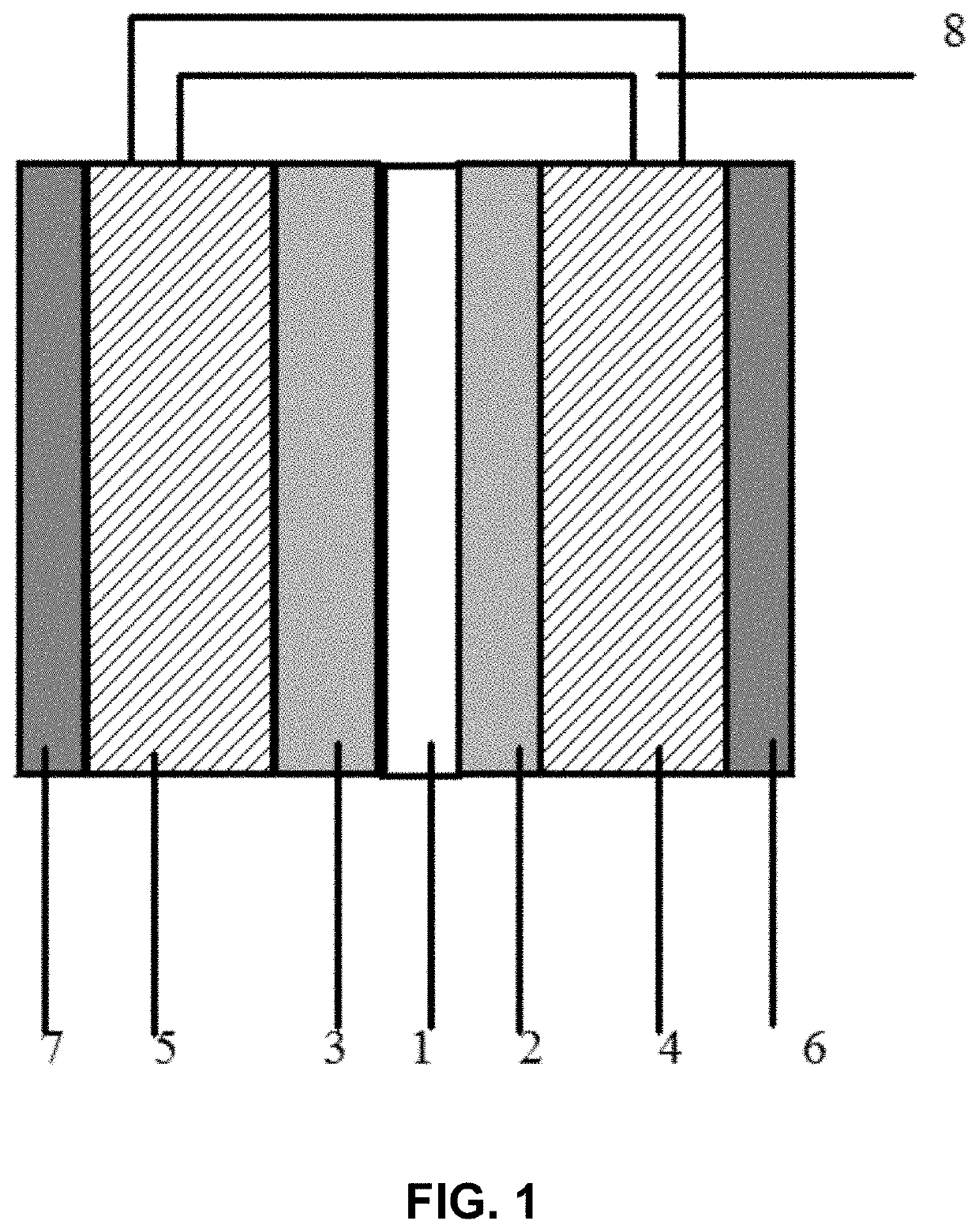
Method for manufacturing electrochemical battery
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing an electrochemical battery. The method comprises the following steps: feeding a negative electrode material into a cathode chamber of the electrochemical battery when the electrochemical battery is in a base state, vacuuming the cathode chamber, and sealing up the electrochemical battery so as to isolate the electrochemical battery from an external environment. The electrochemical battery further comprises an anode chamber which is isolated from the cathode chamber through electrolyte and is in ion communication with the cathode chamber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
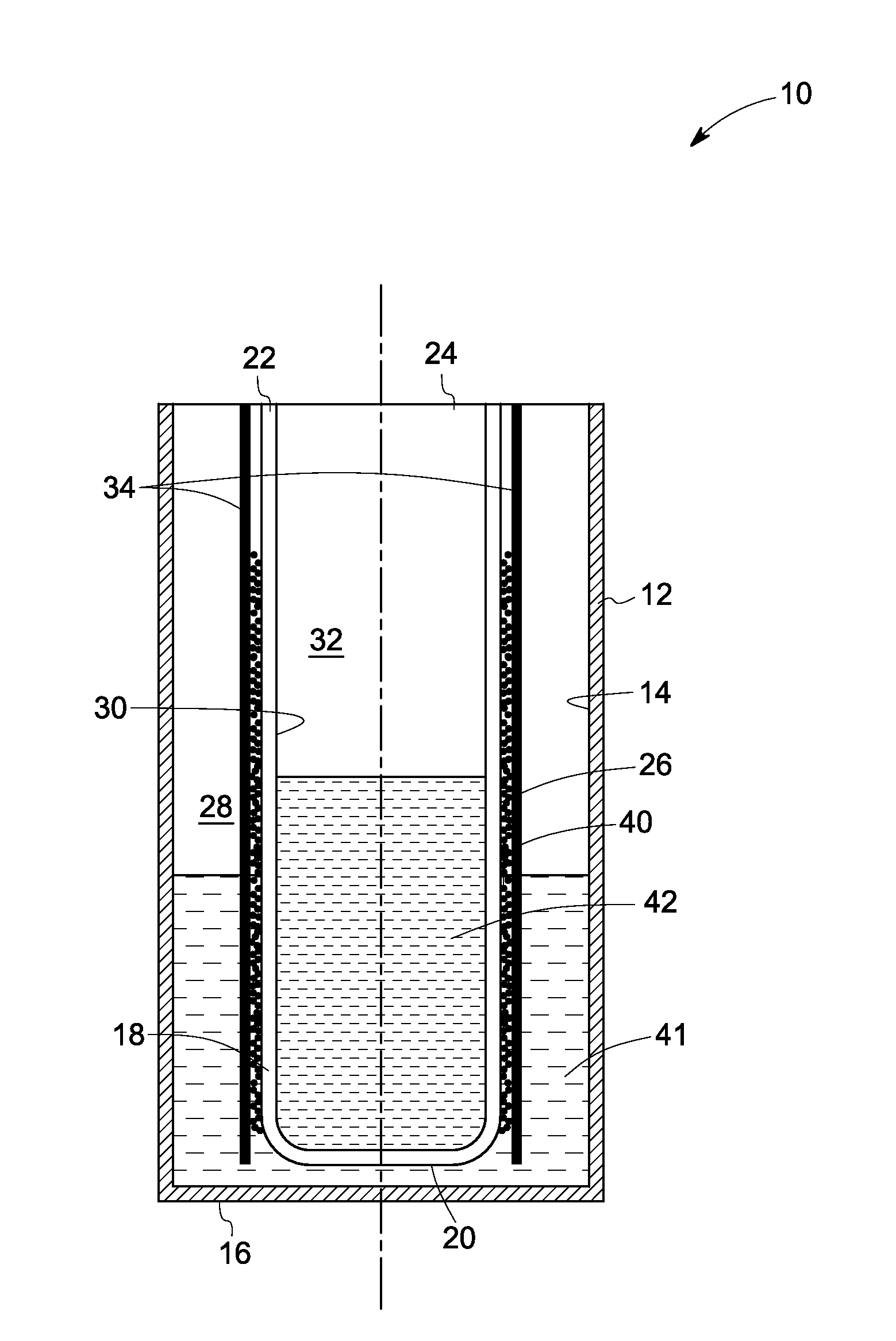
Electrochemical cells
ActiveUS20130084485A1Reduce oxidationPrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureSacrificial metalElectrochemical cell
An electrochemical cell is presented. An anode compartment in the cell contains a sacrificial metal in an amount between about 10 volume percent and about 40 volume percent, based on the volume of the compartment. The sacrificial metal has an oxidation potential less than the oxidation potential of iron. An energy storage device including such an electrochemical cell is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
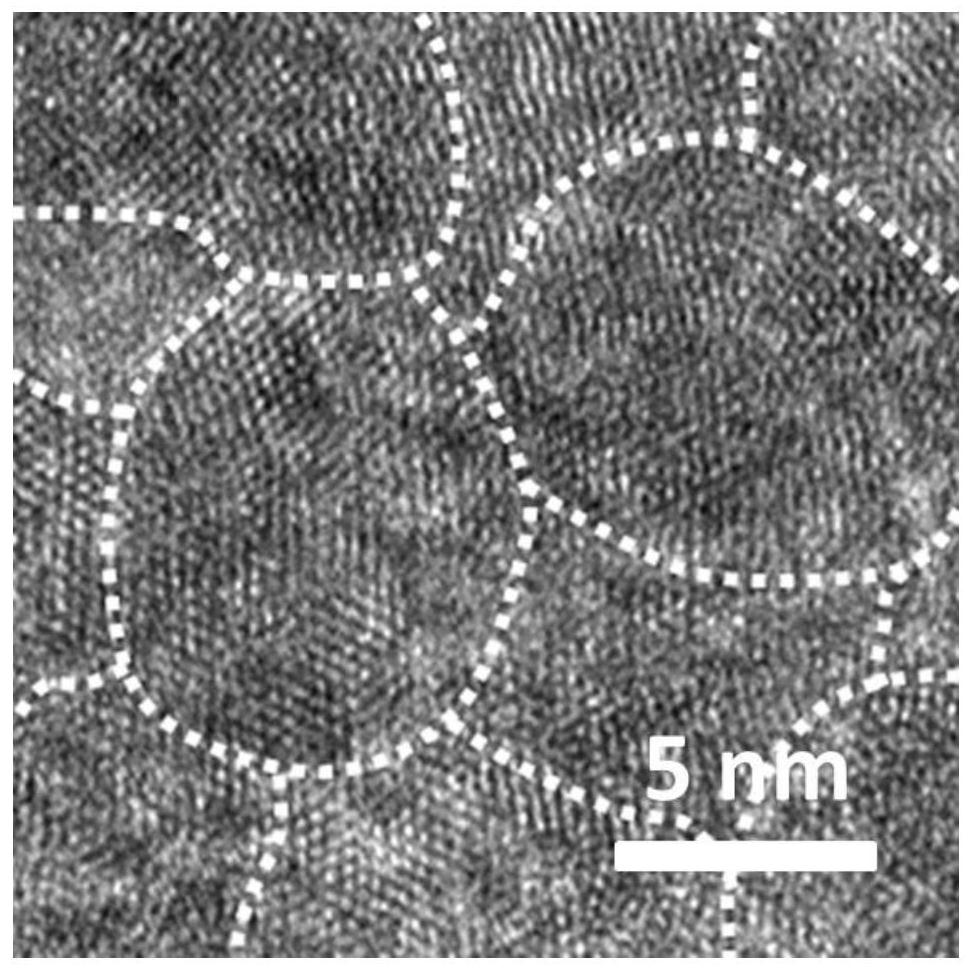
Method for improving performance of zinc-iodine battery based on halogen bond effect
ActiveCN112563586AImprove responseImproved magnification performanceCell electrodesZinc-halogen accumulatorsElectrical batteryPorous carbon
The invention relates to a method for improving the performance of a zinc-iodine battery based on a halogen bond effect, which belongs to the technical field of aqueous batteries. Iodine serving as apositive electrode material of a zinc ion battery has the application advantages of rich reserves, high reaction activity and the like, but the thermal / electrochemical stability and conductivity of iodine are poor, so that the cycle life of the battery is seriously influenced. In order to improve the performance of an iodine positive electrode, the invention provides