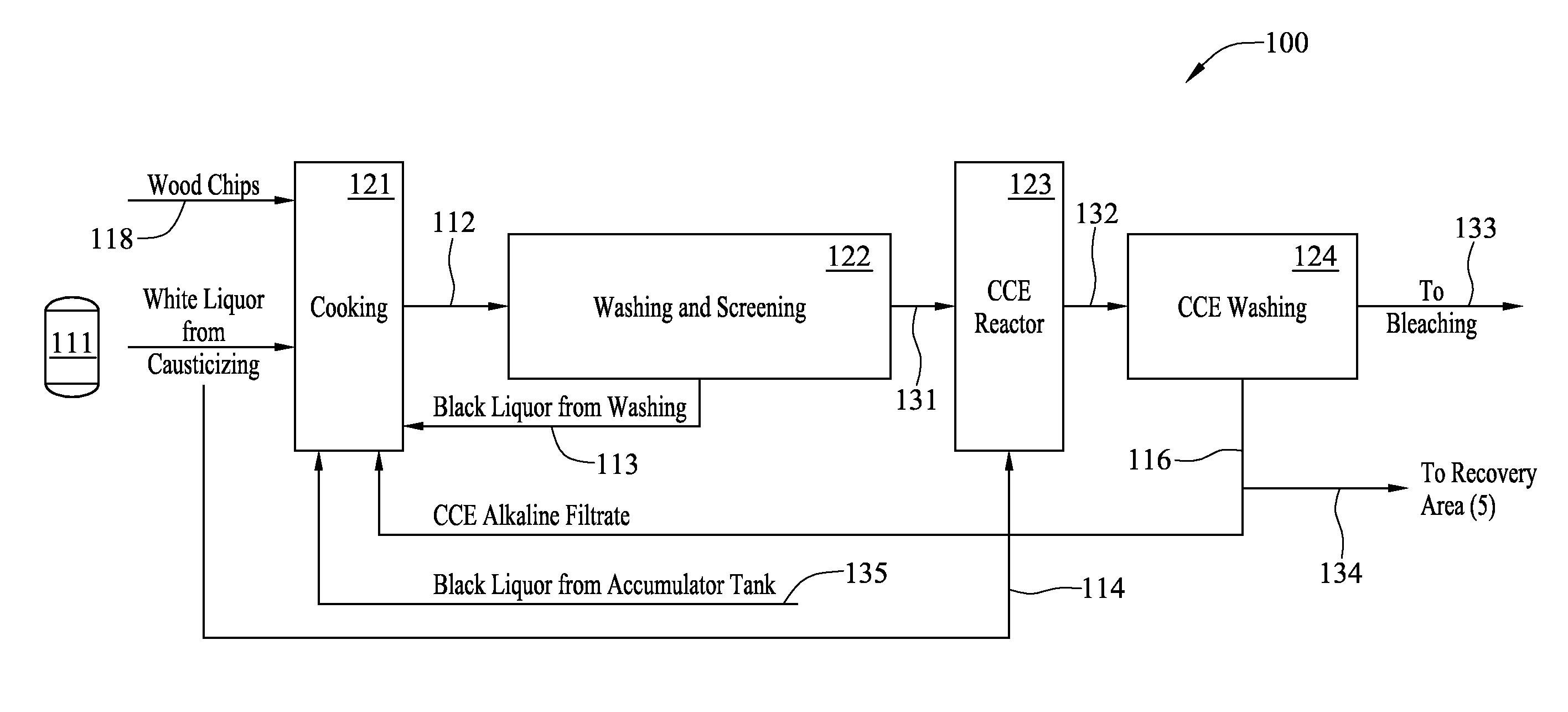
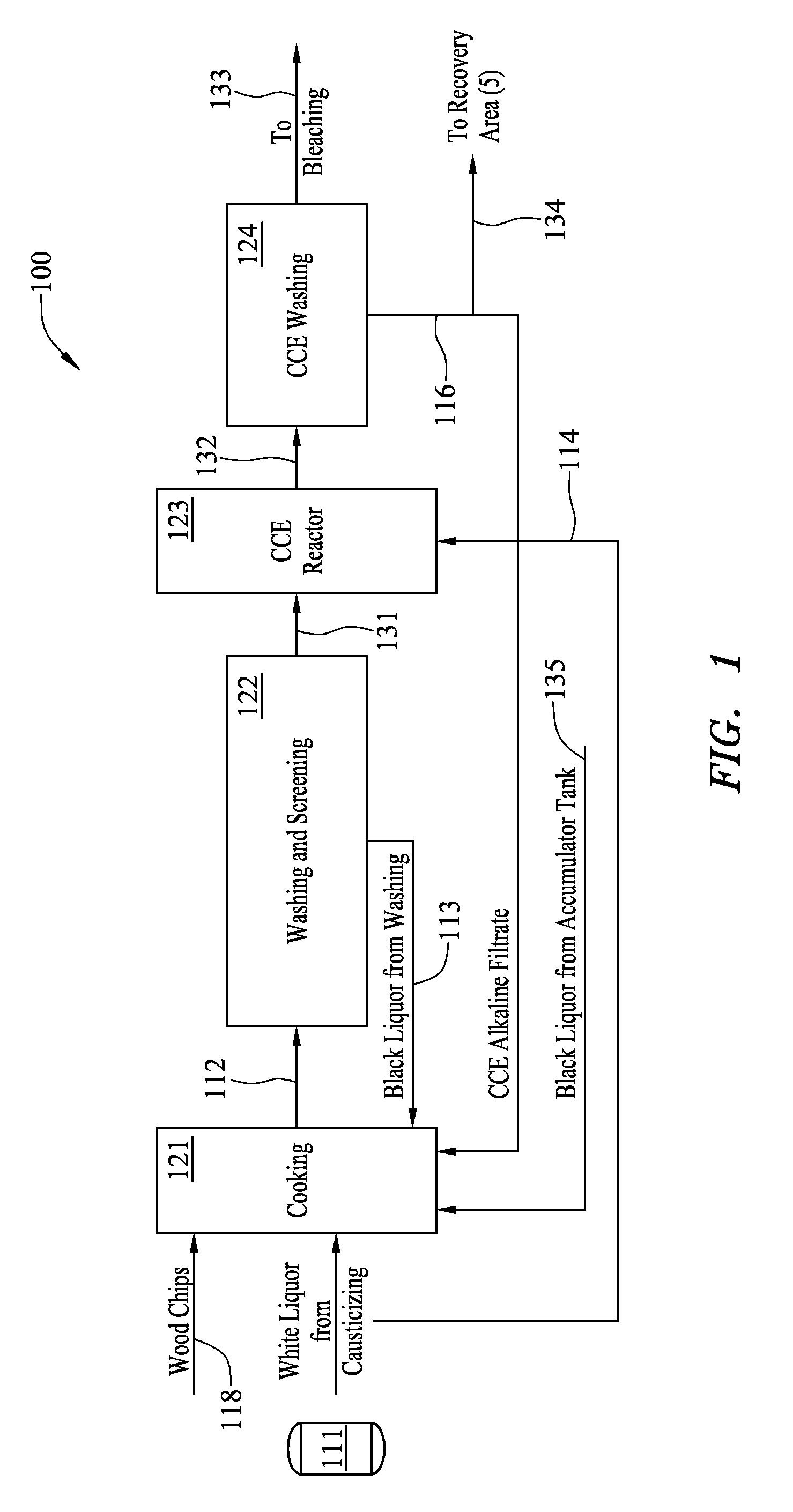
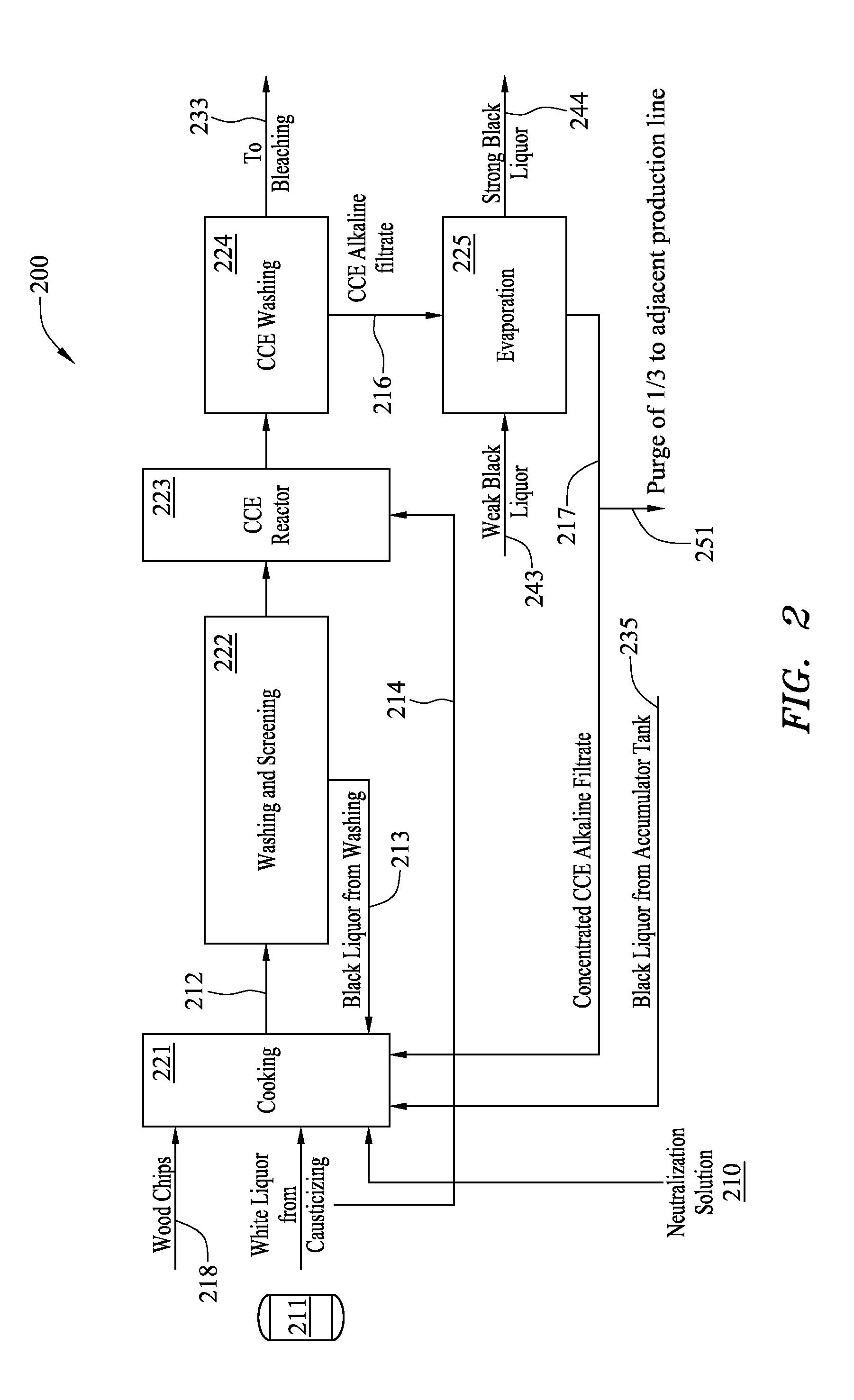
Method and system for pulp processing using cold caustic extraction with alkaline filtrate reuse
a technology of cold caustic extraction and alkali filtrate, which is applied in the field of pulp processing, can solve the problems of increasing production costs and preventing high quality pulp from being achieved, and achieve the effects of enhancing the purity of brown stock and resulting purified pulp, and increasing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Concentration of CCE Filtrate
[0066]According to a first example, a stream of very diluted caustic solution at an effective alkali concentration of 5.6 grams NaOH per liter is introduced into the fifth effect 327 as shown in FIG. 3 to start the plant running and to observe its behavior with different alkali concentration levels. Water is removed from the solution at a reduced pressure of −0.73 bar at a temperature between 51.5° C. and 56.8° C. After 4 hours and 30 minutes, a caustic solution with an effective alkali concentration of about 50 gram NaOH per liter, similar to the raw CCE filtrate, is fed in the fifth effect