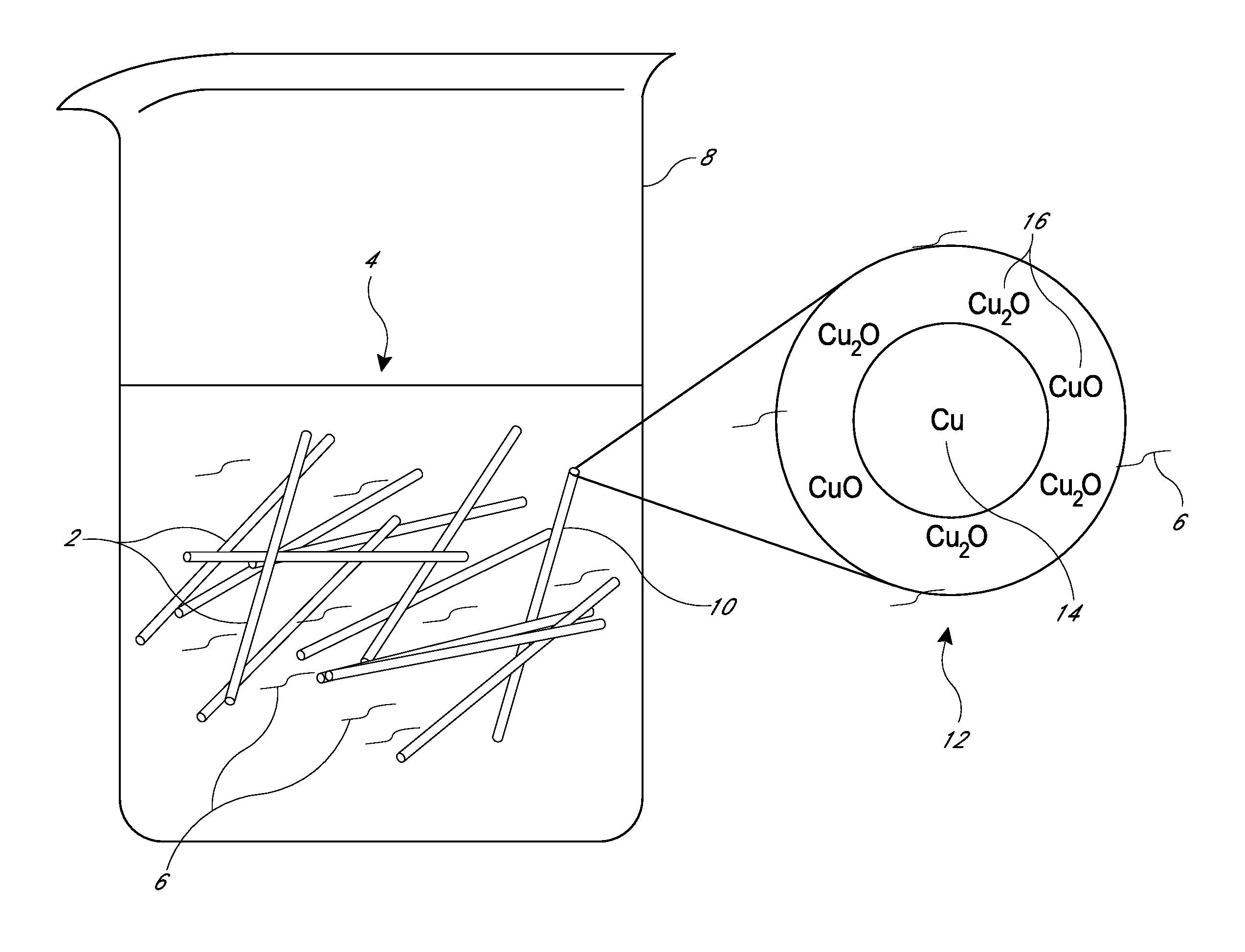
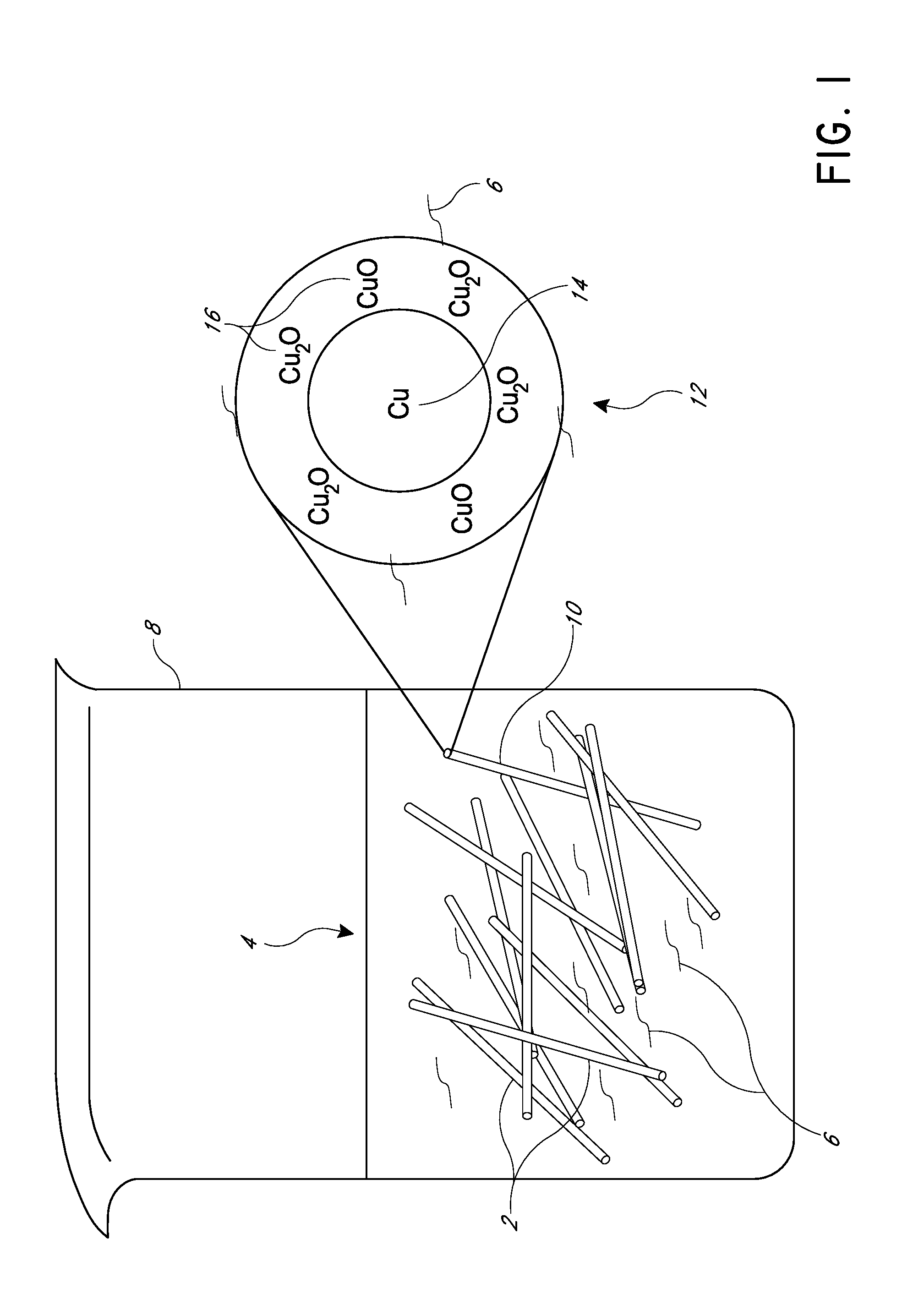
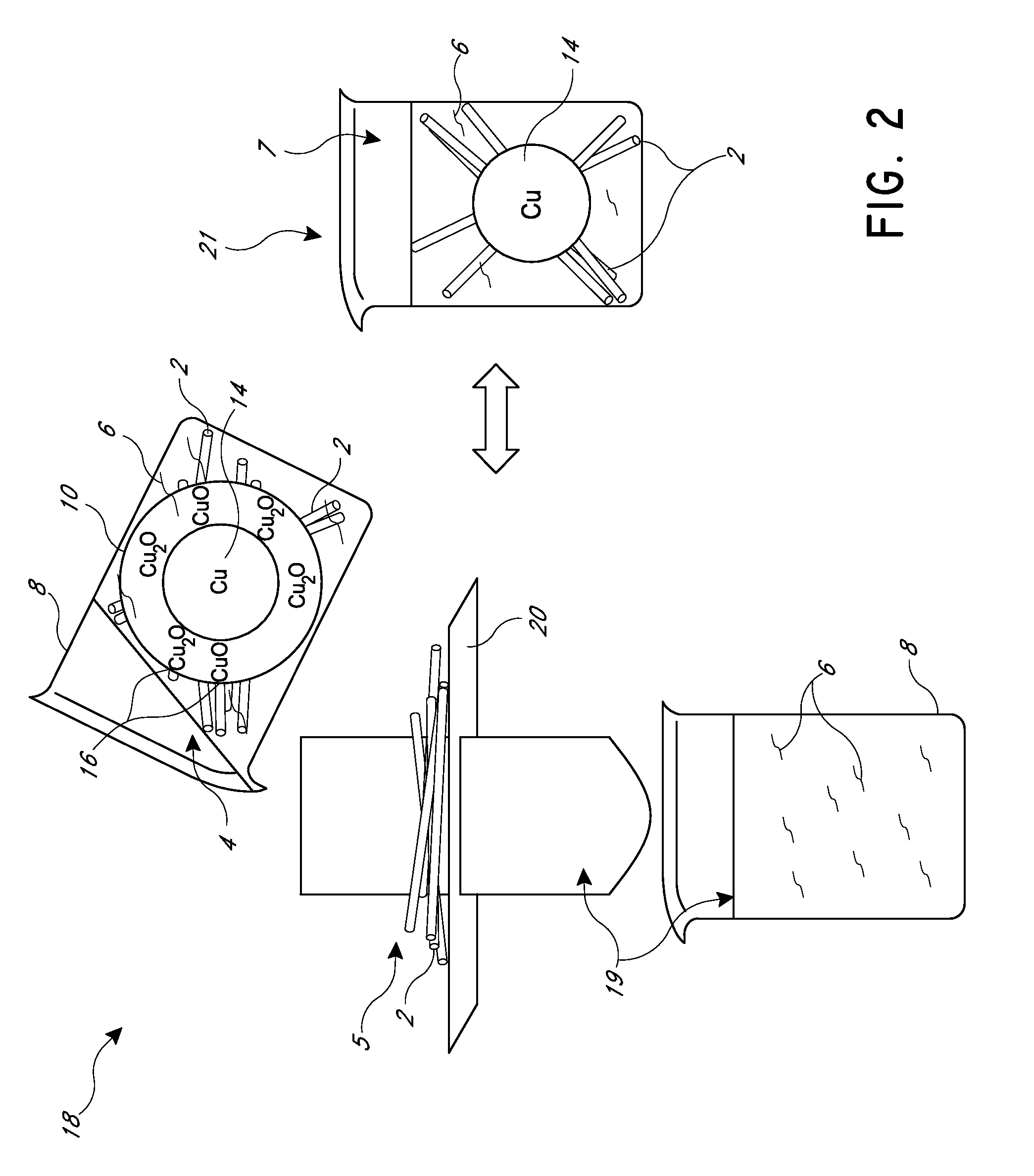
Systems and methods for fabrication of nanostructures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0049]2. The method of Embodiment 1, wherein the nanostructures comprise nanowires.
[0050]3. The method of Embodiment 1 or 2, wherein the first element is copper.
[0051]4. The method of any of Embodiments 1-3, wherein the second element is silver.
[0052]5. The method of any of Embodiments 1-4, wherein a concentration of the nanostructures in the dispersion is between about 0.1 g / L and about 1 g / L.
[0053]6. The method of any of Embodiments 1-5, wherein the dispersion includes at least one of dispersants and surfactants.
[0054]7. The method of any of Embodiments 1-6, wherein the dispersion includes polyvinylpyrrolidone.
[0055]8. The method of any of Embodiments 1-7, wherein the dispersion includes bile salts.
[0056]9. The method of any of Embodiments 1-8, wherein the dispersion includes water.
[0057]10. The method of any of Embodiments 1-9, wherein the dispersion includes organic solvent.
embodiment 10
[0058]11. The method of Embodiment 10, wherein the organic solvent comprises ethanol.
[0059]12. The method of any of Embodiments 1-11, wherein a concentration of the reagent solution is between about 0.1 M and about 0.15 M.
[0060]13. The method of any of Embodiments 1-12, wherein the reagent solution comprises a silver nitrate.
[0061]14. The method of any of Embodiments 1-13, wherein the reagent solution comprises silver ions.
[0062]15. The method of any of Embodiments 1-14, mixing comprises slowly adding the reagent solution.
embodiment 15
[0063]16. The method of Embodiment 15, wherein slowly adding comprises drop-wise adding.
[0064]17. The method of any of Embodiments 1-16, wherein mixing comprises vigorously stirring with a stirrer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com