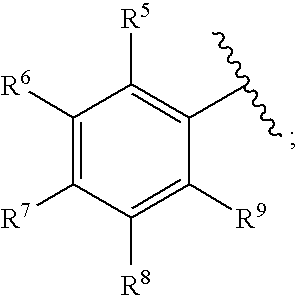
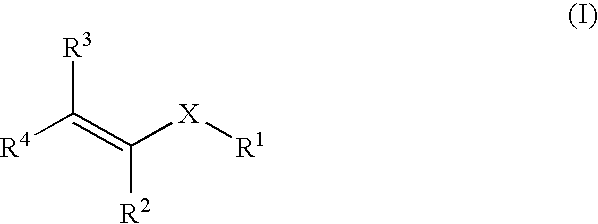Methods for treating blood disorders
a technology for blood disorders and compounds, applied in the direction of drug compositions, peptide/protein ingredients, extracellular fluid disorders, etc., can solve the problems of increased cardiac output, impaired red blood cell production, red blood cell disorders and deficiencies,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification of Small Molecule Inducers of Fetal Hemoglobin
[0209] Small molecule inducers of fetal hemoglobin were identified using computer modeling techniques.
[0210] The pharmacophore was constructed with the TFIT module of the FLO molecular modeling software. It was assumed that the carboxylic acids would bind to the receptor in an analogous fashion, and therefore, the superposition of the carboxylic oxygens was biased by imposing a 5 kJ superimposition energy constraint. Five hundred iterations of TFIT were used in the calculations.
[0211] TFIT produced an ensemble of low energy superimposition. The superimposition with the tightest overlay was taken to be the initial pharmacophore template. This pharmacophore was tested to see if it could distinguish between active and inactive compounds. TFIT was first used to determine the best match between the pharmacophore and four compounds which had been identified as inactive in the β / γ-globin promoter driven reporter gene assay in ...
example 2
IN Vitro Stimulation of Fetal Globin mRNA Expression
[0219] This example demonstrates that the test compounds predicted to be active by reporter gene assays and molecular modeling produce a significant increase in fetal (gamma) globin mRNA in cells cultured in vitro. Furthermore, the concentrations required were significantly lower (5-40 micromolar) than concentrations required for prior generation inducers (100-200 micromolar), making these compounds more suitable for therapeutic and pharmacologic compositions
[0220]γ-globin mRNA was analyzed in control and treated erythroid colonies cultured from cord blood, by RT-PCR.
[0221] Induction (increase) in fetal globin mRNA compared to untreated control levels with each compound is shown in Table 3 below. The R enantiomer of compound Y demonstrated fetal globin inducing action, whereas the S enantiomer did not induce fetal globin in 2 of (the same) 3 cultures.
TABLE 3Increase in Fetal Globin mRNAConcentrationMean changerequired,above co...
example 3
Effects on Erythroid and Myeloid Cell Growth In Vitro
[0224] This example demonstrates that the test compounds predicted to be active by reporter gene assays and molecular modeling produce a significant increase in numbers of erythroid and myeloid colonies or proportion of cells expressing fetal globin in in vitro cultured cells from a variety of sources under a variety of culture conditions. Similar to other in vitro tests described herein, the concentrations required for these biological effects were significantly lower (5-40 micromolar) than concentrations required for prior generation inducers (100-200 micromolar), making these compounds more suitable for therapeutic and pharmacologic compositions.
[0225] Compounds predicted in the molecular model to be γ-globin inducers were evaluated in a series of assays for activity in 1) stimulating activity from the fetal globin gene promoter, (the action which can ameliorate sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia), and 2) for any effect...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| superimposition energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| enantiomers | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com