a method for better fixing iodine to the surface of a polyatomic doped carbon carrier by utilizing the halogen bond effect so as to enhance the stability / conductivity. The method specifically comprises the following steps of calcining a biomass material to convert the biomass material into a multi-atom doped porous carbon microtube, uniformly mixing iodine with the carbon microtube, and heating to obtain the iodine / carbon microtube composite material. The thermal stability of the compound is remarkably enhanced, and the zinc storage reversible specific capacity and the cycling stability of the compound are greatly improved. The method is simple and efficient, the obtained composite material is more stable in physicochemical property and obvious in battery performance improvement effect, and has potential practical value and commercial prospect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Multi-cell battery
ActiveUS8765284B2Easy to foldPrimary cell to battery groupingCylindrical casing cells/batteryEngineeringElectrochemical cell
A flexible battery includes a first substrate layer with a first cell portion, a second cell portion, and a bridge portion connecting the first and second cell portions. An electrical bridge electrically couples a first electrochemical cell to a second electrochemical cell in series or parallel, and an electrical bridge is flexible and extends across the bridge portion of the first substrate layer. A second substrate layer is connected to the first substrate layer such that both of the first and second electrochemical cells are separately sealed. The flexible battery is configured to be folded over itself along the bridge portion such that the first and second electrochemical cells are arranged in a covering relationship. Optionally, an open gap area is disposed over the bridge portion of the first substrate to facilitate folding the flexible battery over itself along a line extending through the bridge portion.
Owner:BLUE SPARK INNOVATIONS LLC
Graphite felt treatment process
InactiveCN108615885ASimple processFinal product manufactureCell electrodesMinor metalsMicrowave oven
