Method for generating oxygen and water electrolysis device
a technology of water electrolysis and oxygen, which is applied in the direction of electrolysis components, electrolysis processes, electrolysis coatings, etc., to achieve the effect of efficient oxygen generation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
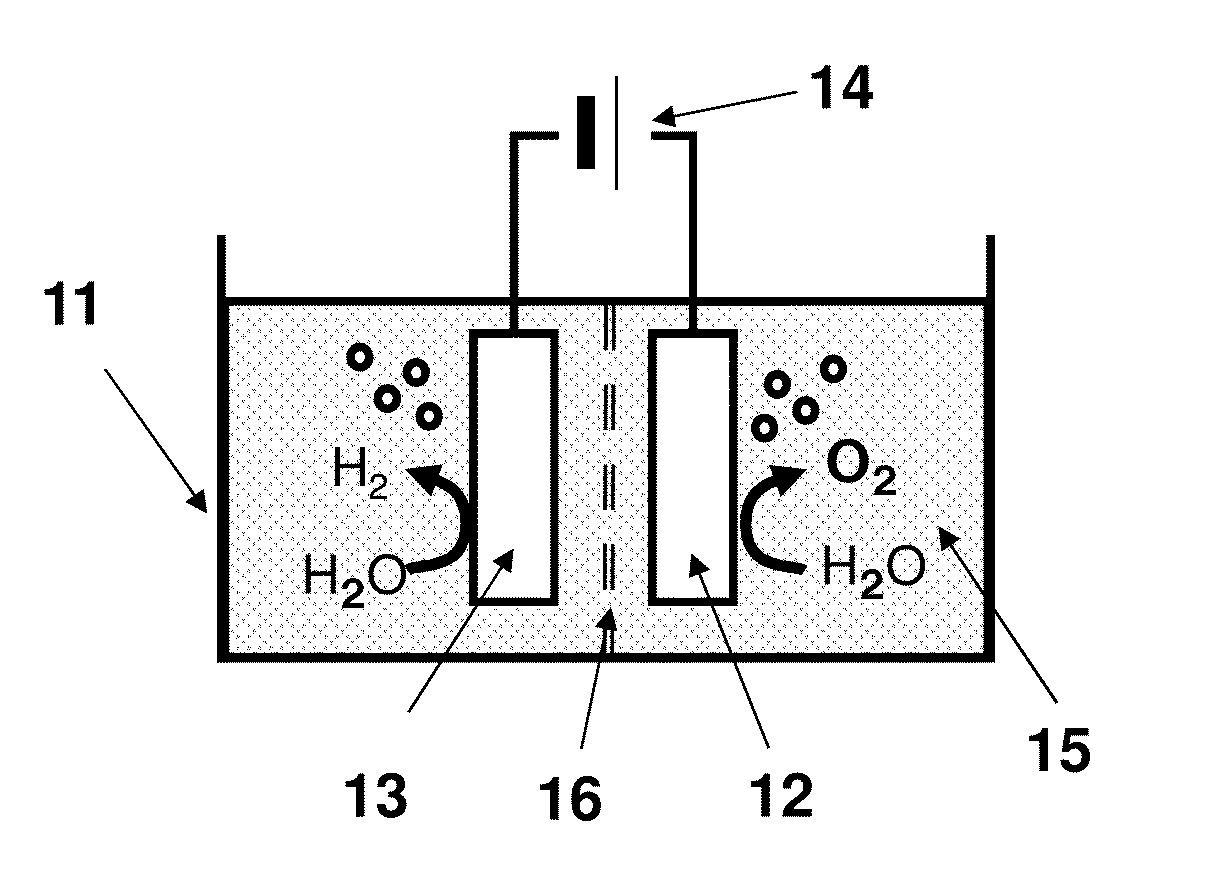
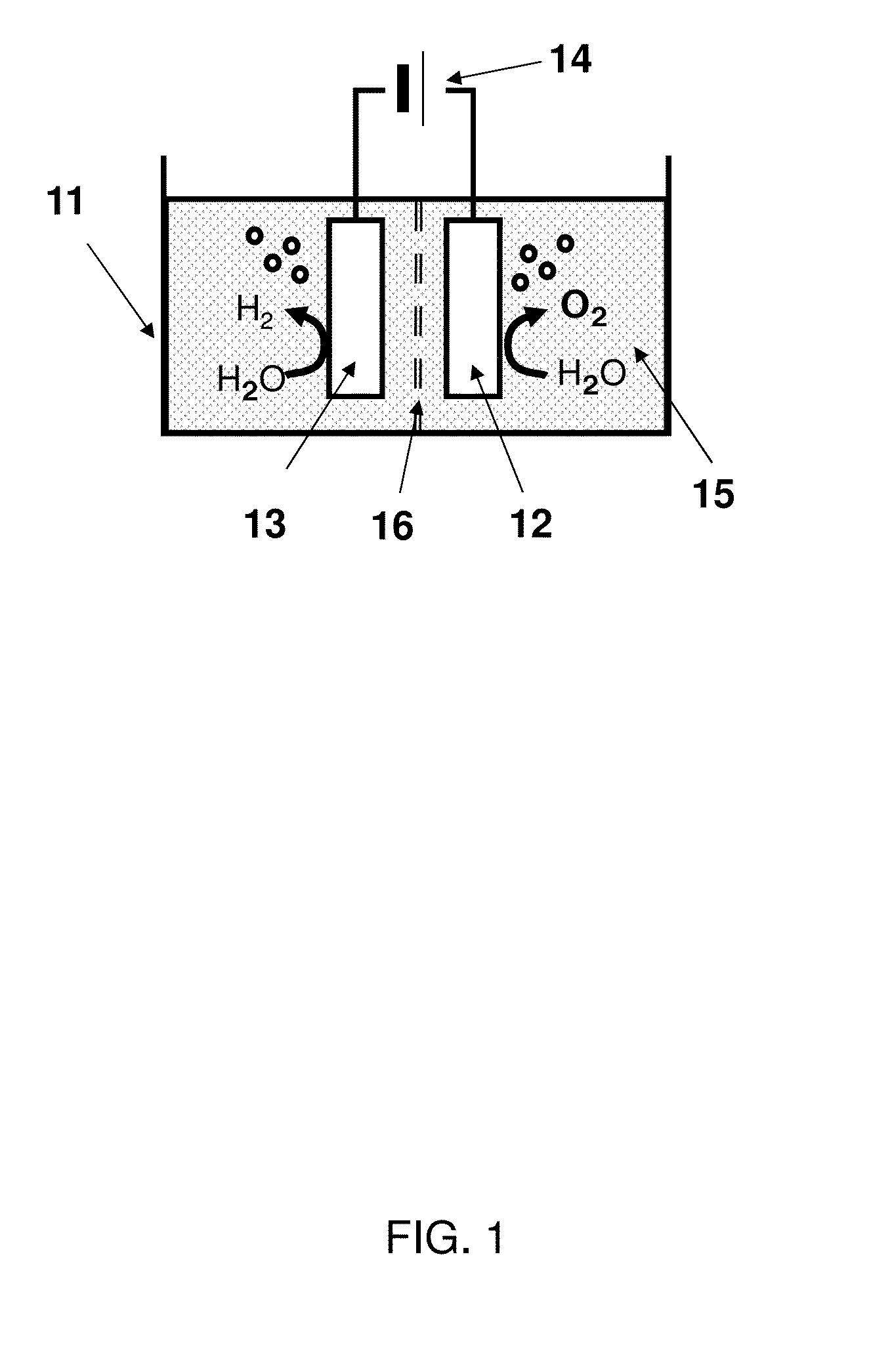
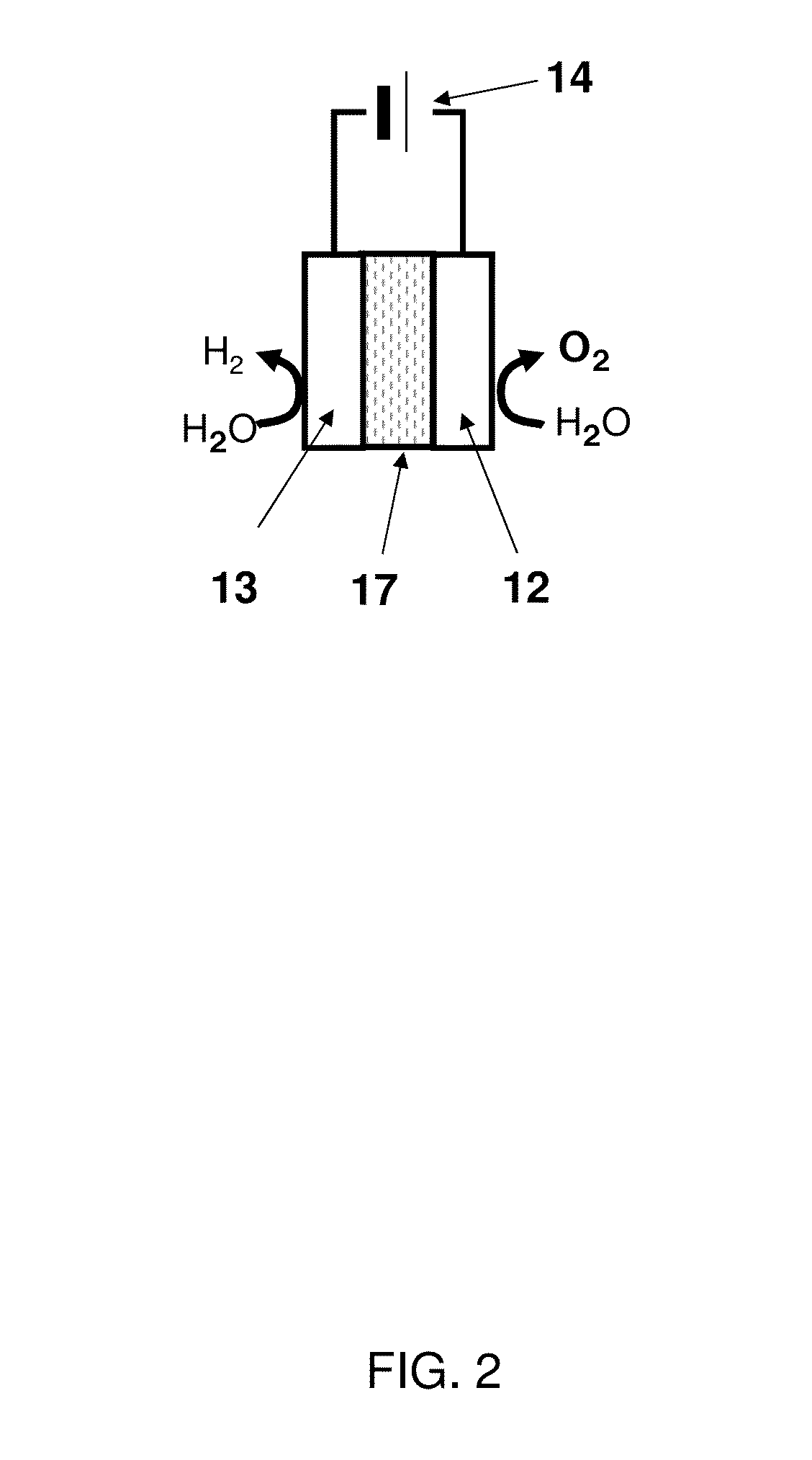
[0034]FIG. 1 shows a schematic view of a water electrolysis device 100 according to a first embodiment. The water electrolysis device 100 according to the first embodiment comprises a container 11, an anode 12, a cathode 13, and a power supply 14.
[0035](Container 11)
[0036]An electrolyte aqueous solution 15 is stored in the container 11. An example of the electrolyte aqueous solution 15 is an alkaline aqueous solution such as potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide. Water is electrolyzed using the alkaline aqueous solution to improve the efficiency of the oxygen generation and to decrease an electric power necessary for the electrolysis.
