Extraction process for reactive metal oxides
A process method and oxide technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of titanium oxide/hydroxide, alkali metal aluminate/aluminum oxide/aluminum hydroxide, etc., can solve unfavorable iron-carbon oxide and oxidation Phase distribution and other issues, to achieve the effect of economic recovery and reduce the impact on the environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
[0085] Example I: Bauxite from Ghana
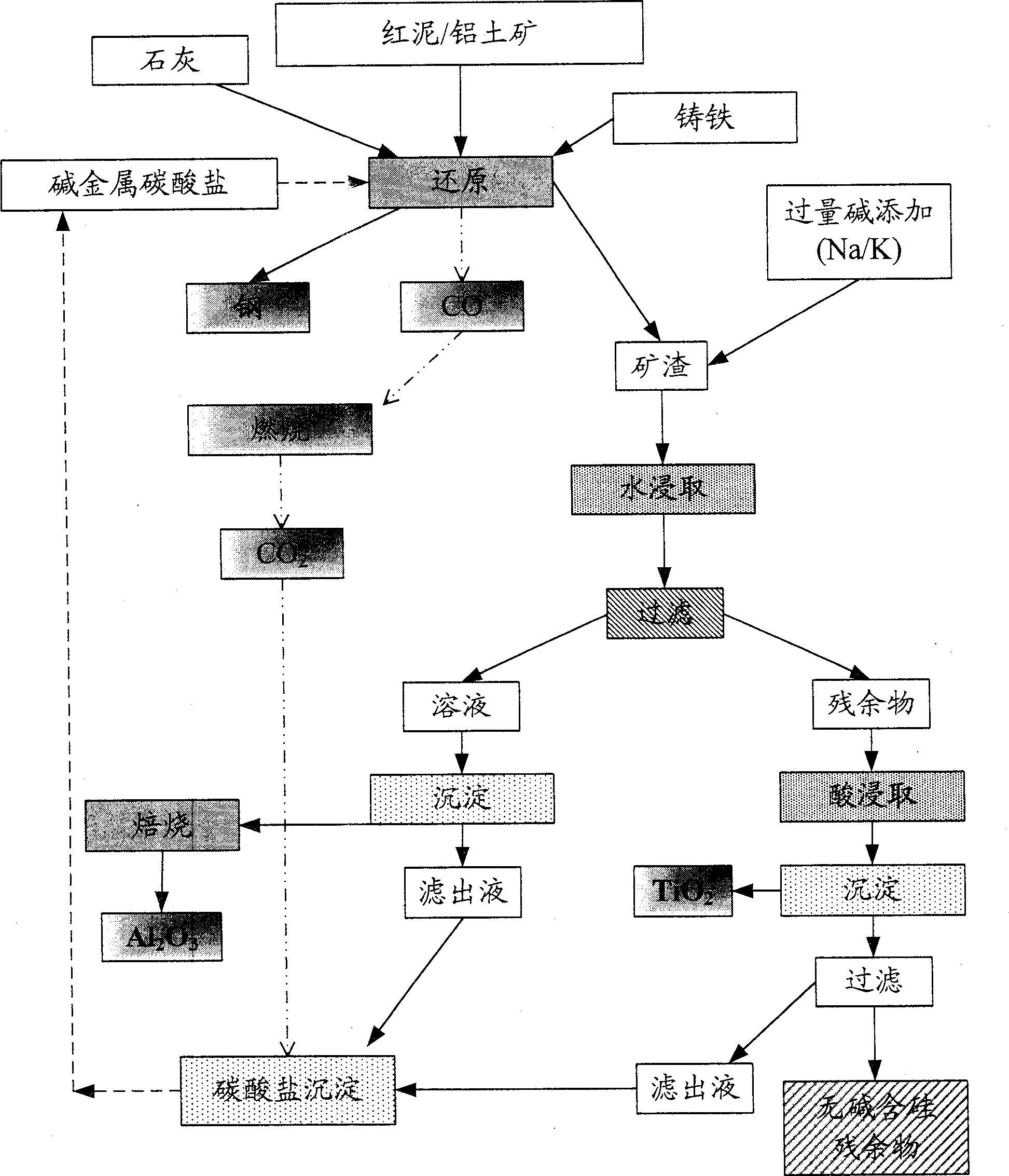
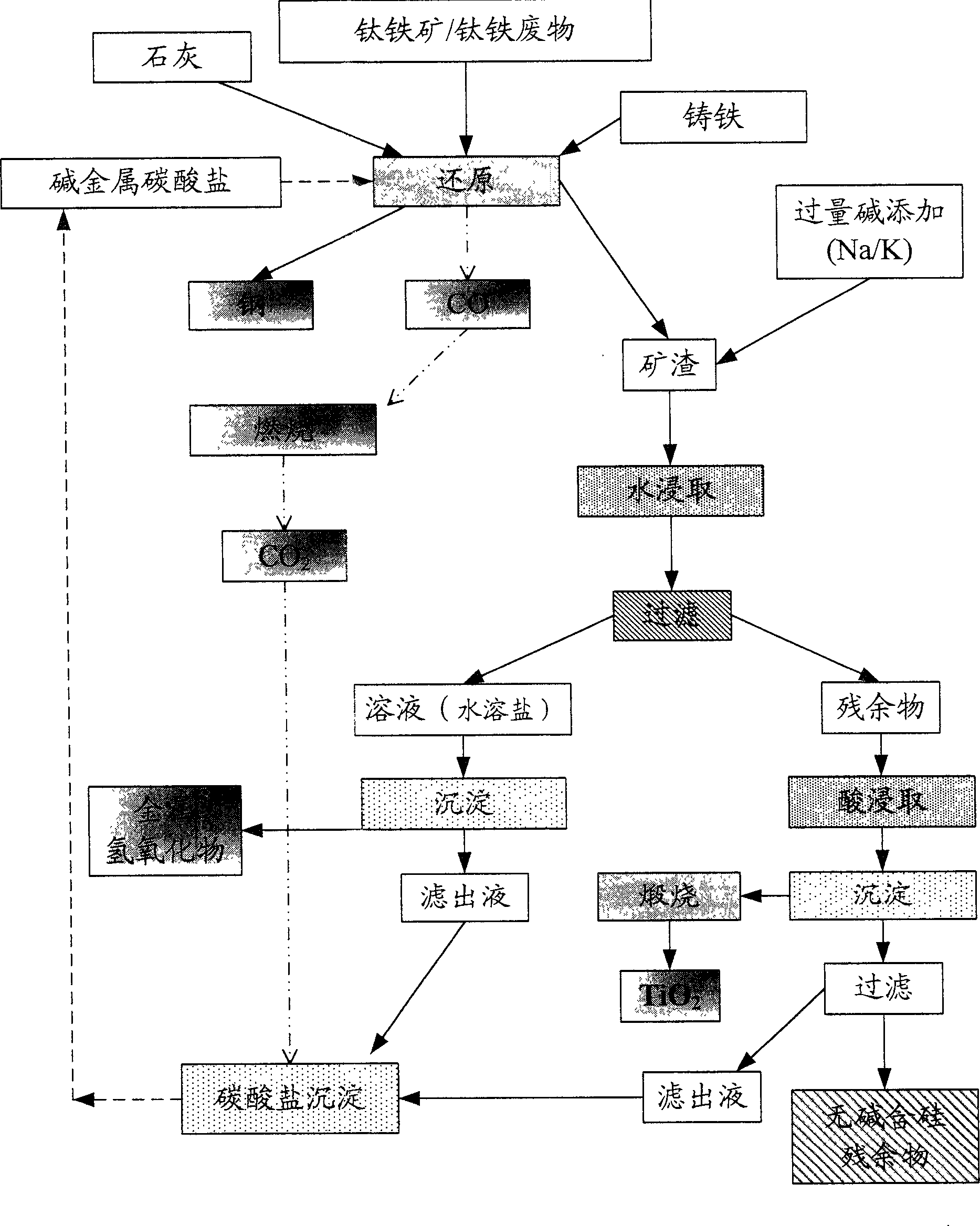
[0086] attached Figure 1a The implementation process of embodiment 1 is represented schematically.
[0087] Gray cast iron containing 1% silicon (Si) and 4.2% carbon is melted in an induction furnace. Ghana bauxite (approximate composition: 55% Al 2 o 3 , 12% Fe 2 o 3 , 2% TiO 2 , 2% SiO 2 and water) mixed with lime and excess carbon, and slowly added to the molten slurry. The temperature of the molten slurry is adjusted to maintain the metal-bearing slag in a molten state.
[0088] Sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate (20% over stoichiometric ratio) is added in the final stage of the reduction reaction and a fluid slag is released. The slag is digested with hot water and filtered. The filtrate is acidified with carbon dioxide to convert the water-soluble sodium / potassium aluminate to Al(OH) 3 precipitation. Filter out Al(OH) 3 and roasted to produce pure Al 2 o 3 . The extraction efficiency of alumina is close to 65%....
Embodiment II
[0091] Embodiment II: (red mud)
[0092] Accompanying drawing 1 has represented the implementation process of embodiment II schematically.
[0093] Red mud (approximate composition: 46% Fe 2 o 3 , 22% Al 2 o 3 , 8% TiO 2 , 8% SiO 2 , 3 to 4% of MgO and CaO and the loss on ignition of 10 to 12%) are added to the molten gray cast iron slurry together with excess lime and carbon. Sodium carbonate / potassium carbonate (more than 20% of the stoichiometric ratio) is added to the slag before tapping. Experiments were carried out according to the methods described in the above examples. The extraction efficiency of alumina exceeds 75%. About 75% TiO in this process 2 is extracted. The residue contains aluminosilicate complexes.
[0094] The red mud obtained in this example contains alkali in the form of potassium ions, unlike soda in red mud which can neither be used as a fertilizer nor as a soil conditioner to exhibit harmful effects.
