Bacillus licheniformis for degrading cellulose and application thereof in straw fermentation
A technology of Bacillus licheniformis and plant cellulose, which is applied in the direction of application, bacteria, and microbial-based methods, can solve problems such as less research, and achieve the effects of increasing utilization, improving the internal environment of animals, and good thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: the separation of bacterial classification
[0045] 1: Take a certain amount of sample and wash it with sterile water, and draw a certain amount of suspension and spread it on the LB plate containing carboxymethyl cellulose.
[0046] 2: Separate a single colony after two to three days, then stain the plate with Congo red (1g / L) for about one hour, and then decolorize it with sodium chloride (1mol / L).
[0047] 3: After decolorization, observe whether there is a transparent circle, and then preliminarily screen out six strains with the ability to decompose cellulose through the ratio of the colony size to the transparent circle.
[0048] 4: Preliminary fermentation enzyme production research, through the supernatant of the fermentation broth and the supernatant after breaking the wall, 8000rpm, 5min, take the supernatant, and 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid color development (DNS method) to preliminarily determine the enzyme-producing genus Inner or extracellular...
Embodiment 2
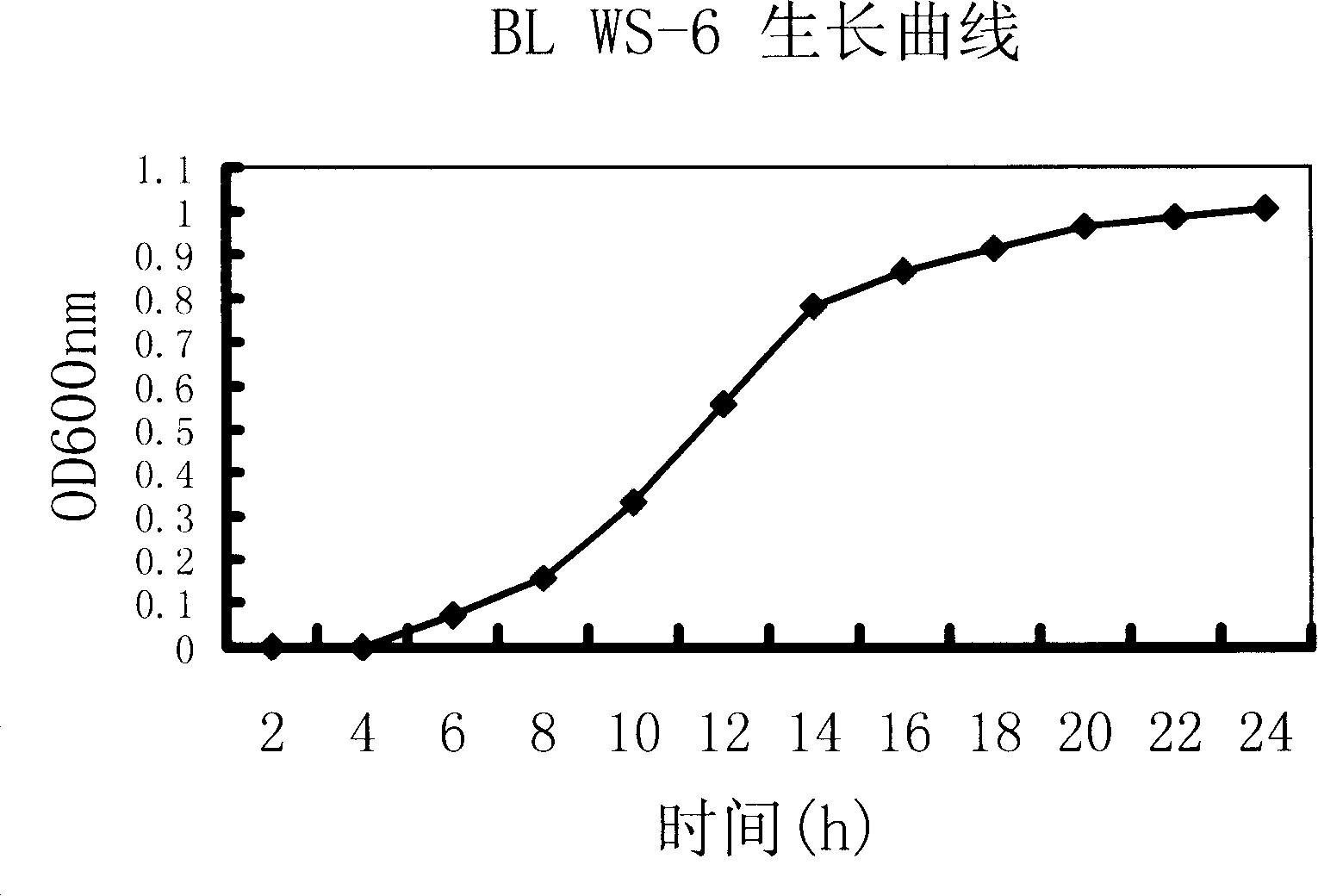
[0051] Example 2: Growth characteristics of bacterial strain B.licheni ws6
[0052] 1: Cultivate with LB liquid medium, first set up four temperature gradients, respectively 30°C, 40°C, 50°C, 60°C, according to the inoculation amount of 1%, 100rpm, sampling once every two hours, measured under the condition of λ540nm OD value. Conclusion It can grow at 30-50℃. It stops growing at 60°C and grows rapidly between 30°C and 40°C. Furthermore, three gradients were set up, respectively 30°C, 35°C, and 40°C, and the optimum growth temperature was determined to be 35-40°C.
