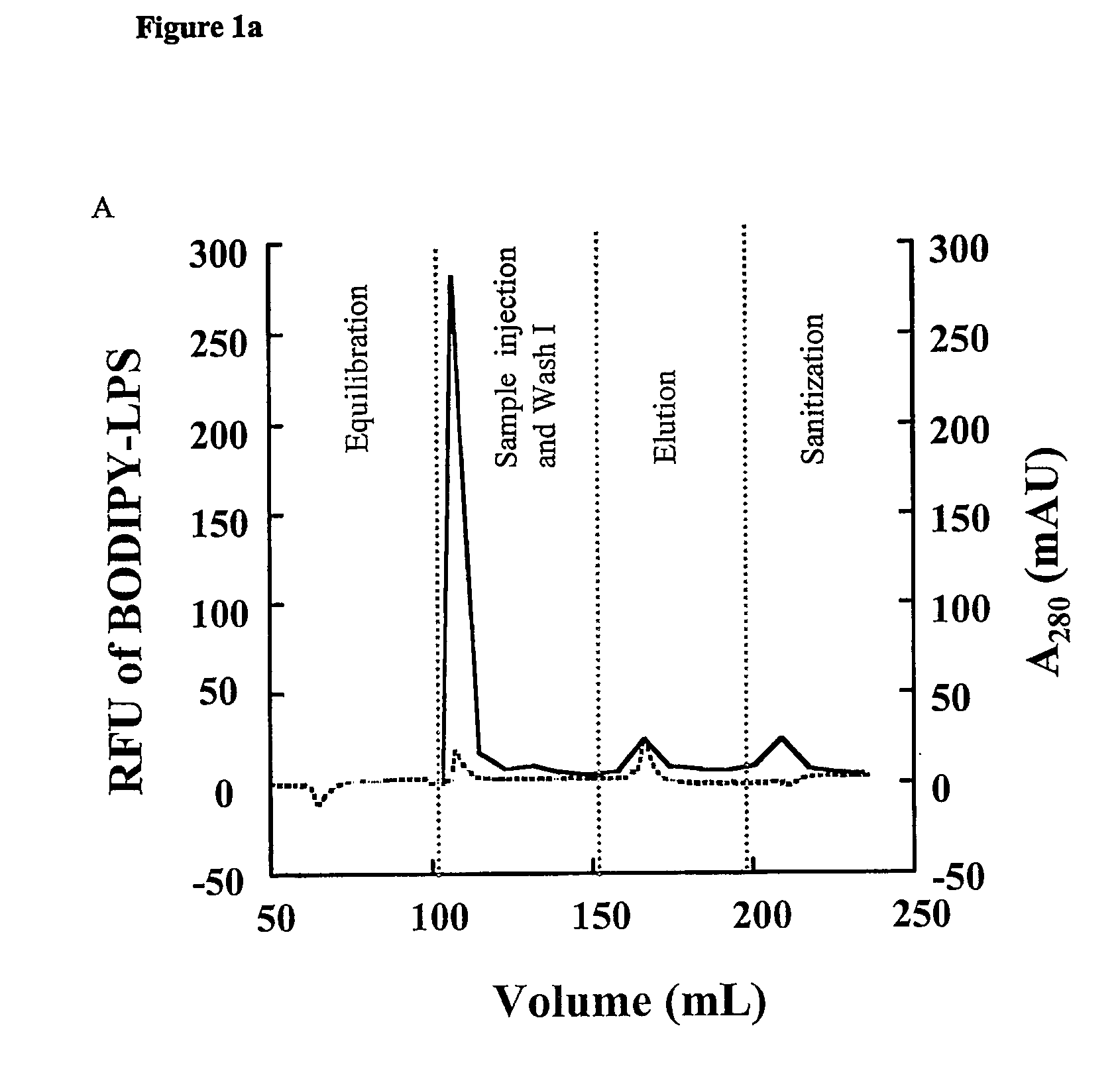
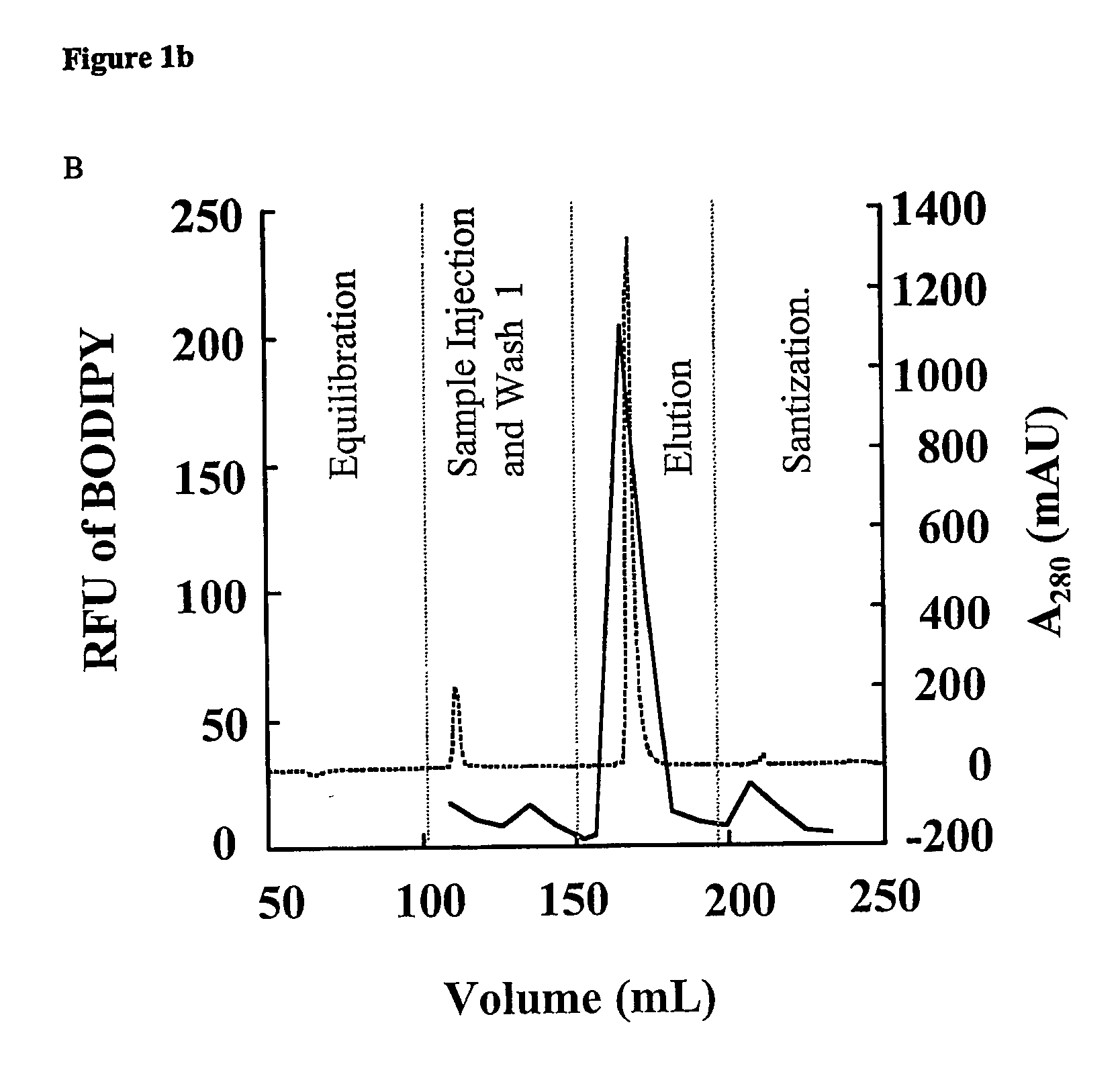
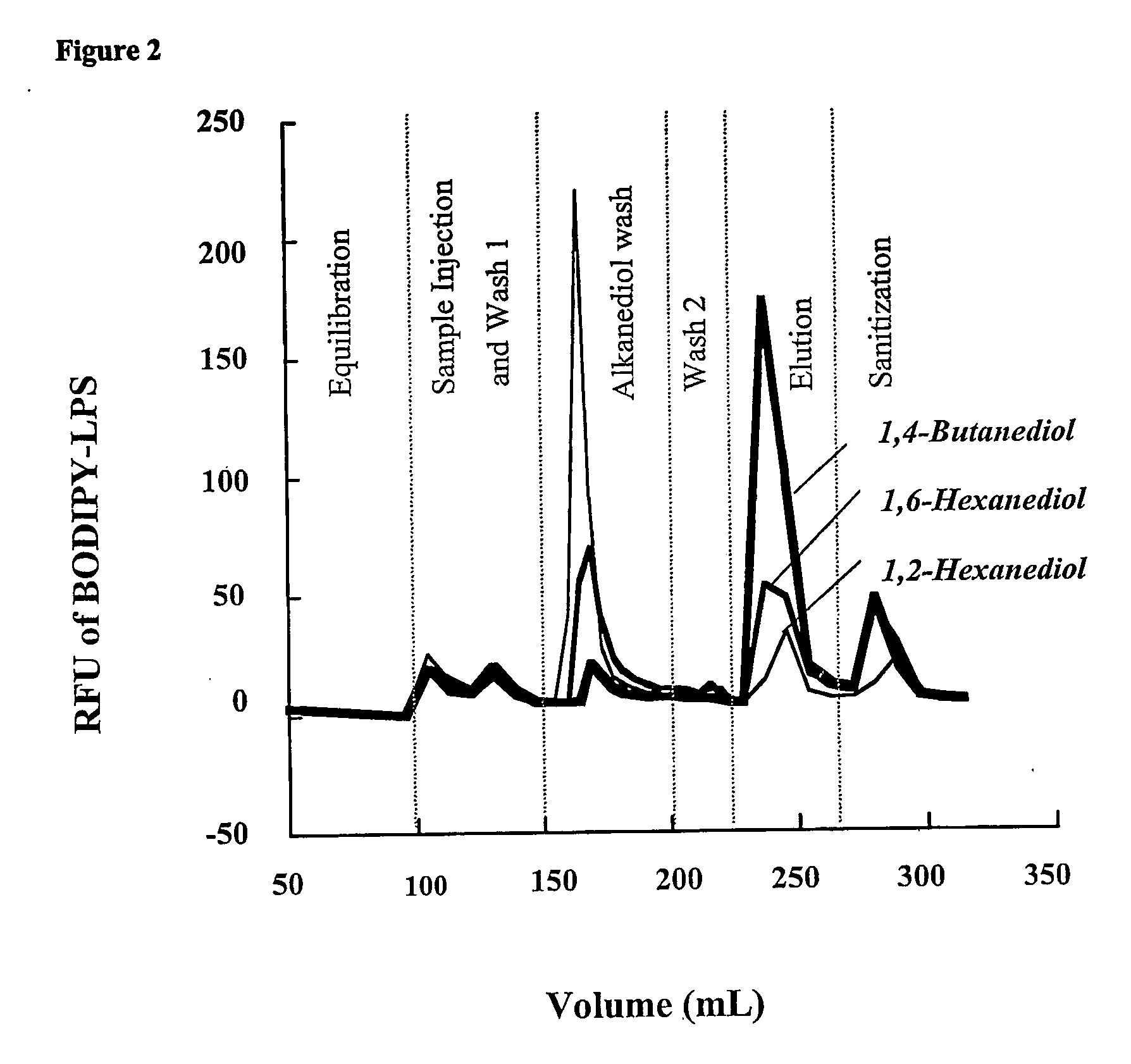
Removal of lipopolysaccharides from protein-lipopolysaccharide complexes by non flammable solvents.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples and experiments
Materials
[0040] Bovine albumin (BSA), bovine holo-transferrin, lactoferrin from bovine milk, lysozyme from chicken egg whites, lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli serotype O55:B5, and BSTFA were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, Mont.). Acetic acid, Tris (base), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride (NaCl), ethanol, isopropanol, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and sodium phosphate dibasic 7-hydrate were purchased from J.T. Baker Chemical Co. (Phillipsburg, N.J.). 1,6-Hexanediol was from BASF Co. (Mount Olive, N.J.). 1,2-Hexanediol, 1,2-butanediol, and Zwittergent 3-14 (Zw 3-14) were purchased from Fluka (Milwaukee, Wis.). 1,4-Butanediol and ethylene glycol were purchased from Aldrich (Milwaukee, Wis.). Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), 10×, was purchased from Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (Hercules, Calif.). Escherichia coli BODIPY® FL conjugate lipopolysaccharide, serotype O55:B5, (BODIPY-LPS) and EnzChek Lysozyme Assay Kit were purchased from Mo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com