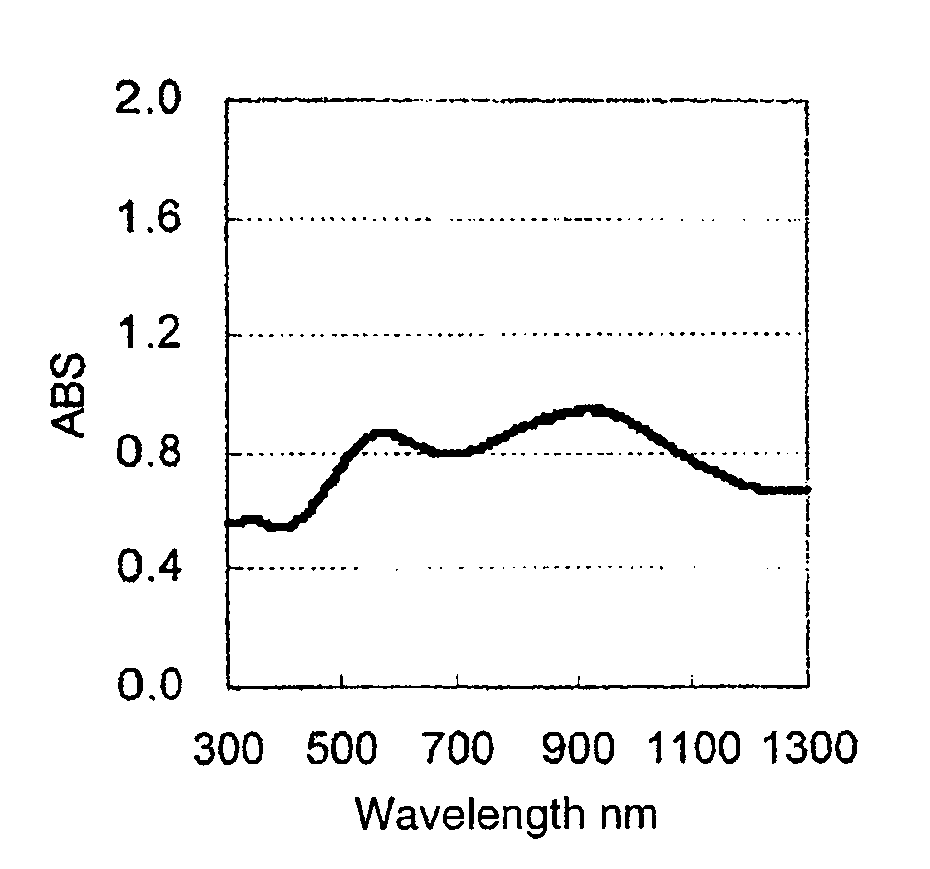
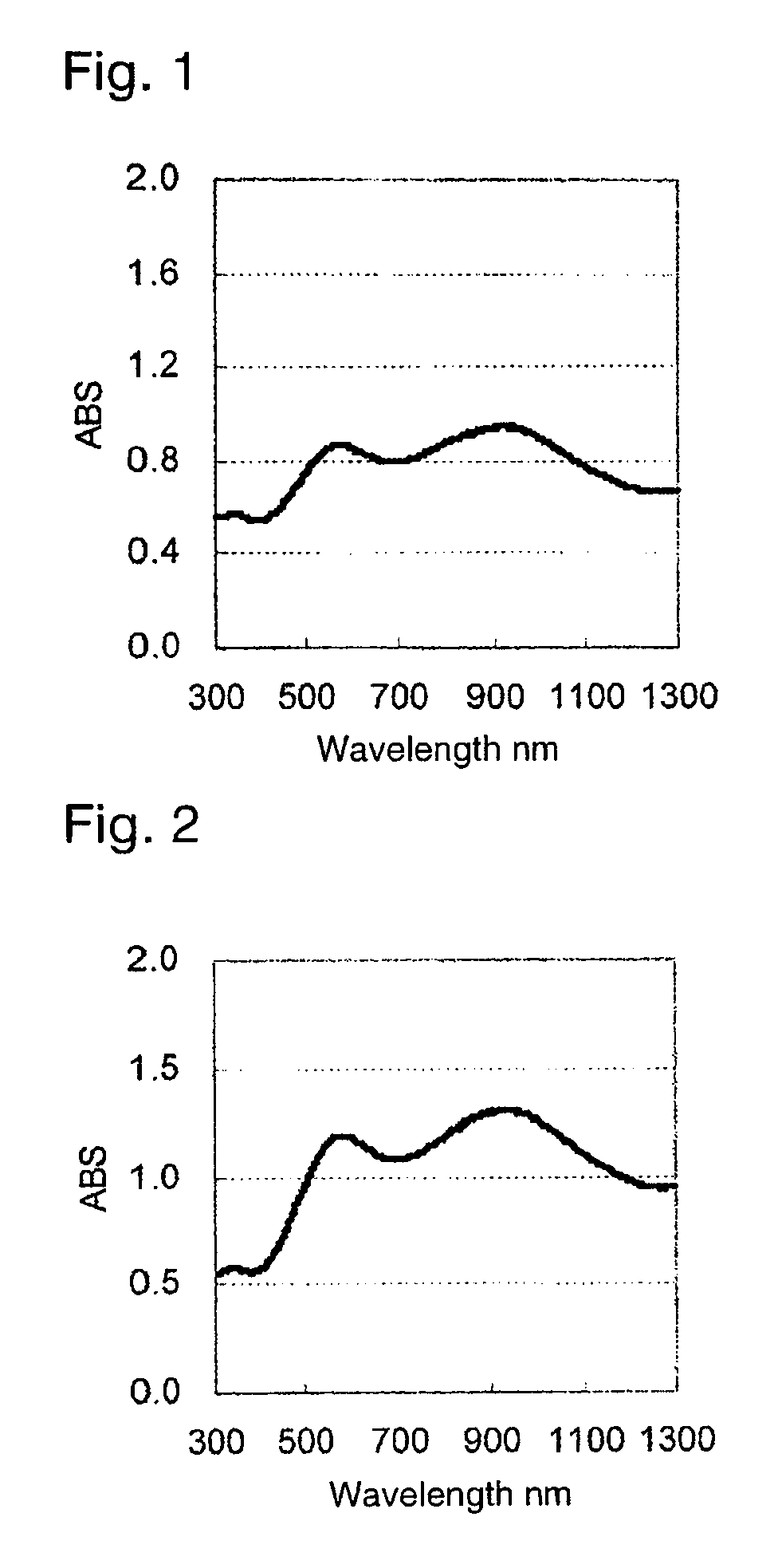
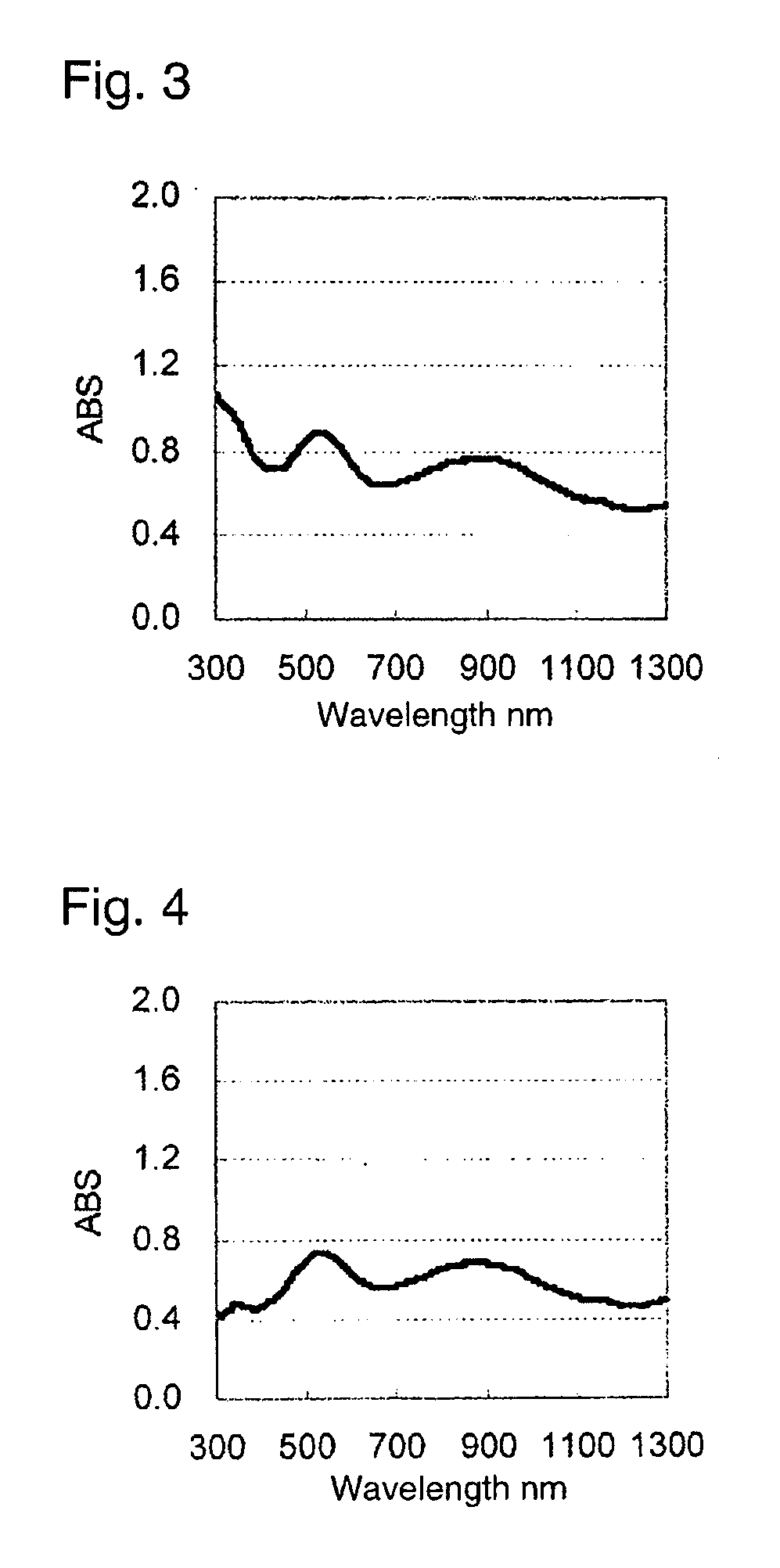
Polythiophene, water-soluble electrically conductive polymer using it, and method for producing it
a technology of electrically conductive polymer and polythiophene, which is applied in the direction of electrically conductive paints, organic chemistry, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of low heat resistance and water resistance, low electrical conductivity, and heavy environmental burden, and achieves good electrical conductivity, good electrical conductivity, and good electrical conductivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
hydro-thieno[3,4-b][1,4]dioxin-2-ylmethyl bromide (Compound Represented by the Following Formula (29))
[0284]Into a 500 mL separable flask equipped with a condenser tube, a thermometer insertion tube, an agitating blade and a nitrogen induction tube, 20.0 g (134.5 mmol) of 3,4-dimethoxythiophene (corresponding to the above compound (27)), 25.0 g (161.5 mmol) of 3-bromo-1,2-propanediol [corresponding to the above compound (28)], p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (5.33 g, 30.9 mmol) and 340 ml of toluene were charged and reacted in nitrogen atmosphere at 90° C. for 20 hours. The obtained black liquid was allowed to cool, diluted with