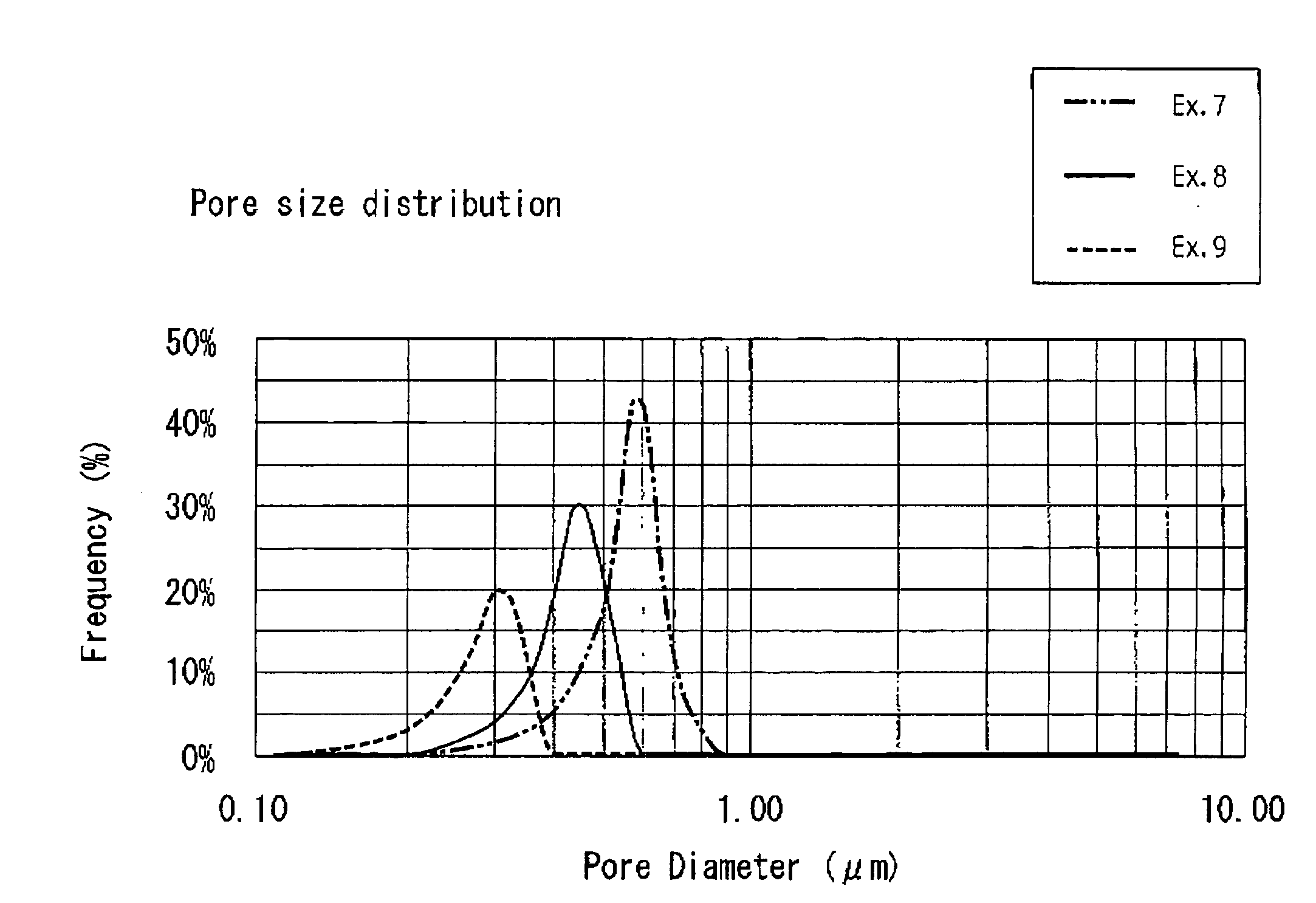
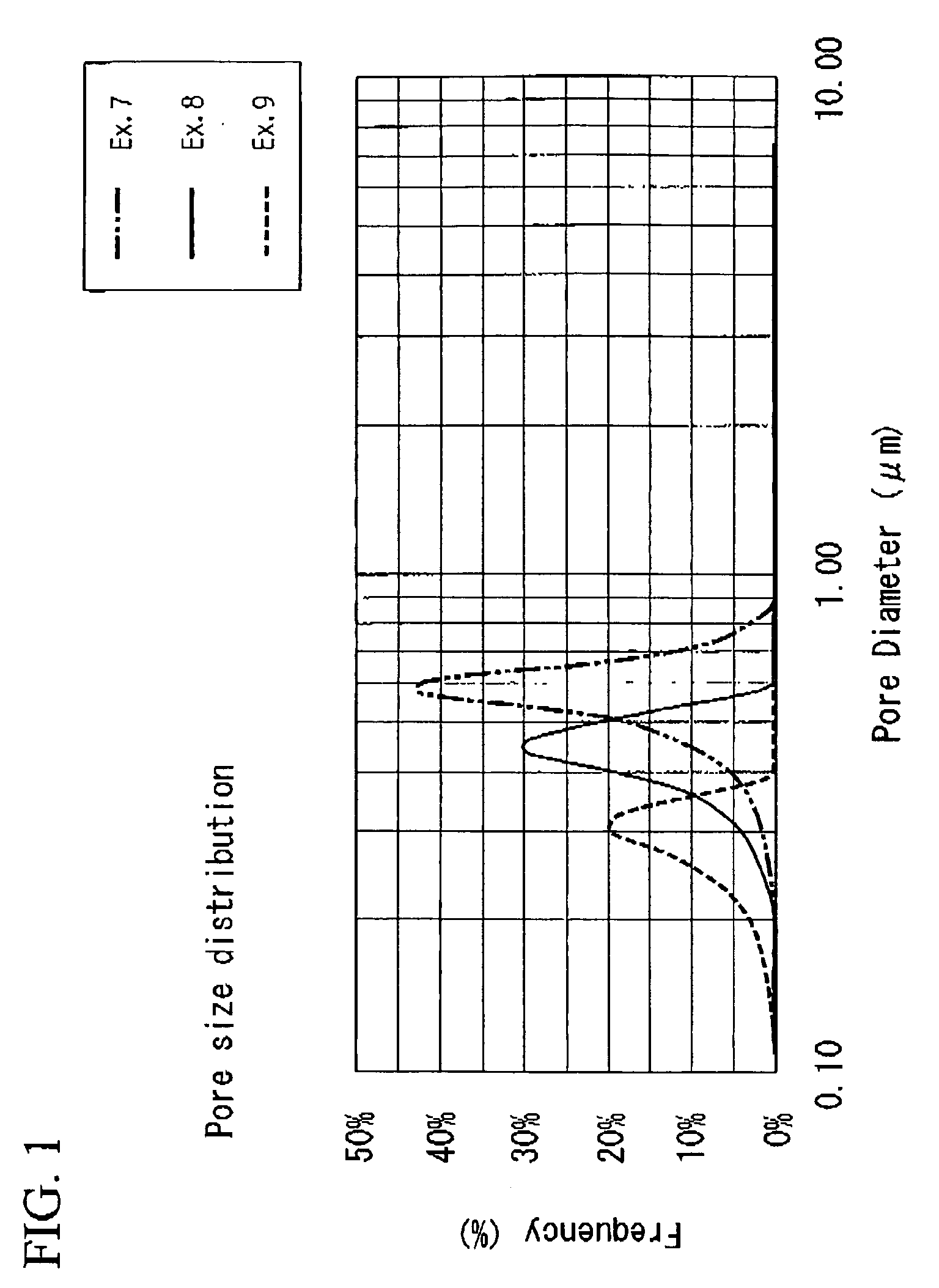
Niobium powder, process for producing the same and solid electrolytic capacitor therefrom
a technology of niobium powder and process, which is applied in the direction of capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, electrical apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of large grain density of powder obtained by oxide reduction method, inability to incorporate impurities, and short distance between crystal particles, etc., to achieve excellent electrical properties and high purity niobium powder
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0056] A predetermined amount of potassium fluoride and potassium chloride as diluent salts were introduced into a reaction vessel whose inner surface was formed of nickel material, and it was heated to a reaction temperature. After this, a predetermined amount of potassium niobate fluoride and sodium were added in that order and this process was repeated to conduct a reduction reaction. In this manner, niobium powder was obtained.
[0057] The employed potassium niobate fluoride had a water content of 4000 ppm as determined based on the Karl Fischer method upon heating to 600° C.
[0058] Also, the water content of potassium fluoride and potassium chloride was 500 ppm and 50 ppm, respectively, as determined based on the Karl Fischer method upon heating to 700° C.
[0059] Moreover, the amount of water in the reaction system of the reduction reaction was 16100 ppm converted to the amount of niobium powder obtained.
[0060] The niobium powder thus obtained was subjected to post-processes, a...
example 2
[0061] A predetermined amount of potassium fluoride and potassium chloride as diluent salts were introduced into a reaction vessel whose inner surface was formed of nickel material, and it was heated to a reaction temperature. After this, a predetermined amount of potassium niobate fluoride and sodium were added in that order and this process was repeated to conduct a reduction reaction. In this manner, niobium powder was obtained.
