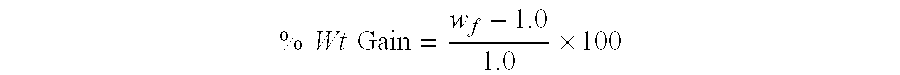Drilling fluid containing microspheres and use thereof
a technology of drilling fluid and microspheres, which is applied in earth drilling and mining, chemistry apparatus and processes, and well accessories, etc., can solve problems such as pumping problems, and achieve the effects of reducing the density of the material, reducing the pressure required, and reducing the associated pumping cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Glossary
[0096] A-174 Silane; 3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl methacrylate, available from Dow Corning; Midland Mich. [0097] Adflex™ KS-359; polyproplylene available from Basell, Wilmington, Del. Blox™ 220; high adhesion thermoplastic epoxy resin, Dow Chemical Co., Midland, Mich. [0098] Cumene hydroperoxide; C6HSC(CH3)2OOH; available from Sigma-Aldirch, Milwaukee, Wis. [0099] Irgacure™ 651; Methylbenzoylbenzoate, available from Ciba Specialty Chemicals, Tarrytown, N.Y. [0100] Lexan 123™; polycarbonate available from General Electric, Pittsfield, Mass. [0101] Moplen™; Polypropylene available from Basell, Wilmington, Del. [0102] SRC 7644™; Polypropylene available from Exxon / Mobil, Edison, N.J. [0103] SR 351™; Trimethylolpropane triacrylate, available from Sartomer, Exton, Pa. [0104] RD 710™; Phenylic resin, available from 3M Company, St. Paul, Minn.
Test Methods
Glass Microsphere Strength Test
[0105] An APP strength tester (available from Advanced Pressure Products, Ithaca, N.Y.) was use...
examples 6-10
Absorbency of Composites to Drilling Fluids
[0110] For Examples 6-10 composite microspheres (1.0 g) were placed in drilling fluids (10.0 g; available from Halliburton Energy Services) as identified in Table 2. The sample was allowed to set at room temperature for four days. The mixtures were then filtered through a 250 mesh screen, and the solid composite microsphere material was allowed to drain for 1 hour. The composite microsphere sample was then weighed (wf) and % wt gain was calculated using the formula: % Wt Gain=wf-1.01.0×100
[0111] Results are listed in Table 2.
TABLE 2% weight gain of microsphere composites in various drilling fluids.% Wt% Wt% WtGainGain% WtGainPetrofreePetrofreeGainExamplePolymerPetrofreeLVSFLVT 2006Blox ™ 2206.33.04.83.47Moplen ™13.615.717.813.98SRC 764417.718.522.928.69Adflex ™55.157.565.293.0KS-35910Lexan ™2.04.31.71.0
examples 11-13
Preparation of Composite Microspheres with Acrylate Polymers
[0112] The composites were prepared as described in U.S. Pat. No. 6,620,214.
Procedure #1: General Procedure for Making a Composite Microsphere Precursor Slurry
[0113] A slurry was prepared by thoroughly mixing glass microspheres, acrylate resin, and initiators, using a mixer (obtained from Hobart Corporation, Troy, Ohio; model number A120T). Specific formulation can be found in Table 3. The abrasive slurry was mixed in the mixer on low speed using a flat-beater style impeller for 30 minutes and heated to a temperature within the range from about 90° F. (32° C.) to about 120° F. (49° C.) due to mechanical heating and heat of reaction. At this point, the abrasive slurry was very thick with cement-like handling characteristics. The mixed slurry was then placed in a refrigerator for at least 45 minutes to cool before further processing. The temperature of the refrigerator was in the range from about 40° F. (4° C.) to about 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com