Group III-V nitride-based semiconductor substrate and method of making same
a semiconductor substrate and nitride technology, applied in the direction of crystal growth process, crystal growth process, chemically reactive gas, etc., can solve the problems of non-uniform carrier concentration and electrical resistivity, non-uniform in-plane polishing speed, and non-uniform growth speed, so as to improve the uniformity of in-plane properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
##ventive example 1
INVENTIVE EXAMPLE 1
Preventing the Warping by a Thick Sapphire
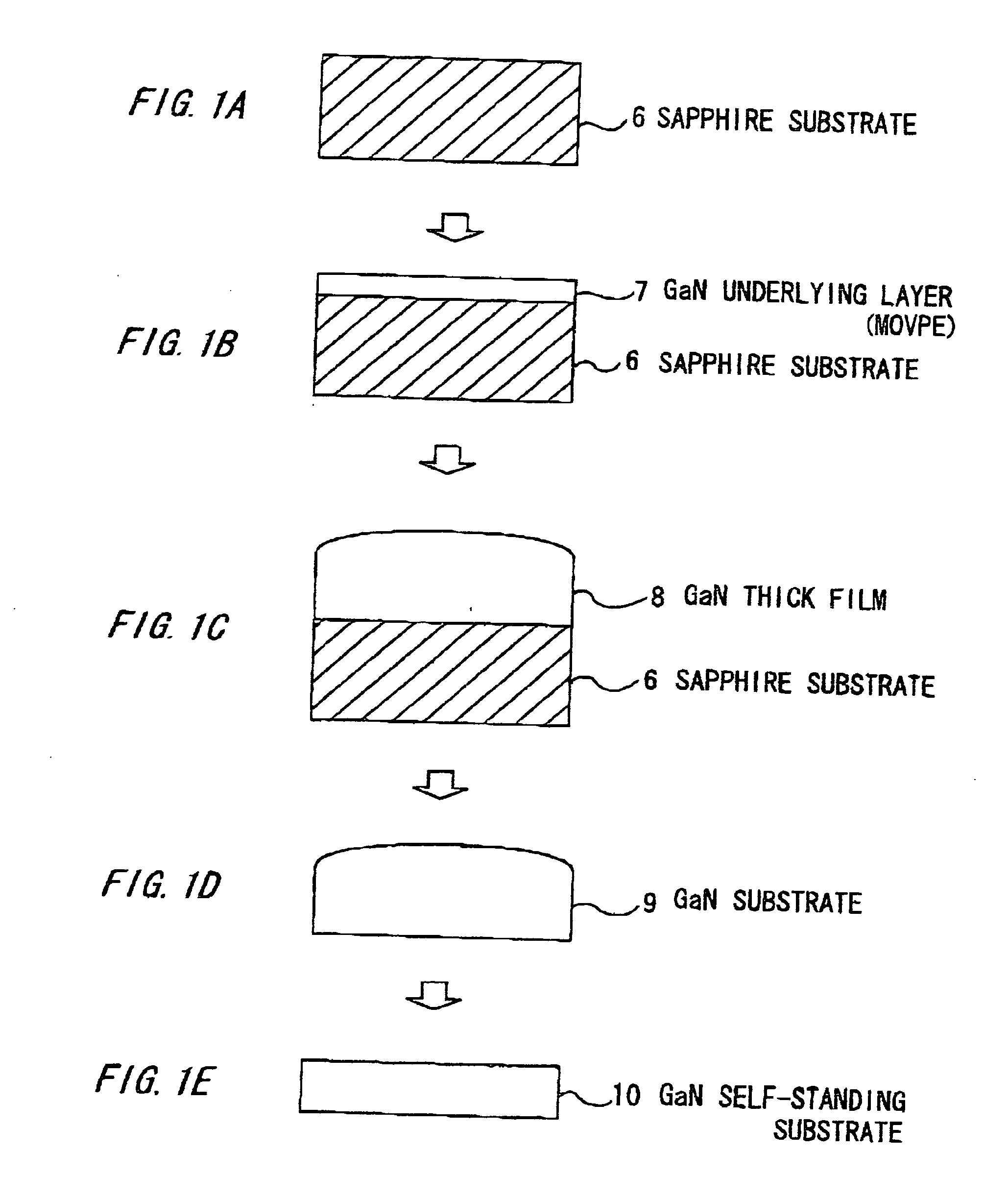
[0087]FIGS. 1A to 1E are illustrative cross sectional views showing of a method of making a group III-V nitride semiconductor substrate in the first preferred embodiment according to the invention.
[0088] As shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B, a 300 nm thick GaN underlying layer 7 is formed on a c-face sapphire substrate 6 with a diameter of 7.62 cm (=3 inches) and a thickness of 650 μm by MOVPE.
[0089] Then, like the conventional example, it is placed in a HVPE furnace and a Si-doped GaN thick film 8 is grown (FIG. 1C). Carrier gas is N2:H2=1:1. Partial pressures are GaCl=9×10−3 atm, NH3=1×10−1 atm. For n-type doping, SiH2Cl2 gas is flown at partial pressure of 5×10−4 atm. Growth temperature is 1070° C.
[0090] By irradiating YAG laser from the backside of the sapphire substrate 6, a GaN substrate 9 is separated decomposing a GaN crystal at the interface (FIG. 1D).
[0091] The resultant GaN crystal (i.e., GaN thick film 8) has a thi...