The invention discloses a graphite felt treatment process including steps of: 1) organic substance removal: annealing the graphite felt at 500-900 DEG C for 5-15 min; 2) removal common impurities: treating the graphite felt in a first solution (SC-1) at 70-80 DEG C for 5-10 min, and washing the graphite felt for 5-10 min in deionized water, then treating the graphite felt in a second solution (SC-2) at 70-80 DEG C for 5-10 min, and washing the graphite felt for 5-10 min in deionized water; (3) removal of stubborn trace metal impurities: treating the graphite felt in a microwave oven for 5-15 min. The treatment process is simple and can remove the organic substances and metal impurities from the graphite felt. The processed graphite felt can be used for producing zinc-bromine or zinc-iodinebatteries.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Zinc-halide battery using a deep eutectic solvent-based electrolyte
InactiveCN109314273ALarge-sized flat cells/batteriesFinal product manufactureQuaternary ammonium cationElectrochemical cell
The present invention provide a non-aqueous electrolyte for use in static or non-flowing rechargeable electrochemical cells or batteries, wherein the electrolyte comprises a first deep eutectic solvent comprises a zinc salt, a second deep eutectic solvent comprising one or more quaternary ammonium salts, and a hydrogen bond donor. Another aspect of the present invention also provides a non-flowingrechargeable electrochemical cell that employs the non-aqueous electrolyte of the present invention.
Owner:EOS ENERGY STORAGE LLC
Zinc-iodine battery structure
ActiveUS20200343570A1Low conductivitySolve the real problemRegenerative fuel cellsSpecific condition cell workingElectrical batteryPhysical chemistry
Disclosed in the invention is a zinc-iodine battery structure, which includes a housing, a cavity is formed in the housing, and a cation exchange membrane for dividing the cavity into two parts is disposed in a middle of the cavity; a glass fiber component for protecting the cation exchange membrane is disposed at a negative output end; a graphite felt impregnated with a ZnI2 solution is disposed on an outside of the glass fiber component; and the graphite felt of the negative output