Hydroxychloroquine sulfate sustained release microsphere for articular cavity injection and preparation method thereof
A technology of hydroxychloroquine sulfate and sustained-release microspheres, which is applied in the directions of medical preparations, pharmaceutical formulations, and drug combinations containing active ingredients, can solve problems such as toxic side effects and short joint cavity retention time, achieve anti-inflammatory effects, reduce Dosing frequency and dosage, the effect of smooth appearance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Preparation of HCQ Microspheres
[0039] Dissolve 200mg HCQ in 2ml gelatin solution (gelatin solution is prepared by the following method: weigh 0.6g gelatin and put it into a 50ml beaker and add 6ml water) to obtain an aqueous phase, which will be dropped into the oil phase (weigh 1g of splatter). 80, put into a 50ml beaker and add 30ml of liquid paraffin), control the temperature at 55°C, stir for 20min to form a W / O type emulsion, transfer to an ice bath for 5min and add 5ml of glutaraldehyde solution, stir for 1 hour to solidify, Then add 30ml of isopropanol for dehydration for 30min, then carry out suction filtration, rinse with isopropanol, and dry at room temperature to obtain HCQ microsphere powder.
[0040] Microsphere shape:
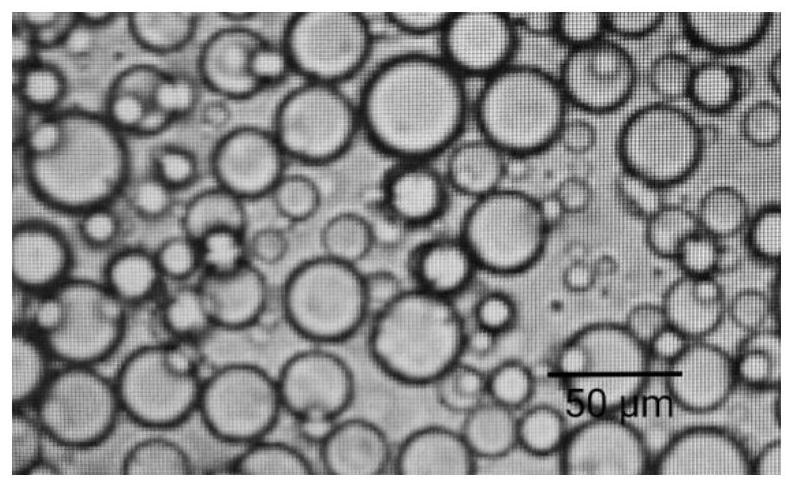
[0041] Take the microspheres prepared in Example 1, and measure the shape of the microspheres with a scanning electron microscope, see figure 1 .
[0042] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the shape of the HCQ microspheres prepa...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Choice of emulsification time
[0045] The preparation methods of the water phase and the oil phase are the same as those in Example 1.
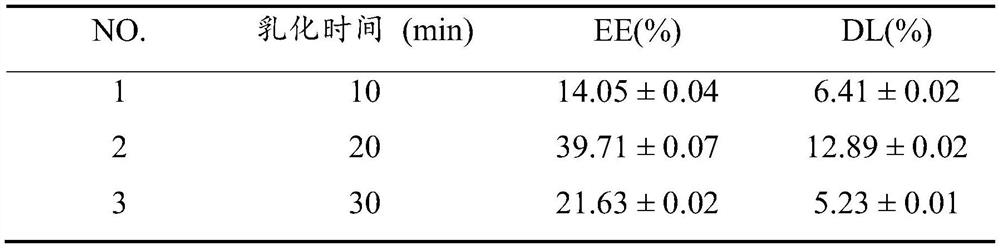
[0046] The water phase was dropped into the oil phase, the temperature was controlled at 55°C, and the mixture was stirred for 10 min, 20 min, and 30 min respectively to form a W / O type emulsion. After being transferred to an ice bath for 5 min, the glutaraldehyde solution was added. The subsequent operations were the same as those in Example 1. The effects of different curing agent addition times on the encapsulation efficiency (EE) and drug loading (DL) were investigated, and the results are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that 20min was selected as the appropriate emulsification time.
[0047] Table 1. Effects of emulsification time on EE and DL ( n=3).
[0048]
Embodiment 3
[0050] The choice of curing agent adding time
[0051] The preparation methods of the water phase and the oil phase are the same as those in Example 1.
[0052]The water phase was dropped into the oil phase, the temperature was controlled at 55°C, and stirred for 20 min to form a W / O type emulsion, which was added immediately after transferring to the ice bath, 5 min after transferring to the ice bath, and 10 min after transferring to the ice bath. Then, 5 mL of glutaraldehyde solution was added, and the subsequent operations were the same as those in Example 1. The effects of different addition times on the encapsulation efficiency and drug loading were investigated, and the results are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that the time for adding the curing agent is selected as the appropriate time for adding the curing agent after 5 minutes after the ice bath.
[0053] Table 2. Effect of curing agent addition time on EE and DL ( n=3)
[0054]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com