methylene chloride and washed with water. The obtained green brown organic layer was dried over magnesium surface, and the filtrate was concentrated to obtain a yellow brown liquid. Continuously, the liquid was purified by silica gel chromatography (eluent: hexane / toluene=4 / 1) and concentrated, to obtain 18.9 g of compound represented by the following for...
example 1
on of Potassium N-(2,3-dihydro-thieno[3,4-b][1,4]dioxin-2-ylmethyl)-2-aminoethanesulfonate (Compound Represented by the Following Formula (30))
[0286]In nitrogen, into a 200 mL three-necked flask, 3.00 g (12.6 mmol) of compound represented by the above formula (29) obtained in Preparation Example A-1, 1.57 g (12.6 mmol) of 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid (corresponding to the above compound (23)), 5.21 g (37.7 mmol) of potassium carbonate (base) and 131 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide (polar solvent) were charged and reacted in nitrogen atmosphere at 100° C. for 17 hours. From TLC (thin layer chromatography) analysis and GC (gas chromatography) analysis, disappearance of compound represented by the above formula (29) was confirmed. After the reaction mixture was allowed to cool, the precipitate was collected by filtration and washed with dimethylformamide. The obtained filtrate was roughly concentrated, washed with a methylene chloride / hexane mixed solvent and subjected to filtration under re...
example 2
on of Sodium N-methyl-N-(2,3-dihydro-thieno[3,4-b][1,4]dioxin-2-ylmethyl)-2-aminoethanesulfonate (Compound Represented by the Following Formula (31))
[0290]Into a 500 mL four-necked separable flask equipped with a condenser tube, a thermometer insertion tube, an agitating blade and a nitrogen introduction tube, 3.00 g of compound represented by the above formula (29) obtained in Preparation Example 1, 3.42 g (13.8 mmol) of a 65 wt % aqueous solution of sodium N-methyltaurine (corresponding the above compound (1-6)), 5.21 g (37.7 mmol) of potassium carbonate (base) and 130 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide (polar solvent) were charged and reacted in nitrogen atmosphere at 90° C. for 22 hours. From TLC analysis and GC analysis, disappearance of compound represented by the above formula (29) was confirmed. After the reaction mixture was allowed to cool, the precipitate was collected by filtration and washed with dimethylformamide. The obtained filtrate was roughly concentrated, washed with a ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size distribution measuring apparatus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size distribution measuring apparatus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com