end is coated with Bi powder, and a graphite felt of a positive output end is coated with Sm powder. Carbon plates serving as current leading-out channels of a battery are disposed on outsides of the graphite felts; and a return flow channel is disposed between the two graphite felts. By using a homogeneous cation exchange membrane with a low electrical resistance, a problem of serious self-discharging is overcome; and by using a flow battery with an open flow system, a problem of a change in pressure caused by a change in volume during charging and discharging is effectively solved. By disposing glass fiber products on two sides of the cation exchange membrane, a dendritic crystal generated during charging is unable to reach a separator, so that short circuit caused by puncture of the separator is avoided.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
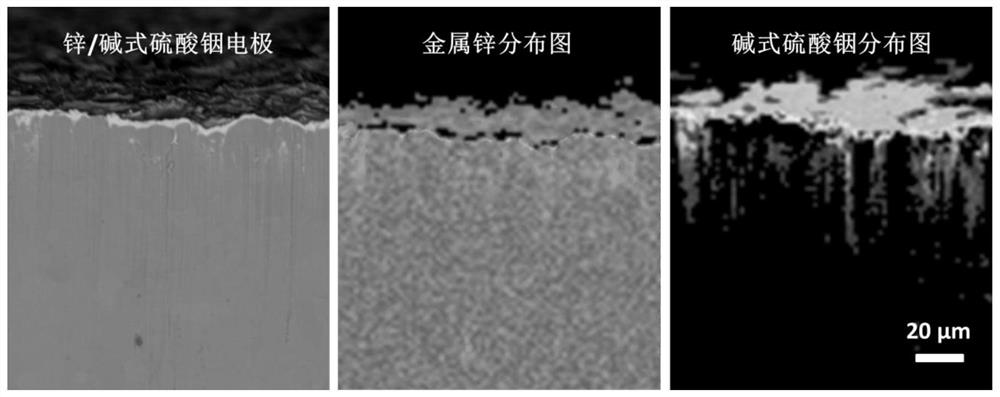
Long-cycle-life aqueous zinc secondary battery negative electrode and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN112331933AImprove Coulombic efficiencyInhibition of dendrite growthFinal product manufactureZinc-halogen accumulatorsSolid state electrolyteElectrolytic agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a long-cycle-life aqueous zinc secondary battery negative electrode, and belongs to the technical field of zinc secondary batteries. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out chemical replacement reaction on zinc and metal salt to deposit a metal simple substance on the zinc metal surface and further to obtain a zincmetal surface covered solid electrolyte precursor; covering a solid electrolyte precursor on the surface of zinc metal to serve as a negative electrode to assemble a battery; and after the solid electrolyte precursor material is subjected to in-situ electrochemical cycle activation, generating solid electrolyteon the surface of zinc metal in situ, and obtaining the zinc secondary battery negativeelectrode material. The obtained zinc / solid electrolyte electrode has a large actual electrochemical active area and high mechanical stability, and meanwhile, the solid electrolyte isolates zinc metal from liquid electrolyte, so that the defects of active metal corrosion, surface passivation, dendritic crystal growth and the like of a traditional zinc metal electrode are inhibited, and the cycling stability of an electrode material is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bipolar electrode comprising a loaded carbon felt