[0037]Another example of the electrolyte included in the electrolyte aqueous solution 15 is sulfuric acid, nitric acid, or perchloric acid. More specifically, an example of a cation of the electrolyte included in the electrolyte aqueous solution 15 is a proton, an alkali metal ion, or an alkali earth metal ion. An example of an anion of the electrolyt...
example 1
(Preparation of the Anode 12)
[0072]The anode 12 according to the example 1 was made by supporting a copper rhodium delafossite compound on a conductive carbon substrate.
[0073]First, the copper rhodium delafossite compound was prepared by a solid-phase reaction method.
[0074]Particularly, copper(I) oxide represented by the chemical formula Cu2O (available from Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., 1.17 grams) and rhodium(III) oxide represented by the chemical formula Rh2O3 (available from Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., 2.0 grams) were ground and mixed sufficiently in an agate mortar to give a mixture.
[0075]The mixture was supplied to a tableting machine. Then, the mixture was pressed at a pressure of 40 MPa to give a tablet containing copper(I) oxide and rhodium(III) oxide. The tablet had a diameter of 25 millimeters.
[0076]The tablet was subjected to sintering in a muffle furnace (available from Full-tech Furnace Co. Ltd., trade name: FT-101FMW) under a tempareture of 1,050 degre...
reference example 1
[0106]An anode supporting a copper oxide represented by the chemical formula CuO was prepared as below and the overvoltage thereof was calculated.
[0107]Copper(II) oxide represented by the chemical formula CuO (available from Kojundo Chemical Laboratory Co., Ltd., 25 milligrams) was dispersed in pure water (2 milliliters) to prepare a slurry. Similarly to the case of the example 1, an anode was prepared using the slurry and the oxygen generation property thereof was evaluated. The curve (b) in FIG. 6 is an electric current-voltage property of the anode according to the reference example 1. The anode according to the reference example 1 had an electric potential difference EPD1 of 1.85 volts. Therefore, the anode according to the reference example 1 had an overvoltage of 0.62 volts.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| overvoltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com