[0053] 2: Observation by puncture culture of LB solid medium, growth everywhere in the puncture tube, the strain belongs to facultative anaerobic bacteria.
[0054] 3: Cultivate with LB liquid medium, set the medium at pH 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, use 1% inoculum, 100 rpm, take samples every two hours, measure OD value under the condition of λ540nm, conclusion: It grows well around pH 4.0 to 5.0, and also grows at pH 8.0....
Embodiment 3
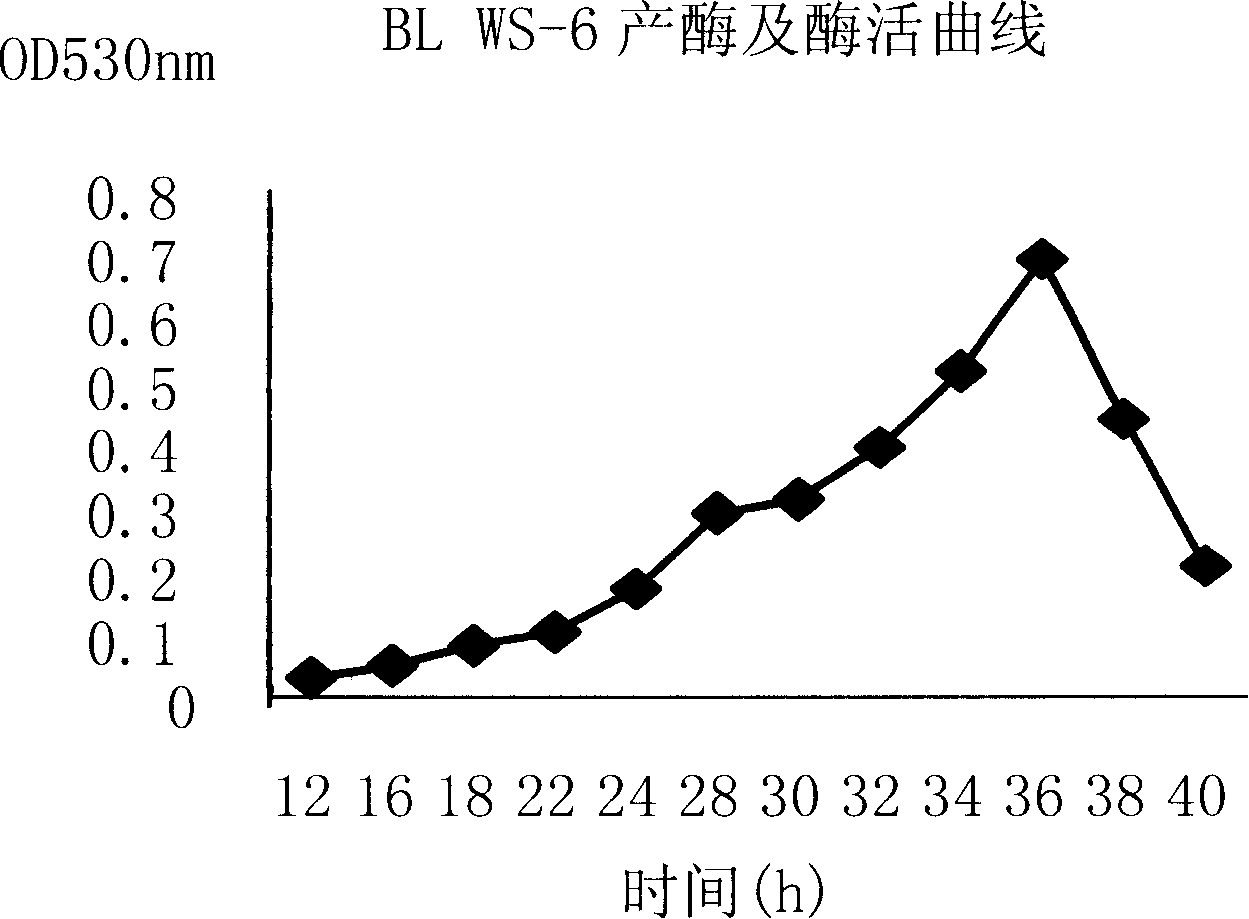
[0055] Example 3: Enzyme Activity Characteristics of Bacterial Strain B.licheni ws-6
[0056] 1: Inoculate at 1% inoculum size, use LB liquid medium containing carboxymethyl cellulose as the primary fermentation medium, 100rpm, 37°C, sample once every two hours, 8000rpm, 5min, take the supernatant with carboxymethylcellulose Cellulose is used as the substrate, and the optimum time for enzyme production is measured to be 36 to 38 hours by DNS chromogenic method.
