Electrochemical processing method for micro-structure of P type silicon surface
A technology of electrochemical processing and microstructure, which is applied in the field of silicon surface processing, can solve the problems of difficult general application and slow processing speed, and achieve the effects of high replication accuracy, low processing cost and fast etching speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
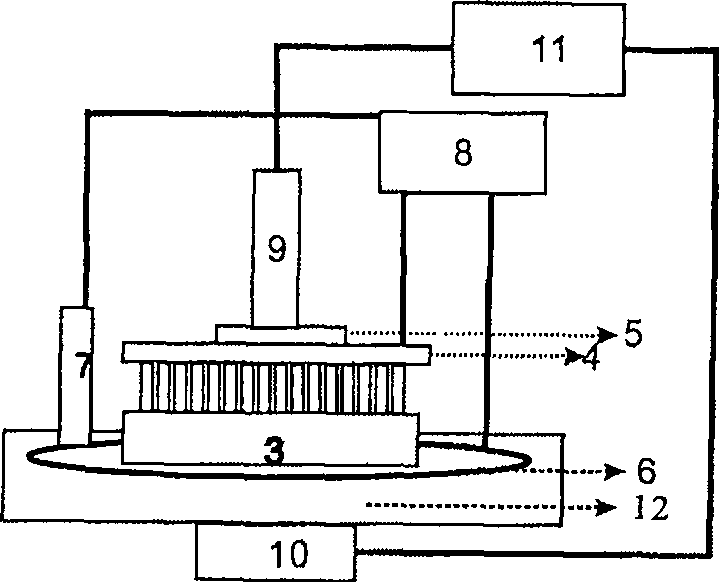
[0030] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram for preparing an agarose gel template in Example 1 of the present invention. exist figure 1 Among them, the picture above shows the thermoplastic replication process. Firstly, agarose powder and ultrapure water are mixed at a mass ratio of 1:(8-1):12, heated and dissolved, and quickly cast on the surface of the original master plate 1 with a microstructure. After removing air bubbles under vacuum and cooling for 2 hours, agarose gel 2 was formed, and the two were carefully peeled off (see figure 1 The lower figure in ) obtained agarose gel template 3 with a structure completely complementary to the original master template 1. The prepared agarose gel template 3 is generally about 2 cm long x 2 cm wide x 1 cm high. The original master 1 with microstructure can be titanium, quartz or silicon wafer with microstructure. The substrate needs to be pretreated before the experiment. Quartz and titanium only need to be ultrasonicated in acet...
Embodiment 2
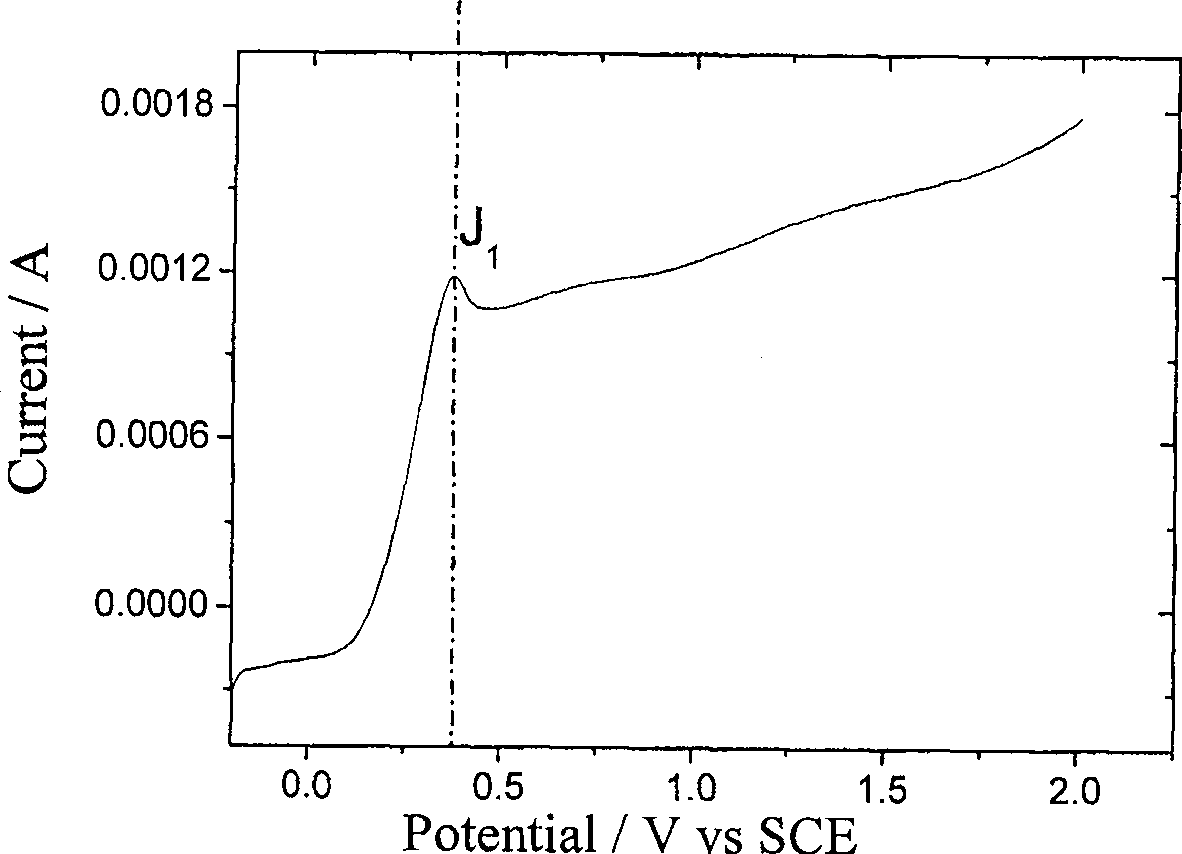
[0035] Figure 5 Micrographs and three-dimensional topography photos of the silicon surface microstructure array processed in Example 2 of the present invention are given. The electrolyte stored in the agarose gel template during processing is 0.8mol / L hydrofluoric acid, the etching potential is 1.5Vvs.SCE (saturated calomel electrode), and the processing time is 4h. The average depth of the etched pattern is 11 μm, and the etching processing speed is about 2.75 μm / h.
Embodiment 3~40
[0037] Its process steps are similar to the above-mentioned examples, and its difference lies in the concentration of hydrofluoric acid stored in the agarose gel template, and the potential of electrochemical polishing, and the specific conditions and its etching processing effect are shown in Table 1 (wherein "+" Indicates that the etching processing effect is good, "—" indicates that the etching processing effect is poor).
[0038] Table 1
[0039]
[0040] 18 0.76 1.5 + 19 0.77 1.5 + 20 0.78 1.5 + 21 0.79 1.5 + 22 0.61 1.6 + 23 0.62 1.6 + 24 0.63 1.6 + 25 0.64 1.6 + 26 0.65 1.6 + 27 0.66 1.6 + 28 0.67 1.6 + 29 0.68 1.6 + 30 0.7 1.6 + 31 0.71 1.6 + 32 0.72 1.6 + 33 0.73 1.6 + 34 0.74 1.6 + 35 0.75 1.6 + 36 0.76 1.6 + 37 0.77 0.35 — 38 0.78 0.3 — 39 0.79 0.2 — 40 0.8 0.1 —
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com