Nikemycin Z component engineering bacterium and its application
A technology of nikkomycin and engineering bacteria, applied in application, genetic engineering, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of expensive reagents and unsuitable for large-scale industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
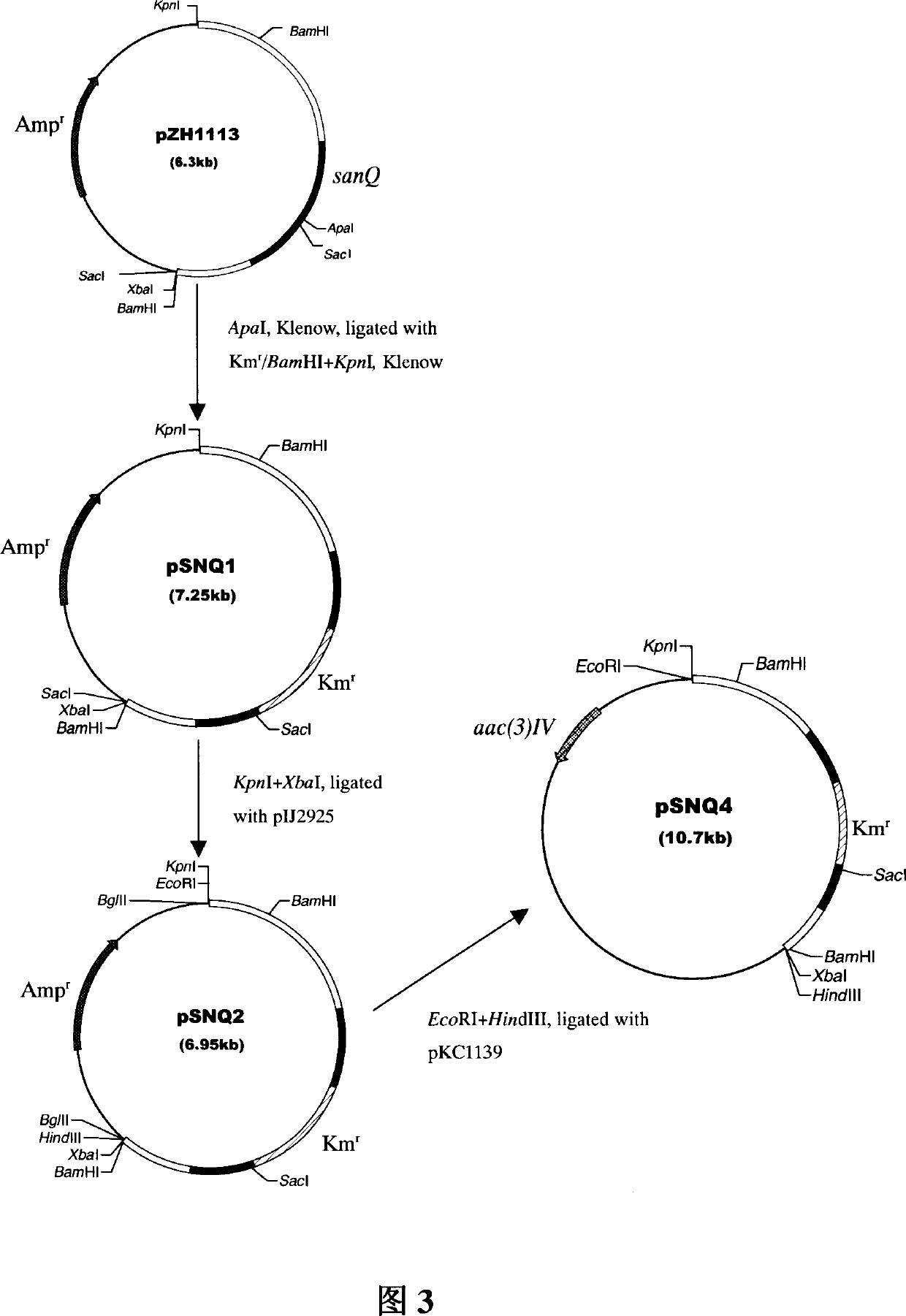
[0028] The present invention is further described in detail through the following examples. Embodiment 1: the cloning of Streptomyces chromogenes CGMCC4.321 sanQ gene, blocking and the construction of nikkomycin Z component engineering bacteria (1) cloning of sanQ gene
[0029] a. Digest the Cos1, Cos2, and Cos3 plasmids in the Streptomyces chromogenes CGMCC4.321 Cosmid library with PstI, and perform agarose gel electrophoresis, using the 1.35-kb BamHI-ApaI fragment that includes part of the sanQ gene sequence As a probe, Southern hybridization was performed, and a positive signal appeared at 10.6-kb in Cos3. The 10.6-kb DNA fragment and the M13 - / PstI fragment, use T4 DNA ligase at 16°C for 4 hours to connect the two pieces of DNA. Transform the ligation product into E.coli DH5α competent cells, and select the correct transformants.
[0030] b. Select the appropriate enzyme to digest the 10.6-kb DNA fragment, draw a physical map of the 10.6-kb DNA fragment, perform subclo...
