Method for producing reinforced platinum material
a platinum alloy and platinum alloy technology, applied in the field of reinforced platinum material, can solve the problems of material requirements, material yield cannot be improved, and troublesome maintenance including shaving off adhered matter, and achieve excellent high-temperature creep properties, enhance the effect of process melt-sprayed platinum alloy particles minutely, and improve high-temperature creep properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
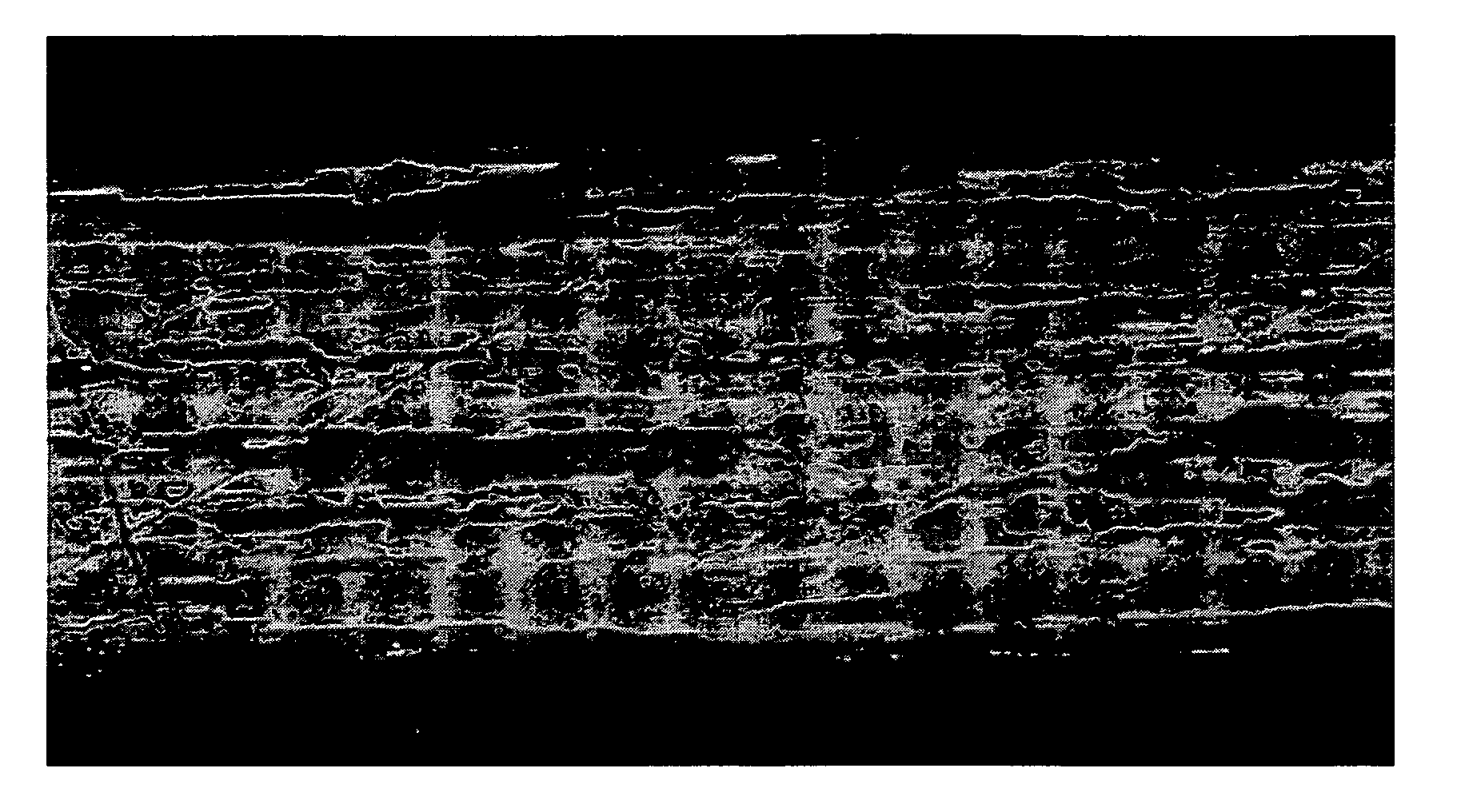