ActiveUS20200388844A1Fuel and secondary cellsFinal product manufacturePolymer scienceElectrical battery
Bipolar electrodes comprising a carbon felt loaded with a polymer material and a nanocarbon material are described herein. The bipolar electrodes are useful in electrochemical cells. In particular, the loaded carbon felt can be used in bipolar electrodes of zinc-halide electrolyte batteries. Processes for manufacturing the loaded carbon felt are also described, involving contacting (e.g., dipping) a carbon felt in a mixture of solvent, polymer material and nanocarbon material.
Owner:EOS ENERGY TECH HLDG LLC
Method of operating metal-bromine cells
A method for generating molecular bromine in bromide-containing electrolyte solution suitable for use in a metal bromine cell, involves chemically oxidizing bromide (Br−) in the electrolyte solution in an acidic environment, to produce the molecular bromine.
Owner:BROMINE COMPOUNDS
Gelated ionic liquid film-coated surfaces and uses thereof
ActiveUS20160351969A1Minimise self-dischargeEasy dischargeGel electrodesFinal product manufactureElectrochemical cellIonic liquid
The invention relates to an assembly comprising a first gelated ionic liquid film in contact with a first electrically conductive surface, wherein the first gelated ionic liquid film comprises a first ionic liquid encapsulated within a gel matrix; and a second gelated ionic liquid film in contact with a second electrically conductive surface, wherein the second gelated ionic liquid film comprises a second ionic liquid encapsulated within a gel matrix; wherein the first and second gelated ionic liquid films are in contact with each other. There is also described an electrochemical cell comprising an assembly according to the invention, and methods for producing same.
Owner:GELION TECH PTY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com