getting at the outlet of the sixth effect from an inlet filtrate concentration about 50 grams NaOH per liter. Table I lists the flow rate, temperature, effective alkali concentration and vacuum level as a function of time.
TABLE IEffective alkaliFeeding(g NaOH / l)TimeFlowTemperatureInput atOutput atPressure(min.)(m3 / h)(° C.)Effect 5Effect 6(bar)035051.55.6−0.736537054....
example 2
Conventional Kraft Process
[0067]According to a second example, an experimental kraft process is carried out in a bench scale digester (approximately 20 liters volume) to simulate the industrial processing. A 20-liter bench scale digester is pre-heated with steam to 120° C. over a period of 30 minutes. A suitable quantity (such as 4.7 kg oven dry basis) of eucalyptus wood chip is added to the digester. The digester is heated to 165° C. over a period of 60 minutes and held at 165° C. for a further 40 minutes to complete the pre-hydrolysis stage. For a conventional kraft process (not using filtrates from the CCE), 4.51 liters of a first white liquor (“WL1”) with an effective alkali concentration of 124.7 g NaOH per liter is added to the digester over fifteen minutes at a temperature of 152° C. The typical alkali charge for the neutralization is about 12% of Effective Alkali (EA) as NaOH on the dry chips weight. The digester is then filled with 10.8 liters of hot black liquor with an ef...
example 3
Use of Weak Concentration CCE Filtrate as Neutralization Solution and Cooking Solution
[0068]According to a third example, the same pulping process as described in Example 2 is repeated, except that the white liquor for the neutralization and cooking stages is replaced with a filtrate from the CCE step having an EA of 54 g NaOH per liter (“CCE54”). The Neutralysate has a pH of 11.0, and the cooking mixture has an EoC of 18.5 g NaOH per liter. The P factor for the pre-hydrolysis is 297 and the H factor for the cooking reaction is 419. For this example the total equivalent effective alkali charge on the wood are respectively: 12% EA as NaOH for the Neutralization phase and 11% EA as NaOH for the Cooking phase.
[0069]The resulting brown stock shows a Kappa Number of 10.8, a viscosity of 1118 ml / g, an S10 solubility of 4.5% and an S18 solubility of 3.6%. The reaction has a 40.4% yield. When screened, the mixture has a 0.09% rejection rate, resulting in a screening yield of 40.3%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com