Embodiment 2
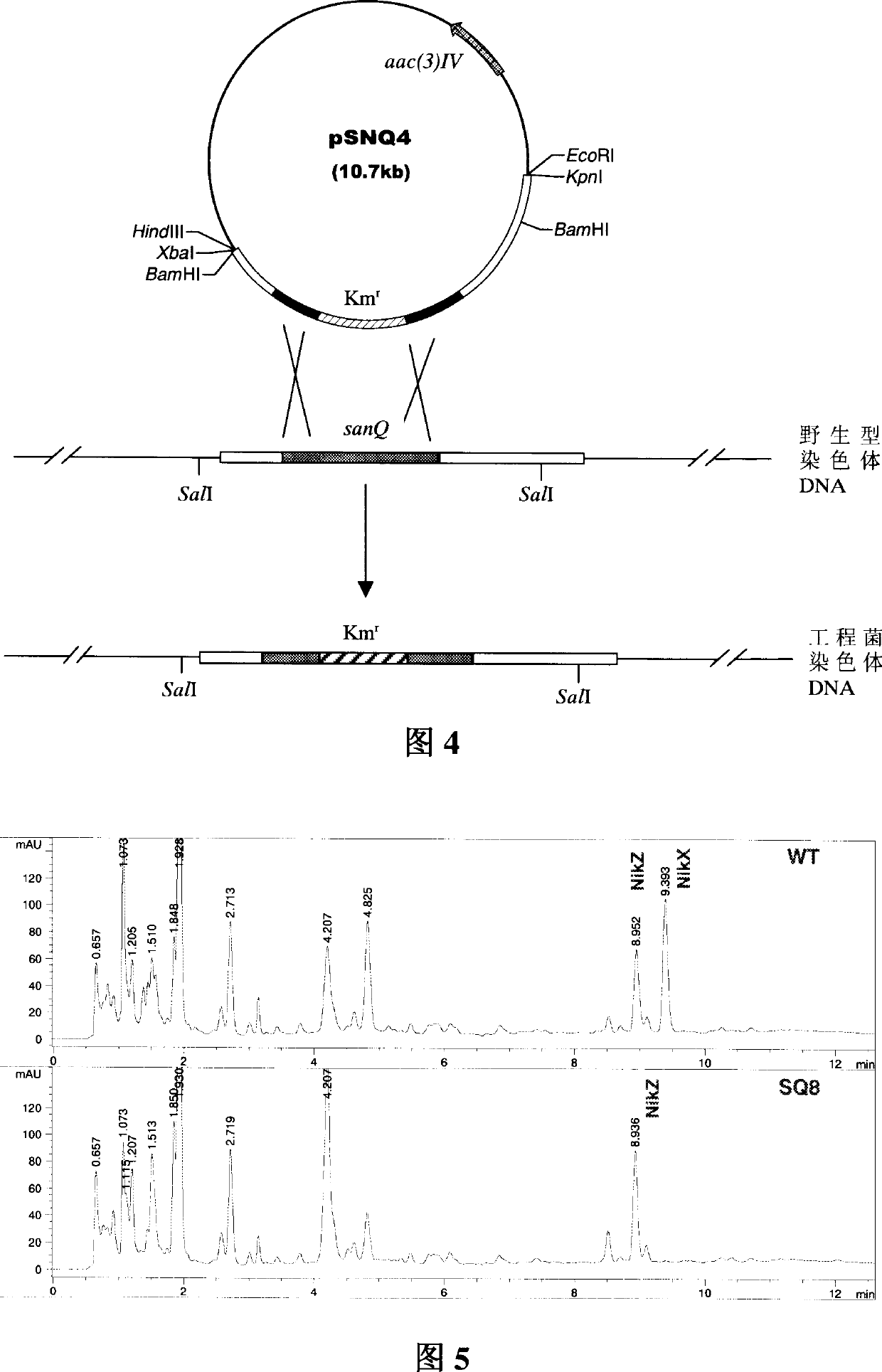
[0036] Inoculate the correct sanQ gene blocking engineered bacteria into SP medium (3% mannitol, 1% starch, 0.8% yeast extract powder, 0.5% soybean peptone, pH6.0) for fermentation, and culture in a shaking table at 28°C and 220rpm After 4 days, the bacterial cells were filtered, and the fermentation broth was taken for HPLC analysis. HPLC analysis condition is, mobile phase A: contain 10mM sodium heptanesulfonate and 2ml acetic acid in every liter of solution; Mobile phase B: contain 10mM sodium hexanesulfonate and 2ml acetic acid in every liter of water: acetonitrile (6:4); Within 10min, the mobile phase B changed from 13% to 45%; RP C-18, HPLC was Agilent1100. The results of HPLC analysis showed that: sanQ gene blocking engineered bacteria (SQ8 strain in Fig. 4) also produced Z component, and its content was the same as wild type; but could not produce X component. Therefore, this sanQ gene blocking engineered bacterium is also called nikkomycin Z component engineered bact...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Inoculate Botrytis cinerea in PDA liquid culture medium (20% potato juice, 2% glucose), 28 ℃, 220rpm cultivates 3 days; The cultured bacterium liquid beats evenly with homogenizer, and by 20% addition Add to PDA solid medium (20% potato juice, 2% glucose, 0.8% agar), pour 70 milliliters of this PDA bacterium liquid in the petri dish of diameter 15 centimeters, after it solidifies, R2YE medium (Kieser T, Bibb M J, Buttner M J, et al. Practical Streptomyces Genetics. Norwich: The John Innes Foundation, 2000) The 4-day-grown wild-type and engineered bacteria blocks were placed in a petri dish, and the antibacterial test of metabolites was carried out. The antibacterial test showed that both the engineered bacteria and the wild-type metabolites of nikkomycin Z components could inhibit the growth of Botrytis cinerea, and the antibacterial ability of the engineered bacteria was equivalent to that of the wild type. Example 3: Inhibitory effect of nikkomycin Z component enginee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com