Mask patterns including gel layers for semiconductor device fabrication and methods of forming the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
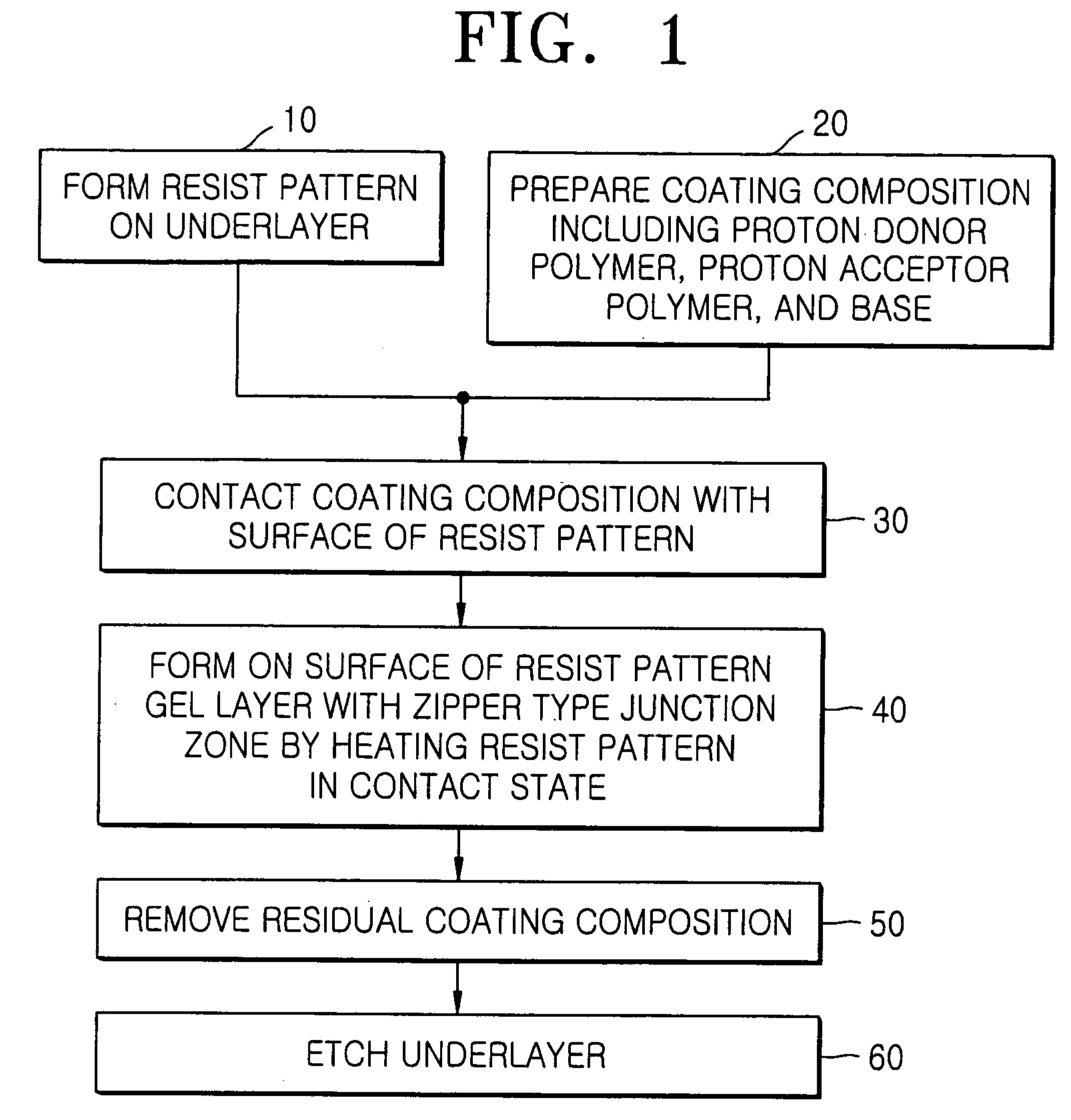
Formation of Resist Pattern
[0083] An antireflective film (DUV-30, Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd.) was formed to a thickness of about 360 Å on an 8-inch bare silicon wafer. A photoresist for ArF (SAIL-G24c, ShinEtsu Chemical Co. Ltd) was subsequently spin-coated on the antireflective film followed by baking at about 105° C. for about 60 seconds to form a resist film with a thickness of about 3,000 Å. The resist film was exposed to light by an ArF (193 nm) stepper followed by post-exposure baking (PEB) at about 105° C. for about 60 seconds. The wafer was developed with a 2.38 wt % tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) solution to form, on the wafer, a resist pattern having a plurality of openings. The resist pattern had an isolated hole pattern (hereinafter, referred to as “i-hole pattern”) with a diameter of 129.7 nm and a dense hole pattern (hereinafter, referred to as “d-hole pattern”) with a diameter of 138.0 nm selected at a center portion of a hole array in which a plurality o...