Embodiment III
[0095] Embodiment III: (alkali-roasted ilmenite)
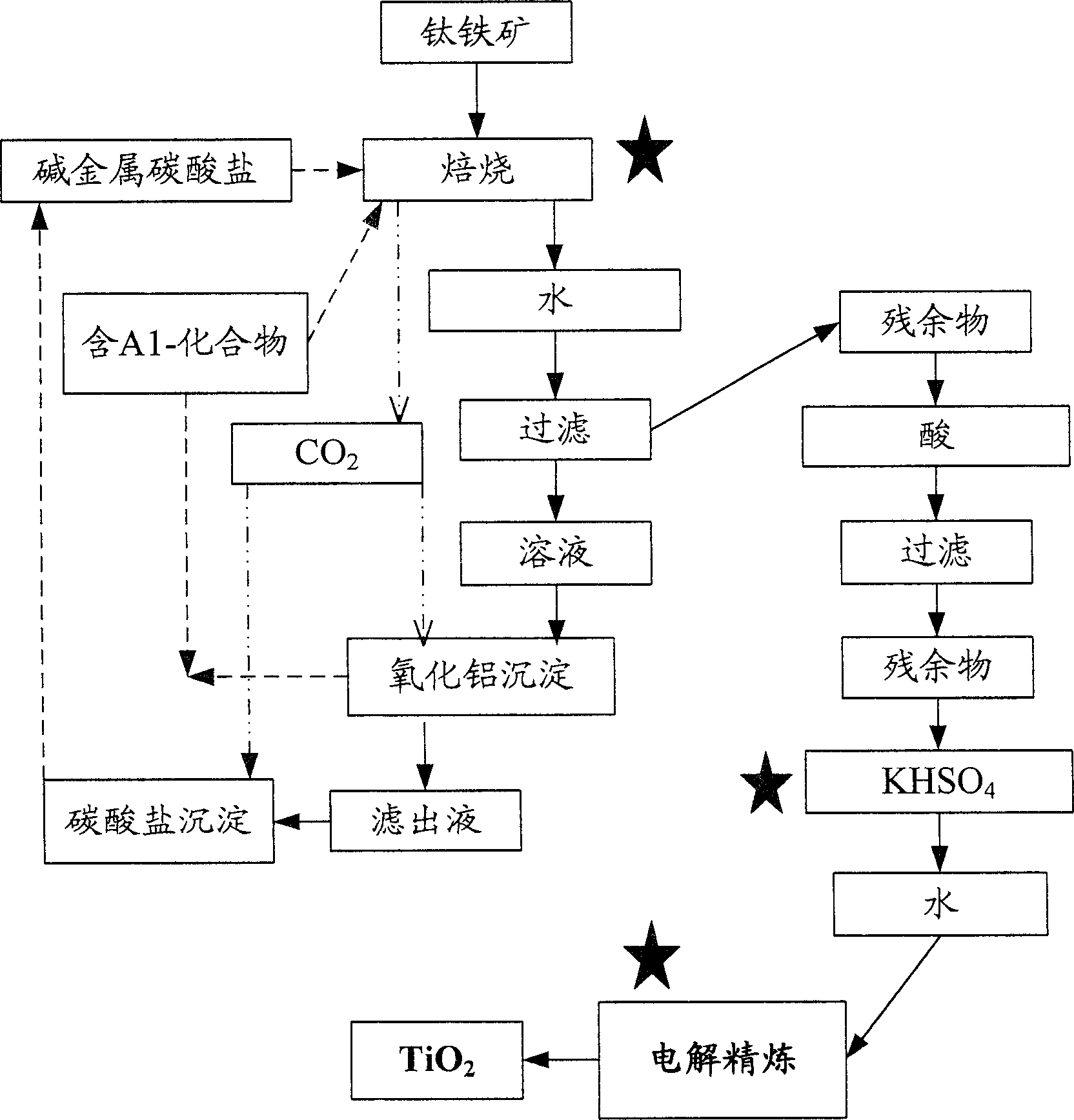
[0096] attached figure 2 The implementation process of embodiment III is schematically represented.
[0097] Contains 63% TiO 2 , 32% Fe 2 o 3 and 2% Al 2 o 3 The ilmenite ore is mixed with 10% alumina and excess alkali metal carbonate, and roasted in air at 1200°C for 2 hours. Add sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate (more than Na 2 O:TiO 2 20% of the stoichiometric ratio). The calcined material was extracted with water and the solution was filtered to separate the residue. The filtrate is acidified with carbon dioxide to convert the water-soluble sodium / potassium aluminate to Al(OH) 3 precipitation. Filter out Al(OH) 3 And recycle to the first step. The filtrate was evaporated and sodium carbonate was recovered. The residue containing titanium dioxide (TiO2) was leached with 5% HCl solution. The residue was filtered and washed with acid solution and then with water. At the end of the process, TiO in the r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com