CMOS comparator
A technology of oxide semiconductors and complementary metals, which is applied in the direction of instruments, differential amplifiers, DC-coupled DC amplifiers, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the speed of comparators, increasing costs, and unable to eliminate the influence, and achieves high precision and high speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
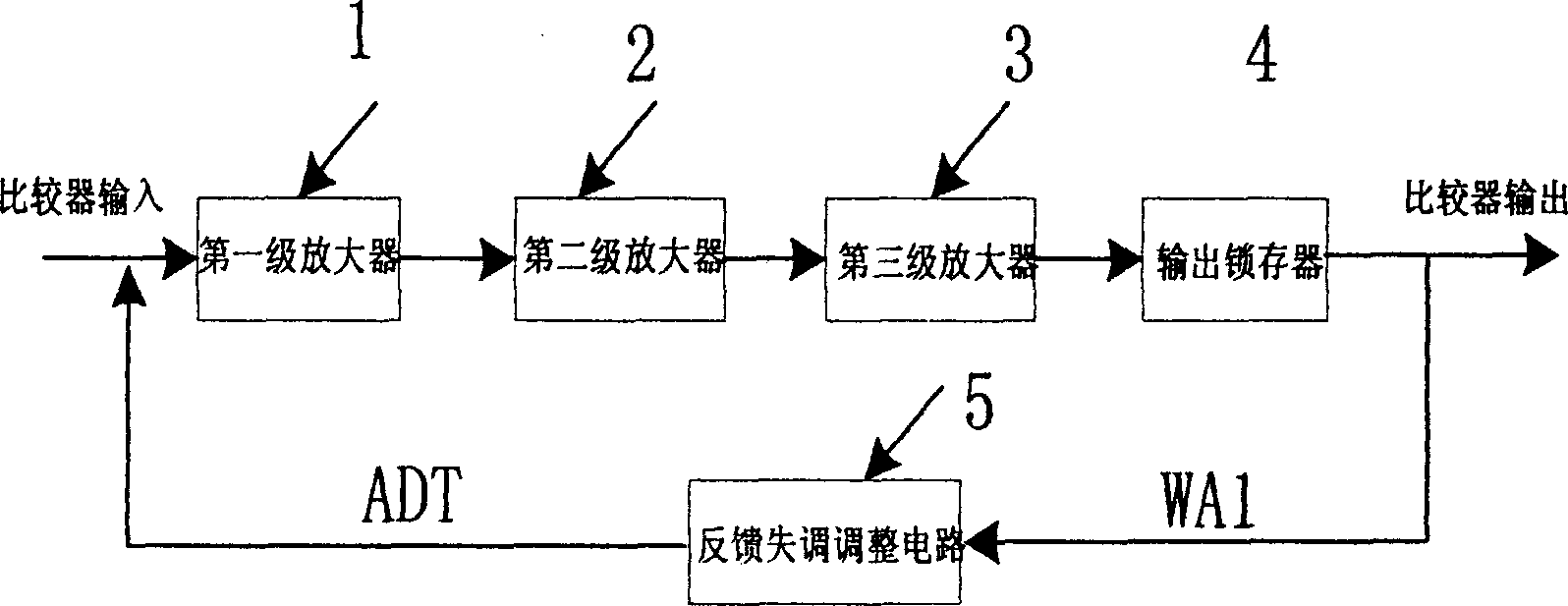
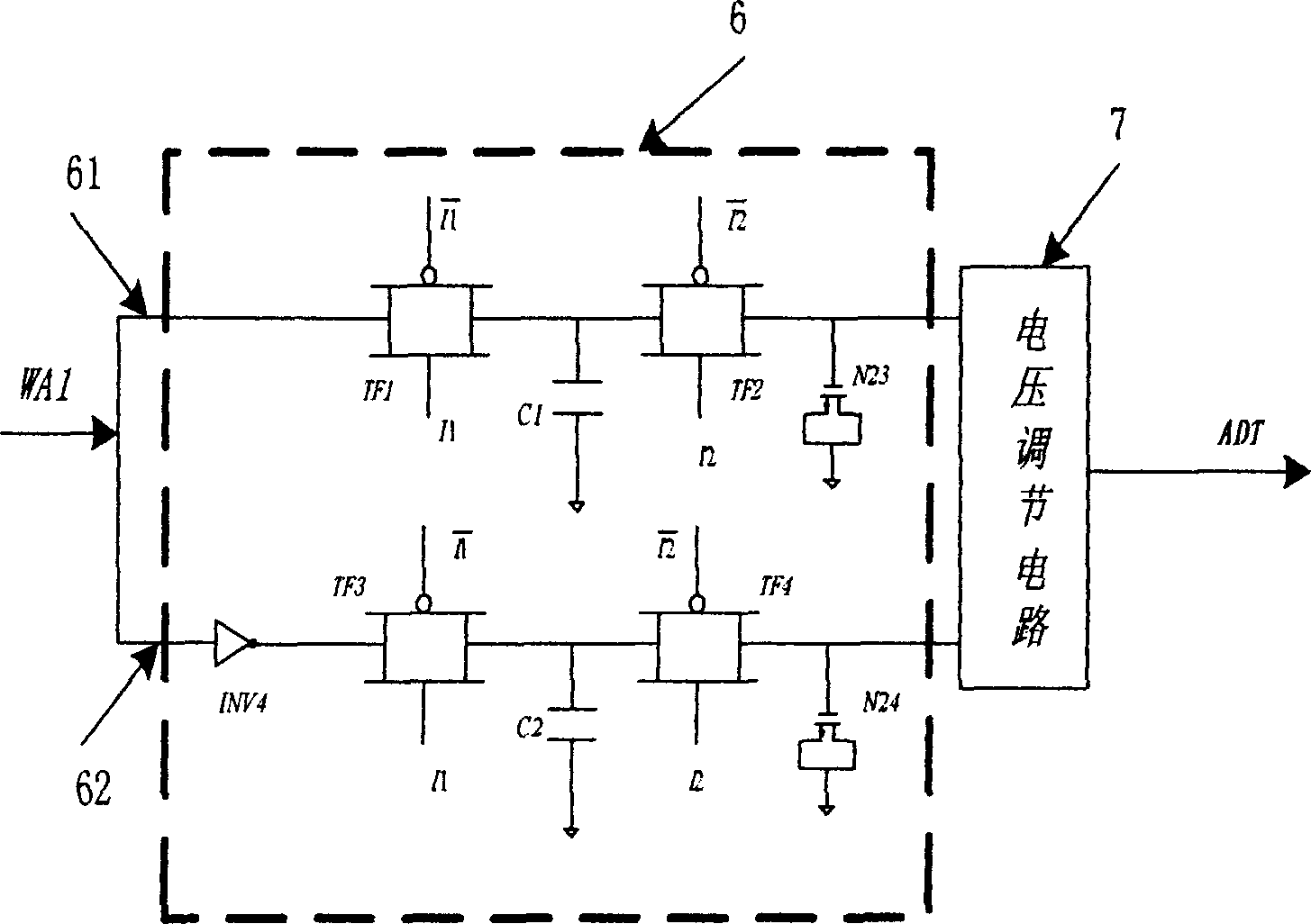
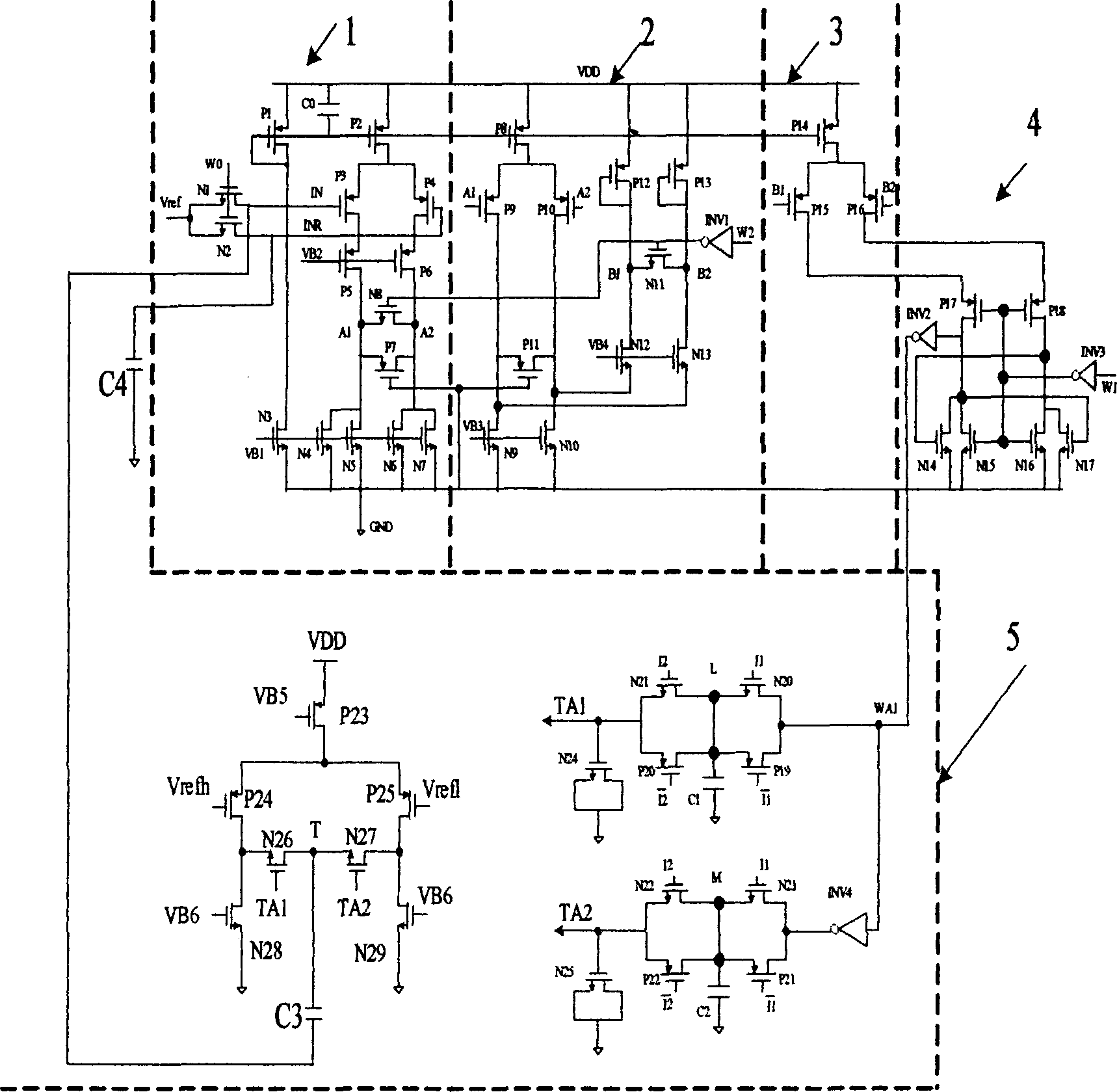
[0012]A complementary metal oxide semiconductor comparator circuit is composed of first, second and third stage differential input pre-amplifiers 1, 2 and 3, an output latch 4 and a feedback offset adjustment circuit 5. The first differential amplifier 1 is composed of bias current transistor P1, bias current transistor P2, differential input transistors P3 and P4, cascaded PMOS transistors P5 and P6, clamping PMOS transistor P7, switch transistors N1, N2 and N8, bias The current tube N3, the load tubes N4, N5, N6 and N7, and the capacitor C0 are composed. The gate terminals of the switch tubes N1 and N2 are connected to the clock signal W0, the source terminal is connected to the bias voltage Vref, and the drain terminals are connected to the gates of the differential input transistors P3 and P4. The source terminal of the bias current tube P1 is connected to the power supply VDD, the gate terminal is connected to the drain terminal and is connected to the gate terminal of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com