example 2
Control
Preparation of Coating Composition
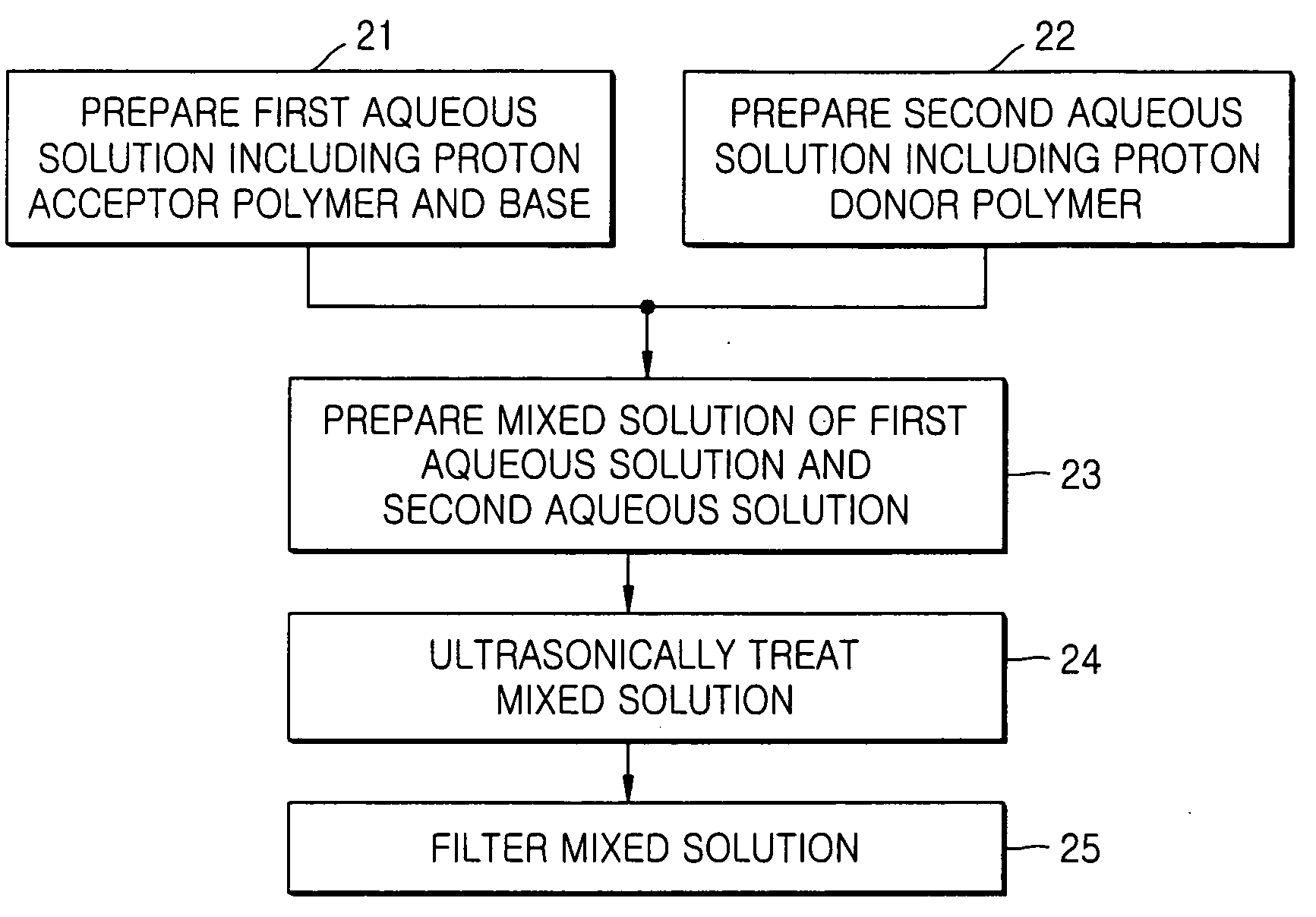
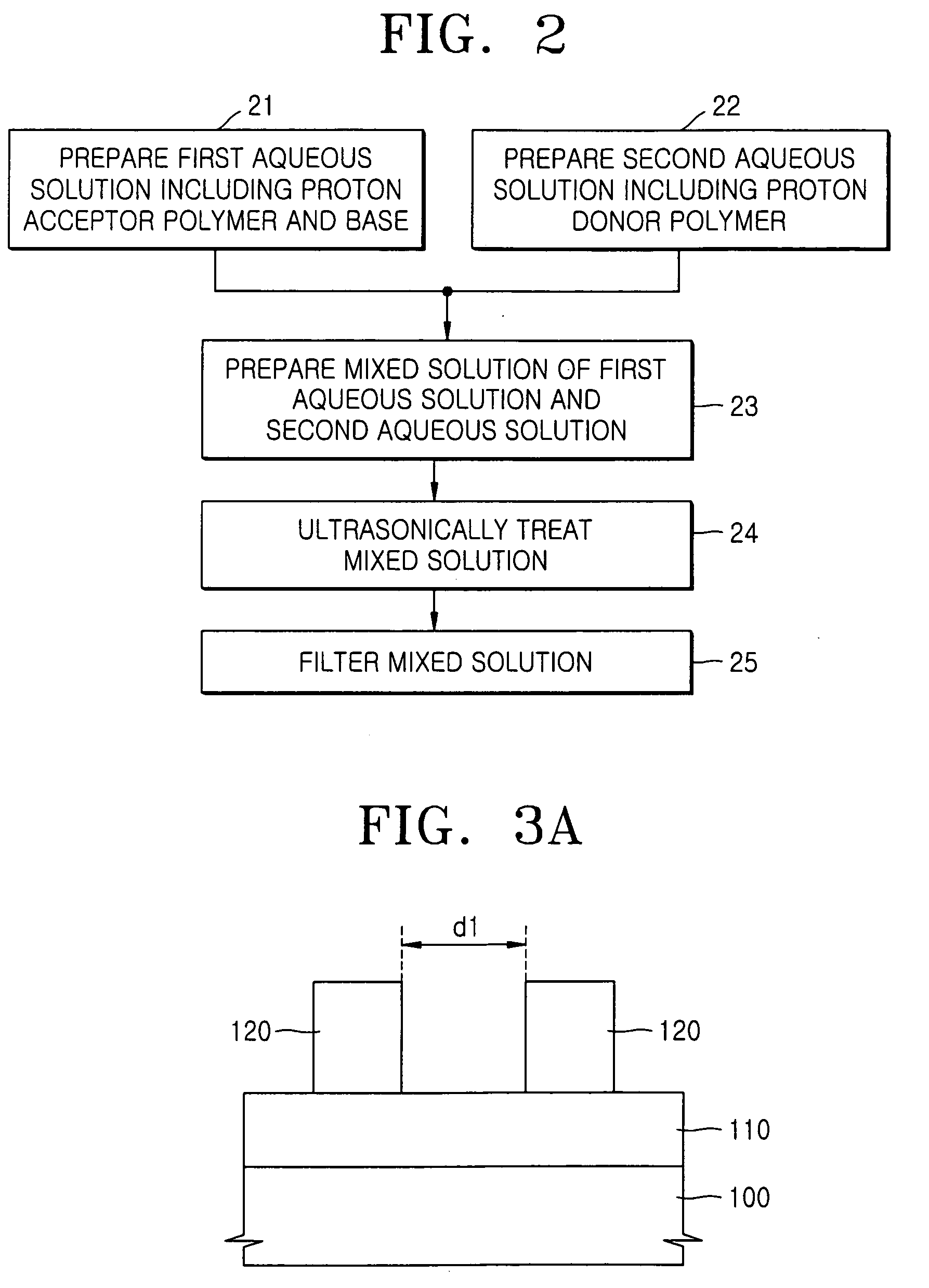
[0090] A solution of 35 mg of TEA in 3,465 mg H2O, a solution of 4.0 mg of Zonyl FSN in 396 mg H2O, and 100 mg H2O were added to a solution of 100 mg of poly(vinylpyrrolidone) in 900 mg H2O to obtain a first aqueous solution. A second aqueous solution of 100 mg of an unprotected poly(acrylic acid-co-maleic acid) in 900 mg H2O, unlike in Example 1, was added dropwise to the first aqueous solution with vigorously stirring. The resultant solution was filtered to provide a clean coating composition. The LCST of the coating composition was about 50° C. To obtain a clear aqueous solution, TEA was used in an amount of 17 wt %, based on the total amount of a resin used. Such an increase in the amount of the base used to obtain a clear aqueous solution in this Example, relative to the amount of the base used in Example 1, can be explained by use of the unprotected poly(acrylic acid-co-maleic acid).
[0091] Formation of Gel Layer
[0092] The coating co...
example 3
Formation of Resist Pattern
[0093] A resist pattern was formed in the same manner as described in Example 1 except that PEB was performed at 115° C. for about 60 seconds. The resist pattern included an i-hole pattern with a diameter of 174.8 nm and a d-hole pattern with a diameter of 134.7 nm.
[0094] Preparation of 10% t-butyl Protected poly(acrylic acid-co-maleic acid) by Esterification
[0095] Poly(acrylic acid-co-maleic acid) (370 mg), N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (10 mg), 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine (3.0 mg), and t-BuOH (2.0 g) were stirred at 23° C. for 4 hours and subjected to precipitation with excess hexane. A supernatant was decanted and the remaining solid was dried under vacuum at 30° C. overnight to provide 10% t-butyl protected poly(acrylic acid-co-maleic acid) (319 mg) as a white solid.
[0096] Preparation of Coating Composition
[0097] A solution of 5.2 mg of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) in 215 mg H2O, a solution of 1.0 mg of Zonyl FSN in 99 mg H2O, and 1.7 g H2O ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com