Composite plant source polypeptide as well as preparation method and application thereof
A plant source and drug technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as unreported, and achieve the effects of reducing blood lipids, effectively regulating blood sugar, and improving antioxidant capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
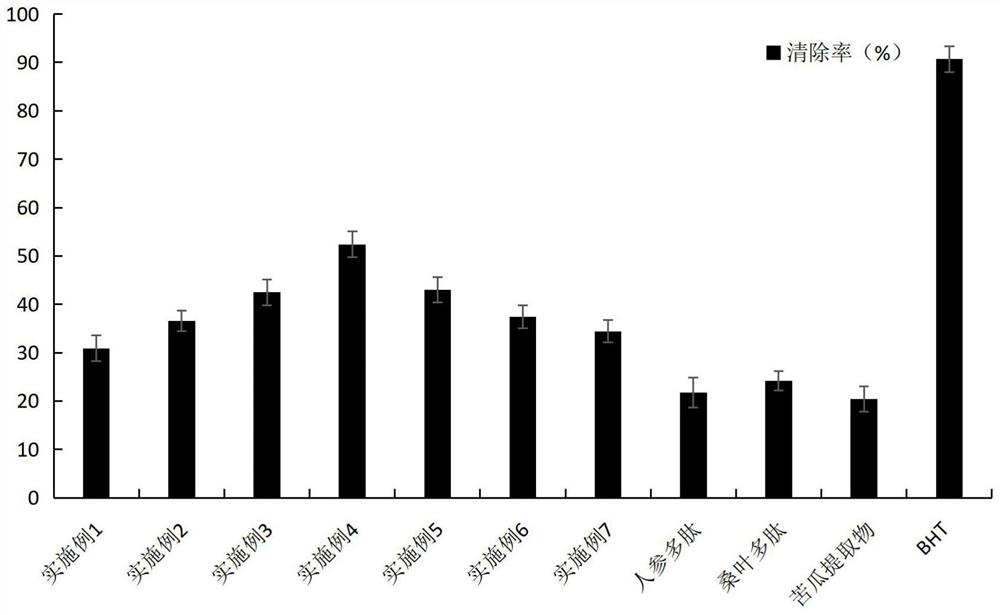
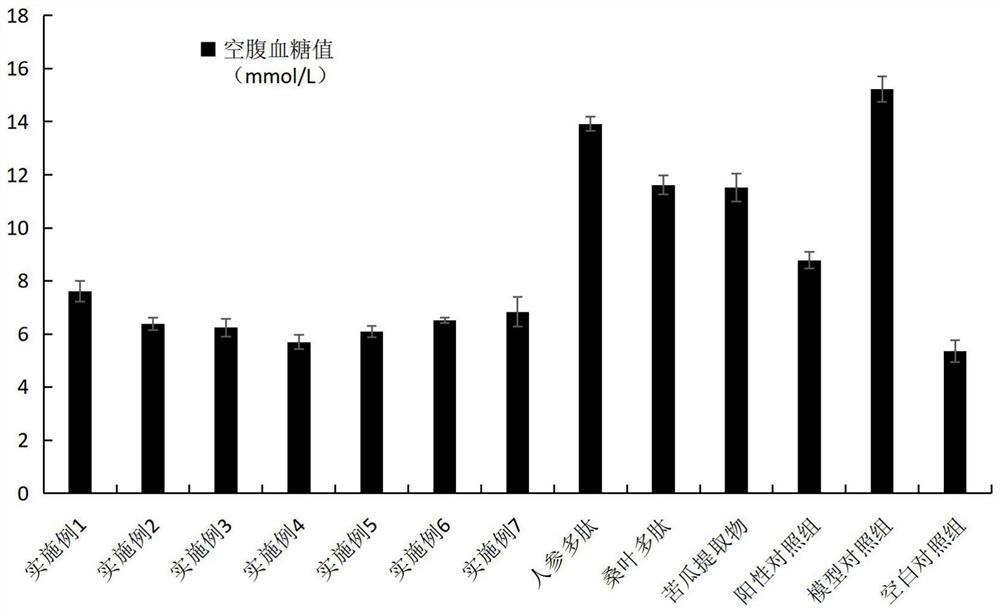
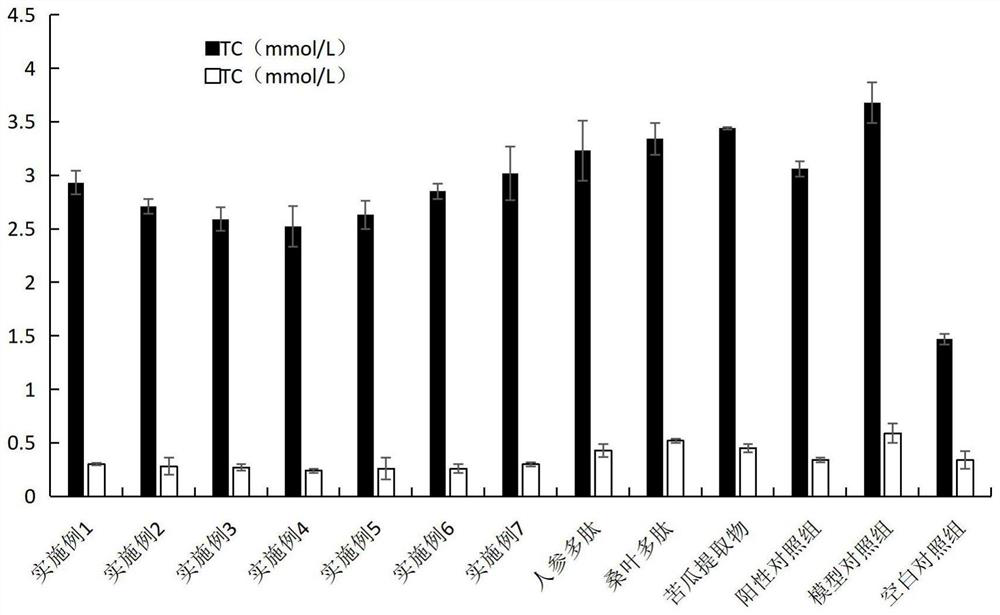
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] This example provides a preparation test of a compound plant-derived polypeptide.
[0025] The preparation method of ginseng polypeptide includes: taking 20g of fresh ginseng, adding 200mL of 0.01mol / L PBS (pH=7), leaching for 12-48 hours, taking the supernatant and adding 400mL ice pre-cooling acetone to precipitate, and mixing well After standing overnight, after centrifugation, the precipitate was taken out and dissolved in 200 mL of 0.01mol / L PBS (pH=7), and then freeze-dried to obtain crude ginseng protein; The 30KDa ultrafiltration is concentrated, the filtrate is collected, and then the 10KDa ultrafiltration is performed to collect the effluent with a molecular weight of less than 10KDa, and freeze-dried to obtain the ginseng polypeptide.
[0026] The preparation method of mulberry leaf polypeptide includes: taking fresh mulberry wood, washing it to remove impurities, drying it, and pulverizing it to 20 meshes to obtain mulberry leaf powder. At room temperature,...
Embodiment 2
[0030] This example provides a preparation test of a compound plant-derived polypeptide.
[0031] The preparation method of this example is the same as that of Example 1, except that, in parts by mass, the compound plant-derived polypeptide described in this example includes component A and component B, and the ginseng polypeptide and mulberry leaf polypeptide in component A are ginseng polypeptide and mulberry leaf polypeptide. The ratio of the compound plant-derived polypeptide is 10:1; the ratio of the component A and the component B in the composite plant-derived polypeptide is 4:1. After mixing according to the above ratio, it is the composite plant-derived polypeptide.
Embodiment 3
[0033] This example provides a preparation test of a compound plant-derived polypeptide.
[0034] The preparation method of this example is the same as that of Example 1, except that, in parts by mass, the compound plant-derived polypeptide described in this example includes component A and component B, and the ginseng polypeptide and mulberry leaf polypeptide in component A are ginseng polypeptide and mulberry leaf polypeptide. The ratio of the compound plant-derived polypeptide is 3:1; the ratio of the component A and the component B in the composite plant-derived polypeptide is 4:1. After mixing according to the above ratio, it is the composite plant-derived polypeptide.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com