[0057] 2: Set up four gradients, respectively 30°C, 40°C, 50°C, and 60°C. The optimum temperature is 40°C (the method is the same as above), the time is 20min, and the enzyme activity is about 1300mu / ml.
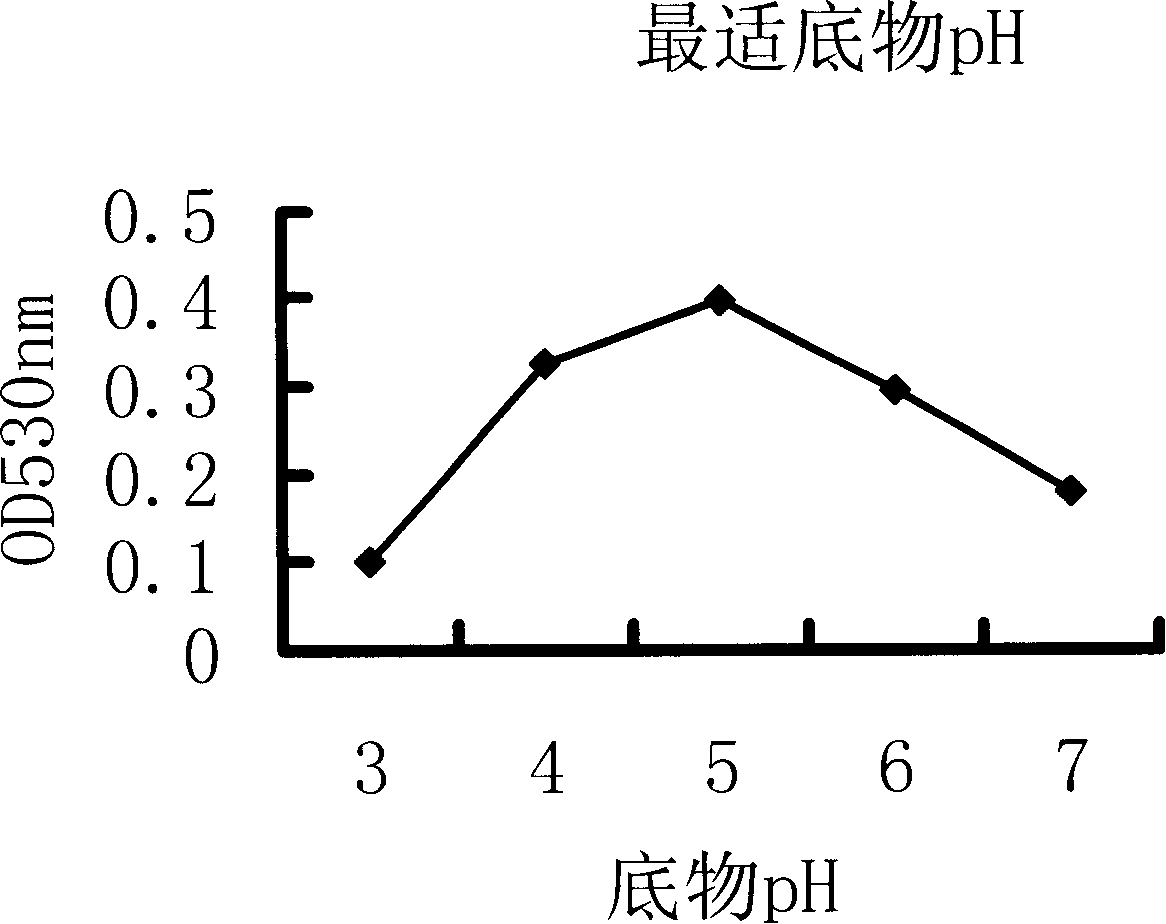
[0058] 3: Set up four gradients, the pH is 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and the optimum substrate pH is measured between 4-5 (the method is the same as above, and the substrate concentration is 0.1g / ml.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com