##ventive example 2
INVENTIVE EXAMPLE 2
Further Enhancing the Uniformity by Coating Carbon on the Back Face of the Sapphire Substrate
[0094] In the inventive example 1, an about 1 μm thick carbon layer is formed on the back face of the sapphire substrate 6 and then the HVPE growth is conducted in like manner. Thereby, the temperature distribution during growth can be further improved The thickness distribution as grown is 800 μm at the central portion and 750 μm at the outermost portion,
[0095] The properties of the GaN substrate are also improved. The dislocation density is 1×107 cm−2 both at the central portion and at the outermost portion The carrier concentration is 1×1018 cm−3 both at the central portion and at the outermost portion. Further, the c-axis is inclined about ±0.18.
##ventive example 3
INVENTIVE EXAMPLE 3
Bonding the Sapphire Substrate to the Susceptor+VAS Method
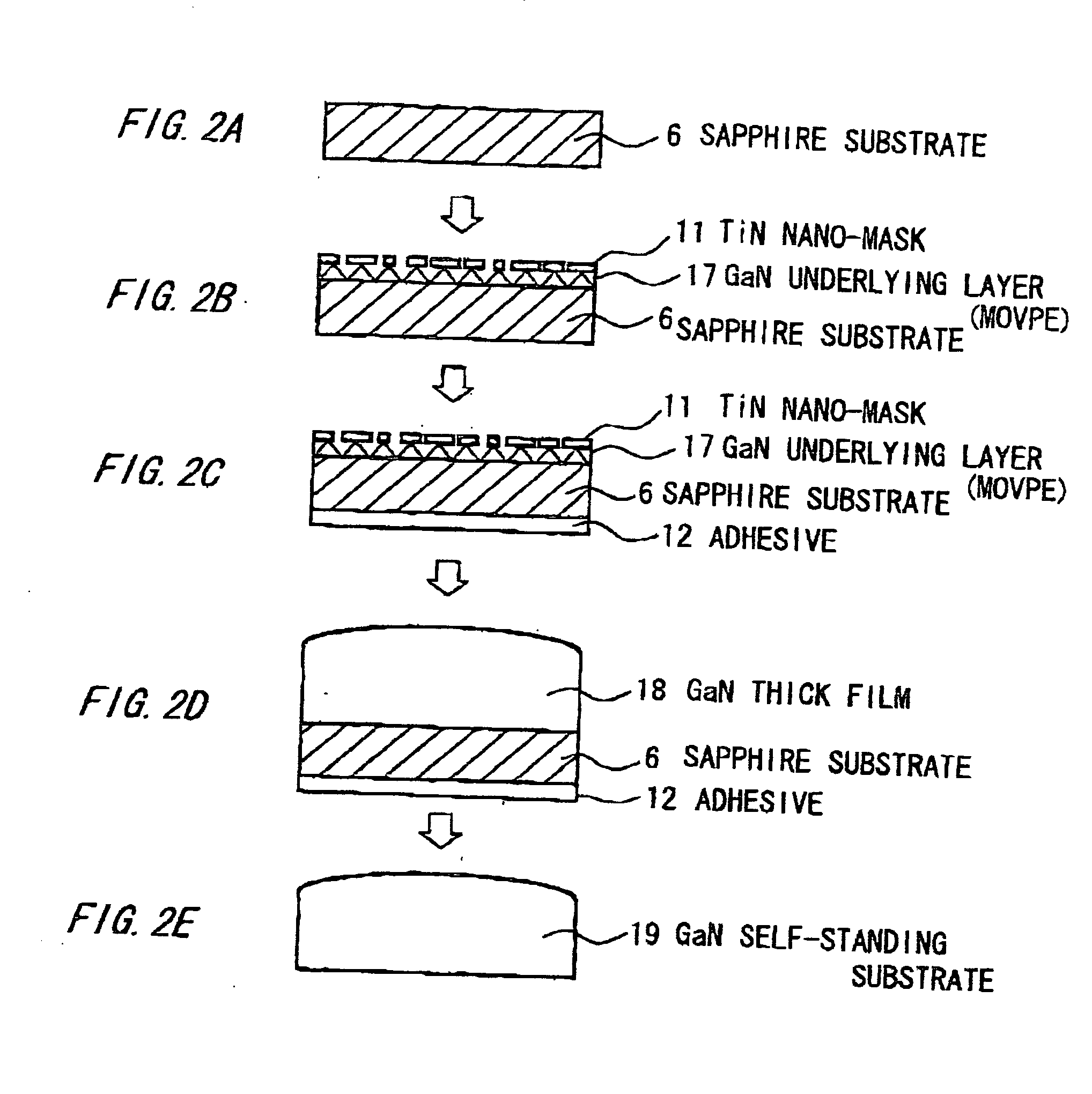
[0096]FIGS. 2A to 2E are illustrative cross sectional views showing of a method of making a group III-V nitride semiconductor substrate in the third preferred embodiment according to the invention.
[0097] As shown in FIG. 2A, a c-face sapphire substrate 6 with a diameter of 7.62 cm (=3 inches) and a thickness of 330 μm is provided.
[0098] Then, a 300 nm thick GaN thin film (=GaN under lying layer 17) is formed on the sapphire substrate 6. Then, a 20 nm thick Ti layer is formed thereon in vacuum deposition. Then, it is thermally treated in carrier gas of H2:NH3=4:1 at 1060° C. for 30 min. Thereby, the Ti layer is nitrided into a TiN layer and formed into mesh-like structure (i.e., TiN nano-mask 11) with a number of fine holes of tens of nanometers. On the other hand, the GaN underlying layer 17 is etched to have therein voids reaching up to the sapphire substrate 6 (FIG. 2B).
[0099] Then, the void-formed su...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com