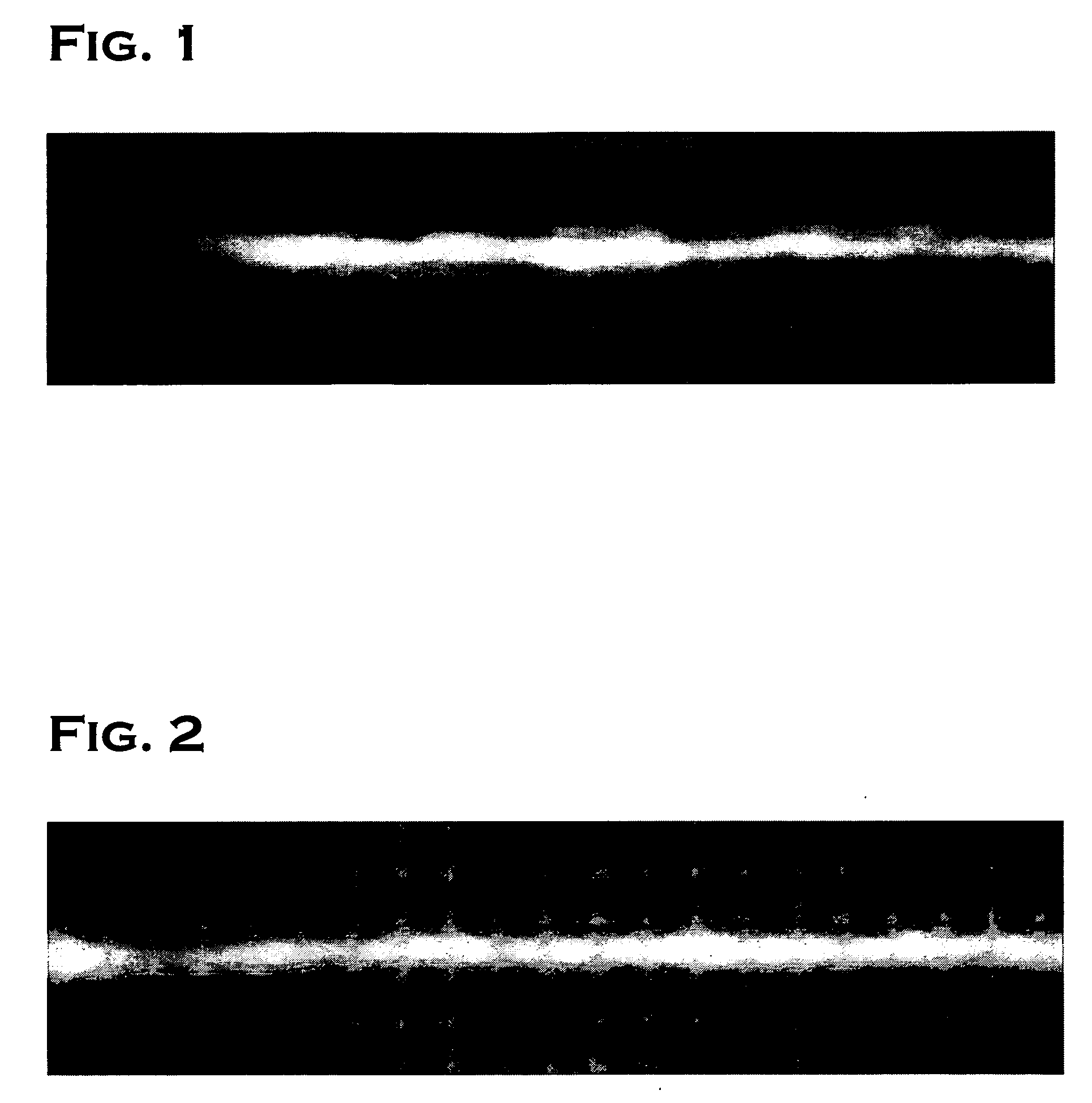
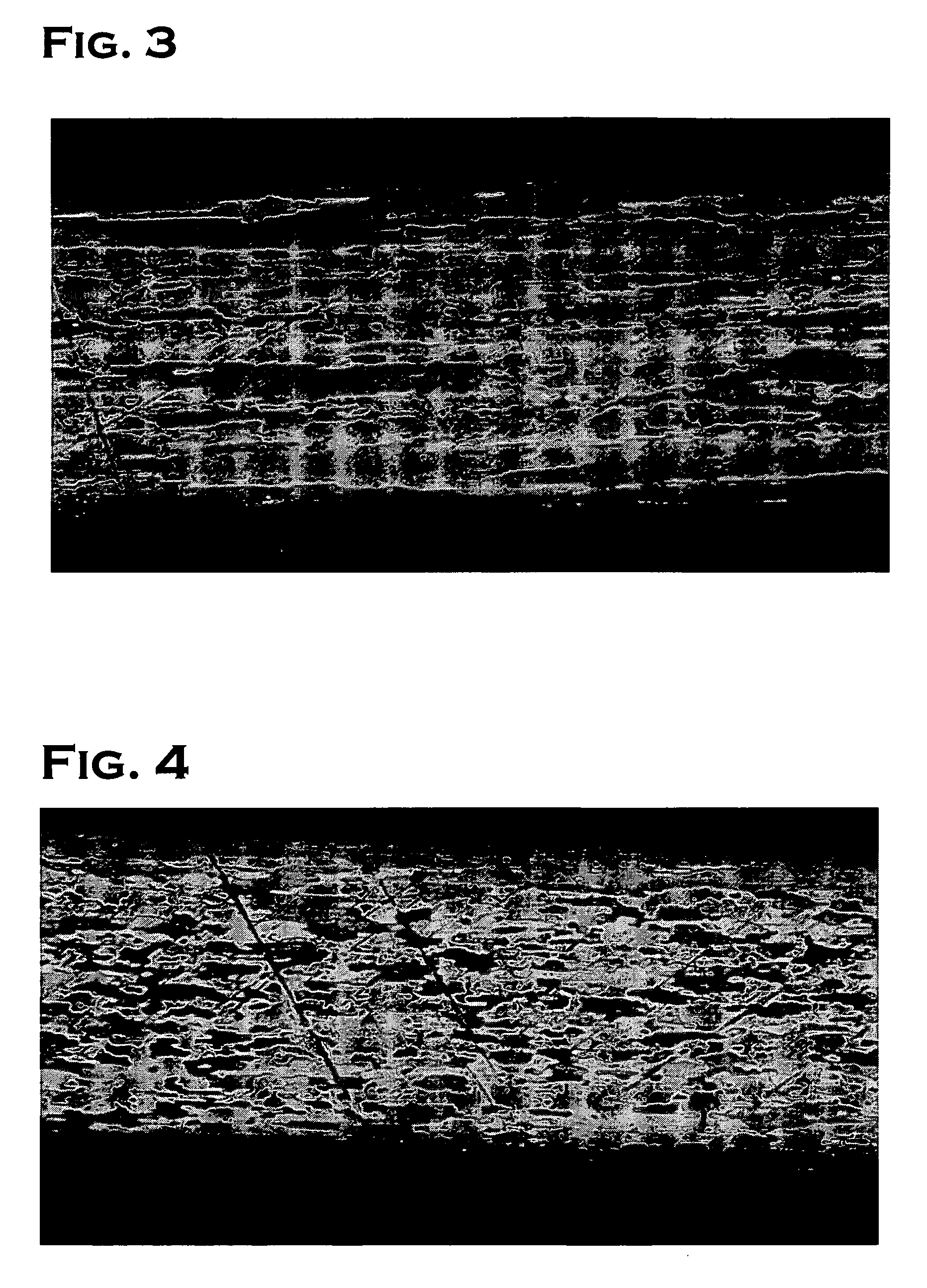
[0030] A Pt (platinum)-Zr (zirconium) alloy ingot of 28 kg containing 0.3 wt % of zirconium was first prepared through vacuum melt casting. The platinum alloy ingot was subjected to groove rolling and die wire drawing to form a wire having a wire diameter of 1.6 mm. The wire rod was then melted with arc discharge by use of an electric arc spray gun, and the molten Pt—Zr alloy was sprayed by means of compressed air toward a distilled water surface, which is 1 m apart from a muzzle of the electric arc spray gun to prepare 24 kg of a spherical powder having a particle diameter of 10 to 200 μm.
[0031] In Example, spherical powder of 12 kg, which is half of 24 kg, was divided equally among three without being subjected to oxidation treatment, and each divided powder was subjected to wet-milling and drying. The wet-milling was carried out through injecting spherical powder of 4 kg and zirconia ball of 7 kg having a diameter of 5 mm into an attritor, which is a wet-milling machine. An attr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com