Hydro-thermal synthetic preparation method for lithium ion battery anode material lithium iron phosphate
A lithium ion battery, lithium iron phosphate technology, applied in the field of phosphate, can solve the problems of poor electrochemical performance, high preparation cost, large equipment investment, etc., and achieve the effects of low preparation cost, short process and small equipment investment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The first step, hydrothermal synthesis reaction
[0028] 1112g or 4mol of FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was dissolved in heated degassed and deoxygenated water, and diluted to 4L. After standing for 12 hours, filtered to remove a small amount of precipitate; Dilute to 1L in deoxygenated water; add 503.3g or 12mol of LiOH·H 2 O was dissolved in heated degassed and deoxygenated water and diluted to 3L.
[0029] Add the above-mentioned phosphoric acid solution and lithium hydroxide solution into a 10L autoclave with a sealed feeding tube and a cooling coil. After purging the air in the dead volume of the autoclave with an inert gas, seal the autoclave and heat it from room temperature to 40°C, open the feed valve and exhaust valve, then add the above-mentioned refined ferrous sulfate solution, then seal the autoclave, and react at 150°C for 300 minutes. At this time, the autogenous pressure corresponding to the system is 0.48Mpa. The proportioning ratio is: Li:Fe:P molar ratio is 3:1...
Embodiment 2
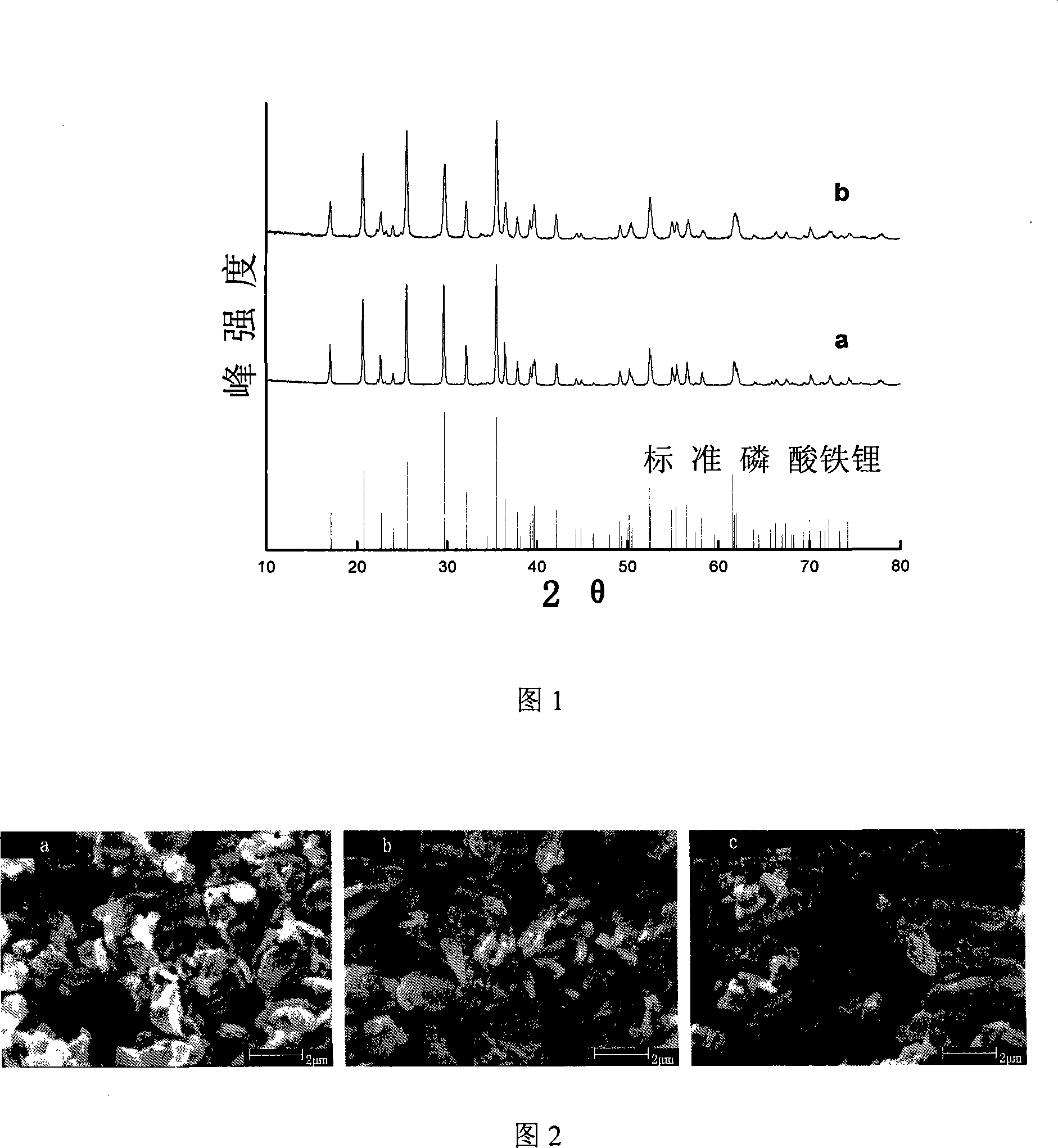
[0054] The heated degassed and deoxygenated water in Example 1 was replaced with ordinary deionized water, and other steps were the same as in Example 1. The scanning electron micrograph and the X-ray diffraction pattern spectrum of the product obtained have no change compared with Example 1. Chemical analysis showed a ferric iron content of about 0.6%. It shows that the oxidation of ferrous iron mainly occurs in the process of dissolution, mixing and reaction, rather than mainly caused by the oxidation of dissolved oxygen in water. Oxidation of ferrous iron is a rapid and spontaneous process as the pH increases during dissolution or mixing.
[0055] The test data results of the product of this embodiment are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0057] The first step, hydrothermal synthesis reaction
[0058] 795g or 4mol of FeCl 2 4H 2 O was dissolved in ordinary deionized water and diluted to 4L with water. After standing for 12 hours, filtered to remove a small amount of precipitate; in water and diluted to 1.5L; then 503.3g or 12mol of LiOH·H 2 O was dissolved in heated degassed and deoxygenated water and diluted to 2.5 L.
[0059] Add the above phosphoric acid solution and lithium hydroxide solution into the autoclave, after purging the air in the dead volume of the autoclave with an inert gas, seal the autoclave, heat it from room temperature to 50°C while stirring at a speed of 200rpm, open the feed valve and exhaust Valve, then add the above-mentioned refined ferrous chloride solution, then seal the autoclave, and react for 200 minutes at 170°C. At this time, the autogenous pressure corresponding to the system is 0.85Mpa, and the ratio of the added substances is: Li: Fe: The molar ratio of P is 3:1:1.15, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com