[0062] The employed potassium niobate fluoride had a water content of 1000 ppm as determined based on the Karl Fischer method upon heating to 600° C.
[0063] Also, the water content of potassium fluoride and potassium chloride was 1000 ppm and 50 ppm, respectively, as determined based on the Karl Fischer method upon heating to 700° C.
[0064] Moreover, the amount of water in the reaction system of the reduction reaction was 14700 ppm converted to the amount of niobium powder obtained.
[0065] The niobium powder thus obtained was subjected to post-processes, ...
example 3
[0066] A predetermined amount of potassium fluoride and potassium chloride as diluent salts were introduced into a reaction vessel whose inner surface was formed of nickel material, and it was heated to a reaction temperature. After this, a predetermined amount of potassium niobate fluoride and sodium were added in that order and this process was repeated to conduct a reduction reaction. In this manner, niobium powder was obtained.
[0067] The employed potassium niobate fluoride had been heat-dried at about 100° C. under a reduced pressure of 2 kPa in a vessel to which a Teflon® lining was applied in advance, and it was introduced into the reaction vessel without being exposed in air. The water content of potassium niobate fluoride subjected to the heat-drying process under a reduced pressure was 1000 ppm as determined based on the Karl Fischer method upon heating to 600° C.
[0068] Also, the water content of potassium fluoride and potassium chloride used as diluent salts was 500 ppm ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| leakage current value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com