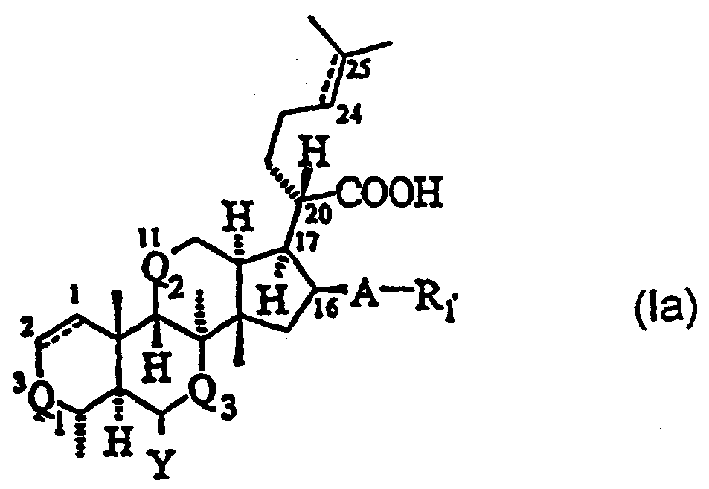
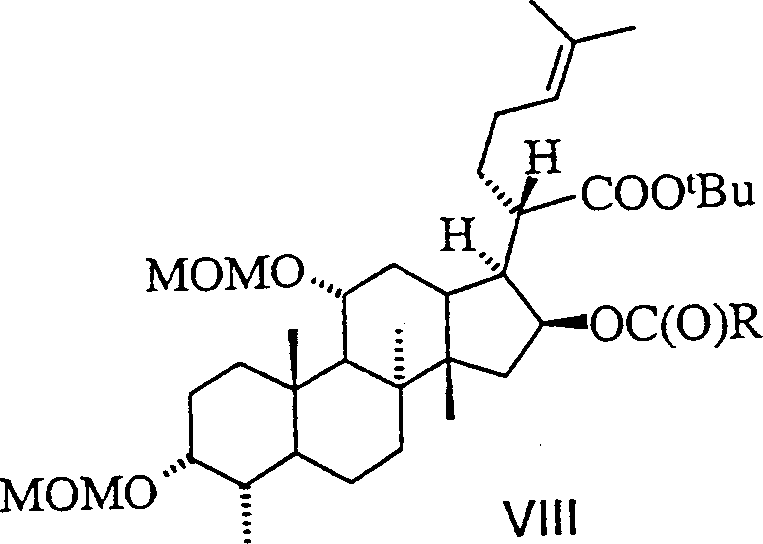
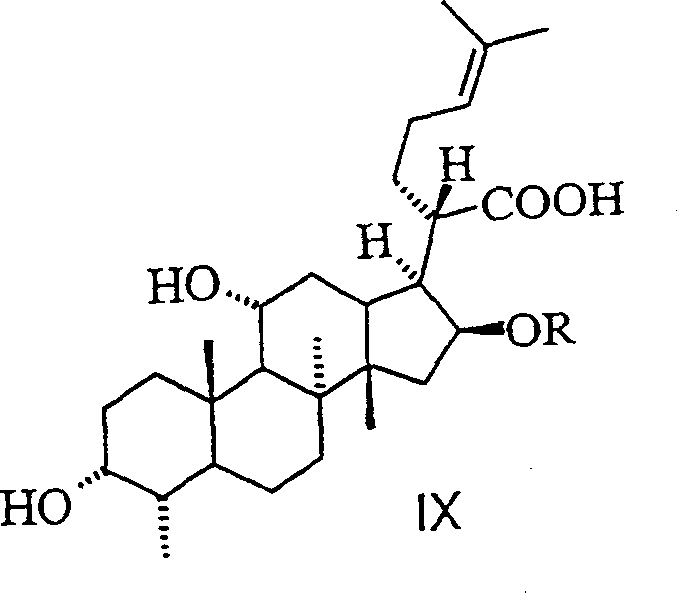
Novel fusidic acid derivatives
A fusidic acid and compound technology, applied in the field of new fusidic acid derivatives, can solve the problems of activity reduction and loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0197] Example 1: 17(S), 20(S)-dihydrofusidic acid (10) (Compound 101)
[0198] The compound of formula 9 (2 g, 3.3 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous dichloromethane (50 mL) in an oven-dried two necked round bottom flask under argon and cooled at -20 °C. To this solution was added 4 Angstrom molecular sieves (6 g) and bromotrimethylsilane (2.7 mL, 20 mmol) was slowly injected with continuous stirring. The reaction mixture was stirred until complete (approximately 5 hours). The reaction mixture was then transferred to a separatory funnel with ethyl acetate and water and the two layers were shaken and separated. The aqueous layer was extracted three times with ethyl acetate (3 x 20 mL) and the combined organic layers were washed with brine (30 mL). The organic solution was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated in vacuo to afford 1.4 g of compound 101 as a colorless solid. Recrystallization from methanol-water gave 1.2 g of colorless crystals, melting at 195-195....
Embodiment 1a
[0200] Example 1a: Another preparation method of 17(S), 20(S)-dihydrofusidic acid (10) (compound 101)
[0201] The compound of formula 16 (3.6 g, 5.7 mmol) was dissolved in THF (15 mL) and 4% aqueous hydrogen fluoride (10 mL) in a round bottom Teflon flask. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 days. The reaction was then neutralized to pH 8 with 27% sodium hydroxide solution and finally adjusted to pH 4 with acetic acid. The reaction mixture was then transferred to a separatory funnel with ethyl acetate and water, the two layers were shaken and separated. The aqueous phase was extracted three times with ethyl acetate (3 x 50 mL), and the combined organic layers were washed with brine (50 mL). Drying over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentration under vacuum gave 4 g of crude product 101 as a colorless solid. Using ethyl acetate, a mixture of low-boiling petroleum ether and a trace of formic acid as an eluent, purified by column chromatography to obta...
Embodiment 2
[0203] Example 2: 17(S), 20(S), 24,25-tetrahydrofusidic acid (compound 102)
[0204] A solution of compound 101 (280 mg, 0.54 mmol) in ethanol (3 mL) was hydrogenated under atmospheric pressure hydrogen in the presence of 5% palladium (30 mg) on calcium carbonate. The reaction mixture was stirred vigorously until the theoretical amount of hydrogen was consumed, and the catalyst was filtered off. Water was added dropwise to the filtrate to obtain 255 mg of crystalline 17(S), 20(S), 24, 25-tetrahydrofusidic acid, melting point 138.5-140°C.
[0205]13 C NMR, (DMSO-d 6 ): 210.7, 176.6, 169.1, 131.2, 123.7, 75.3, 69.0, 57.7, 48.9, 43.8, 43.6, 43.3, 41.8, 41.7, 37.7, 37.2, 34.4, 32.6, 30.1, 27.9, 25.3, 24.8, 22.7, 20. 20.4, 20.1, 17.4, 16.3, 16.0.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com