Methods for producing hybrid seed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
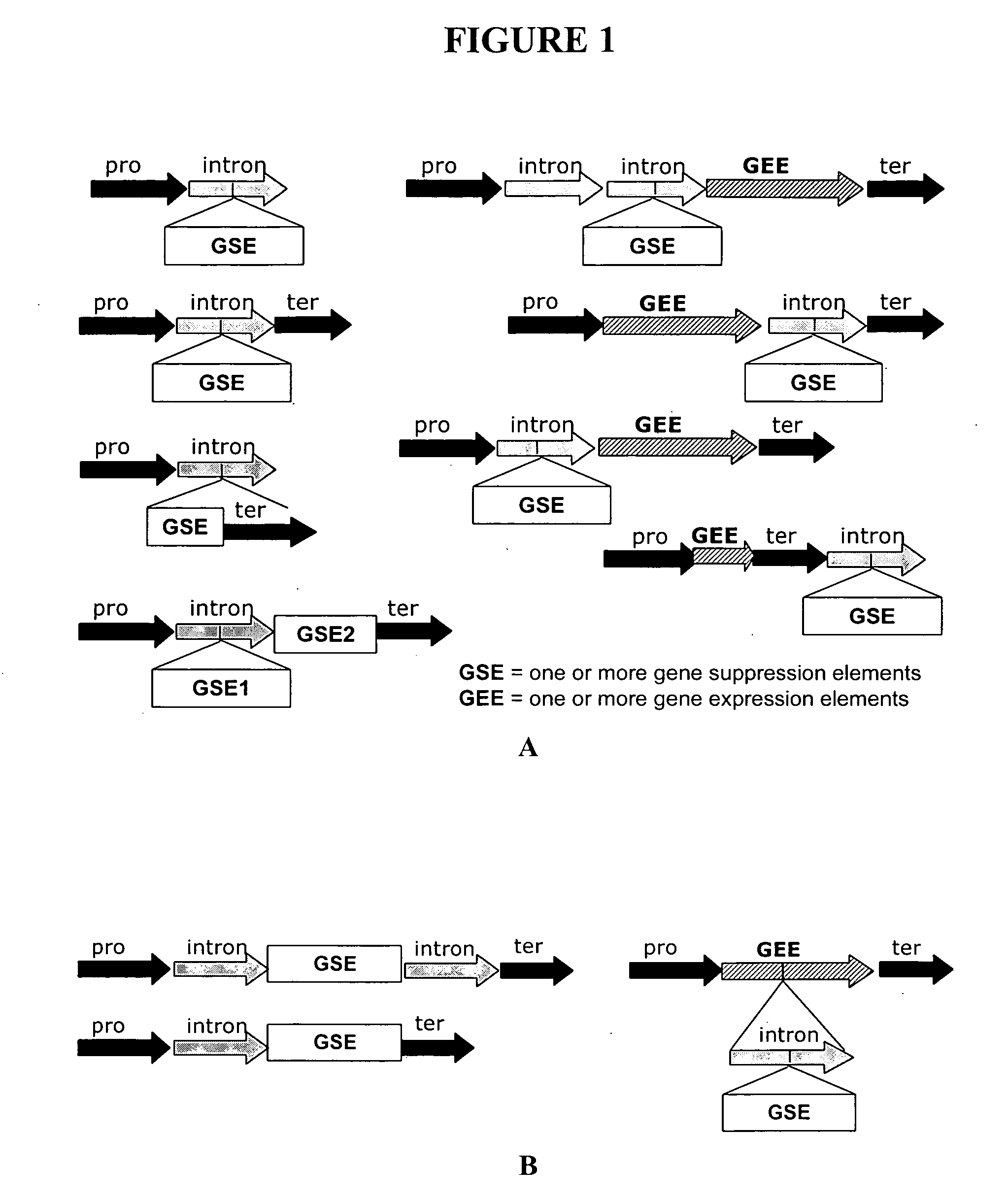
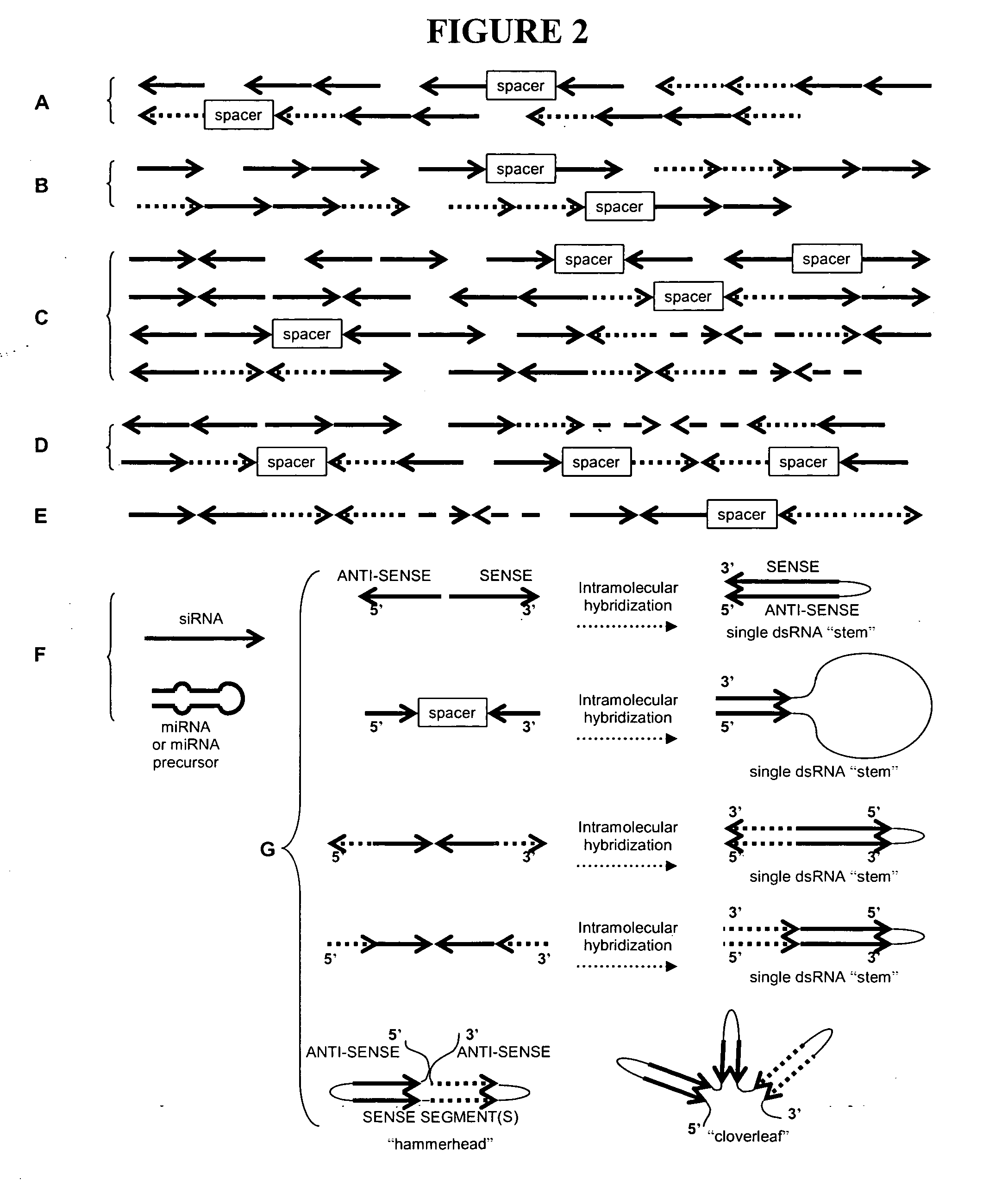
[0189] This illustrates non-limiting examples of recombinant DNA constructs for suppression of at least one target gene; these constructs, when designed to include a miRNA recognition site, allow expression of the gene suppression element in specific tissues.
[0190]FIG. 1A schematically depicts non-limiting examples of recombinant DNA constructs of the invention for suppression of at least one target gene. These constructs include at least one first gene suppression element (“GSE” or “GSE1”) for suppressing at least one first target gene, wherein the first gene suppression element is embedded in an intron flanked on one or on both sides by non-protein-coding DNA. These constructs utilize an intron (in many embodiments, an intron derived from a 5′ untranslated region or an expression-enhancing intron is preferred) to deliver a gene suppression element without requiring the presence of any protein-coding exons (coding sequence). The constructs can optionally include at least one secon...
example 2
[0194] This example describes one non-limiting method of determining the potential usefulness of a miRNA's recognition site, by determining the miRNA's expression pattern. Knowledge of the spatial or temporal distribution of a given miRNA's expression is useful, e.g., in designing recombinant constructs to be expressed in a spatially or temporally specific manner. This example discloses mature miRNA expression patterns in maize and provides sequences of recognition sites for these miRNAs that are suitable for inclusion in recombinant DNA constructs useful in maize and other plants.
[0195] Total RNA was isolated from LH244 maize plants using Trizol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Calif.). Seven developmental stages were used, including roots and shoot meristems from germinating seedlings, juvenile (V1 to V2) and adult leaves (V7 to V8), stalk internode, tassel before shedding, and immature (approximately 1″) ears. Five micrograms total RNA was resolved on 17% PAGE-Urea as described by Allen e...
example 3
[0197] This non-limiting example describes recombinant DNA constructs of the invention, useful for suppressing expression of a target RNA in a specific cell of or derived from a multicellular eukaryote such as a plant cell or an animal cell, and methods for their use. The constructs include a promoter operably linked to DNA that transcribes to RNA including at least one exogenous miRNA recognition site recognizable by a mature miRNA expressed in a specific cell of a multicellular eukaryote, and target RNA to be suppressed in the specific cell, wherein said target RNA is to be expressed in cells of the multicellular eukaryote other than the specific cell.
[0198] Strong constitutive promoters that are expressed in nearly all plant cells have been identified (e.g., CaMC 35S, OsAct), but strong spatially specific (cell- or tissue-specific) and temporally specific promoters have been less well characterized. To limit target RNA or transgene expression to a specific cell or tissue type in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sterile | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com