Leadless high-temperature electronic solder and preparation
A lead-free solder and lead electronics technology, applied in Sn-Sb-Cu-Ni-X multi-component lead-free high-temperature electronic solder and preparation, high-temperature lead-free solder and preparation fields, can solve the problem of wetting in the solid-liquidus interval It can improve the anti-oxidation ability, reduce the dissolution rate and improve the mechanical properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
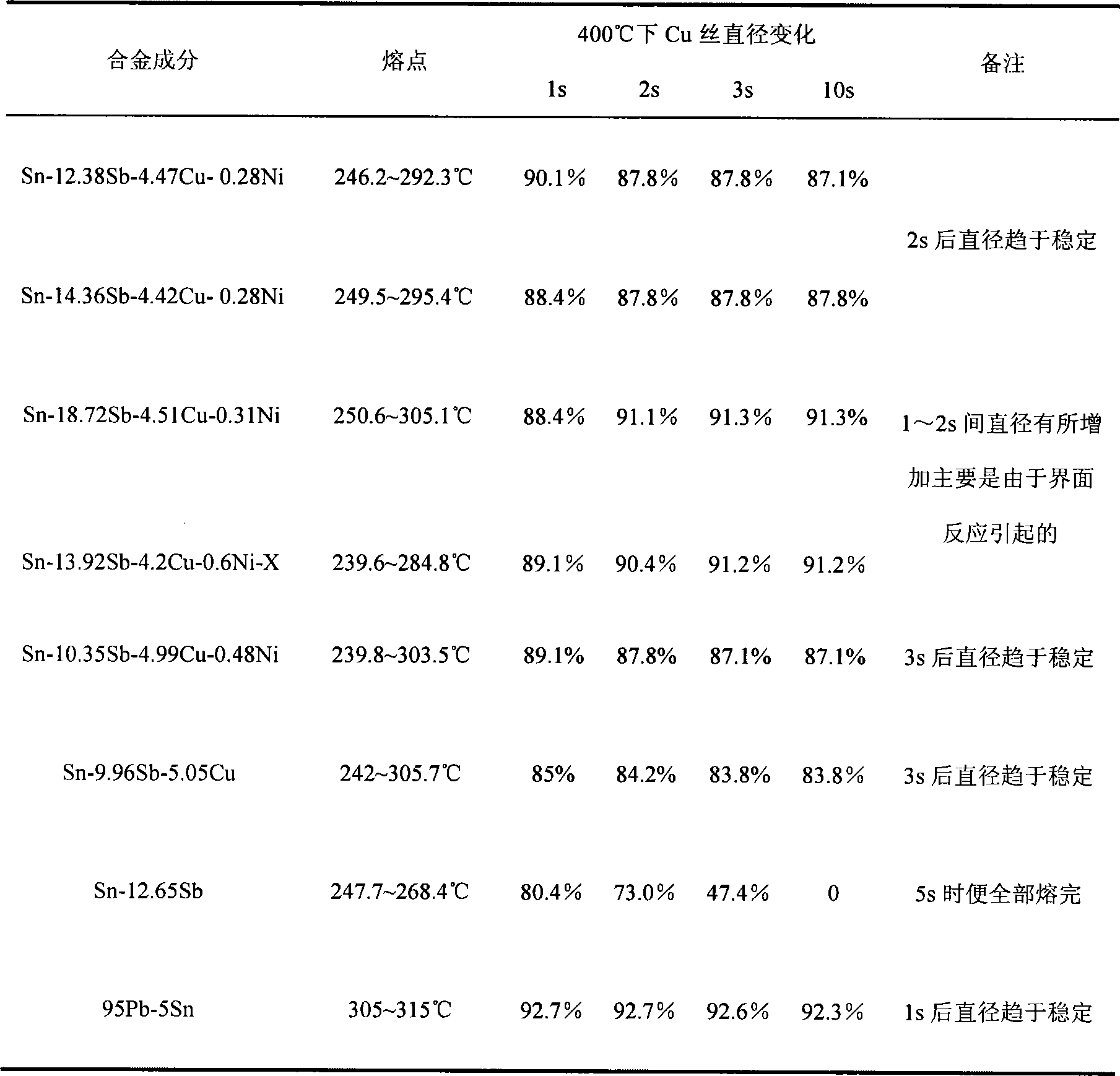
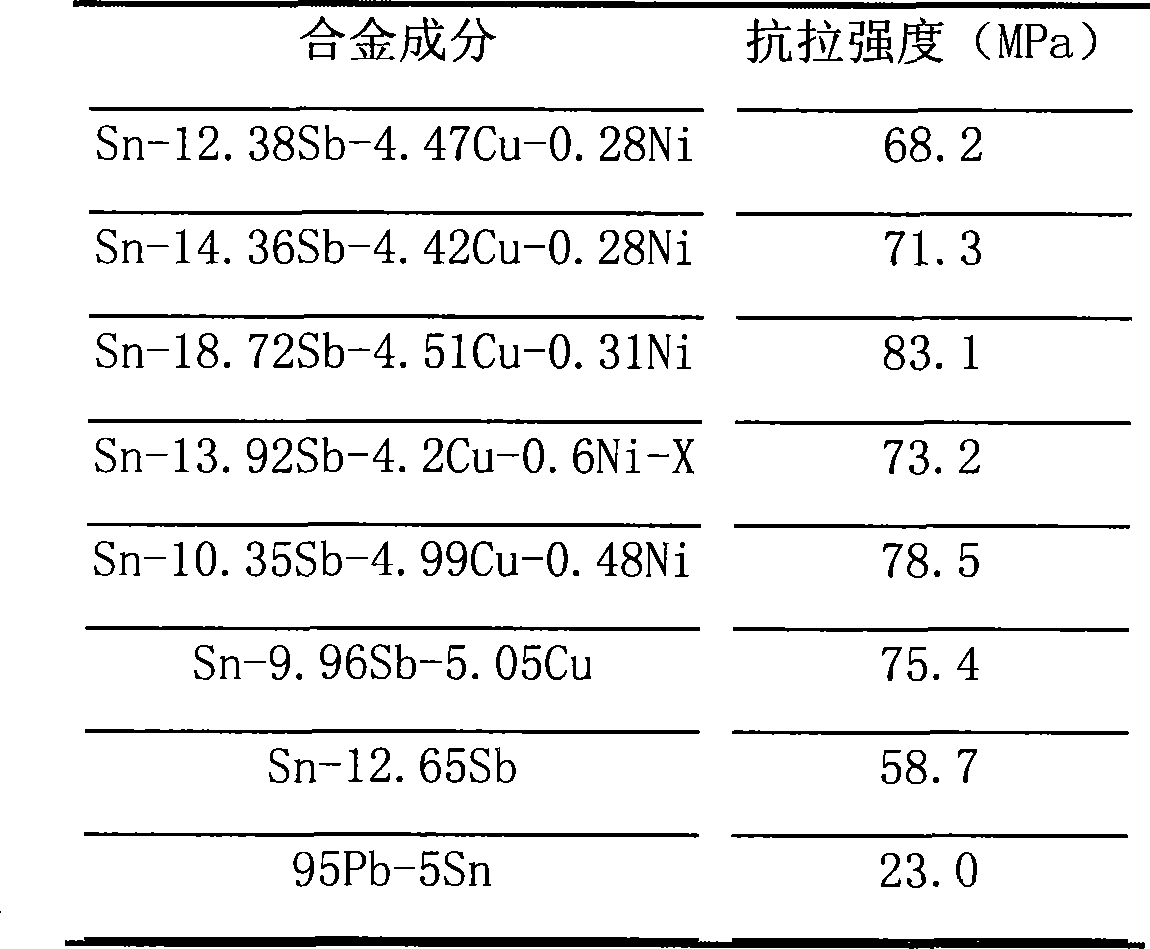
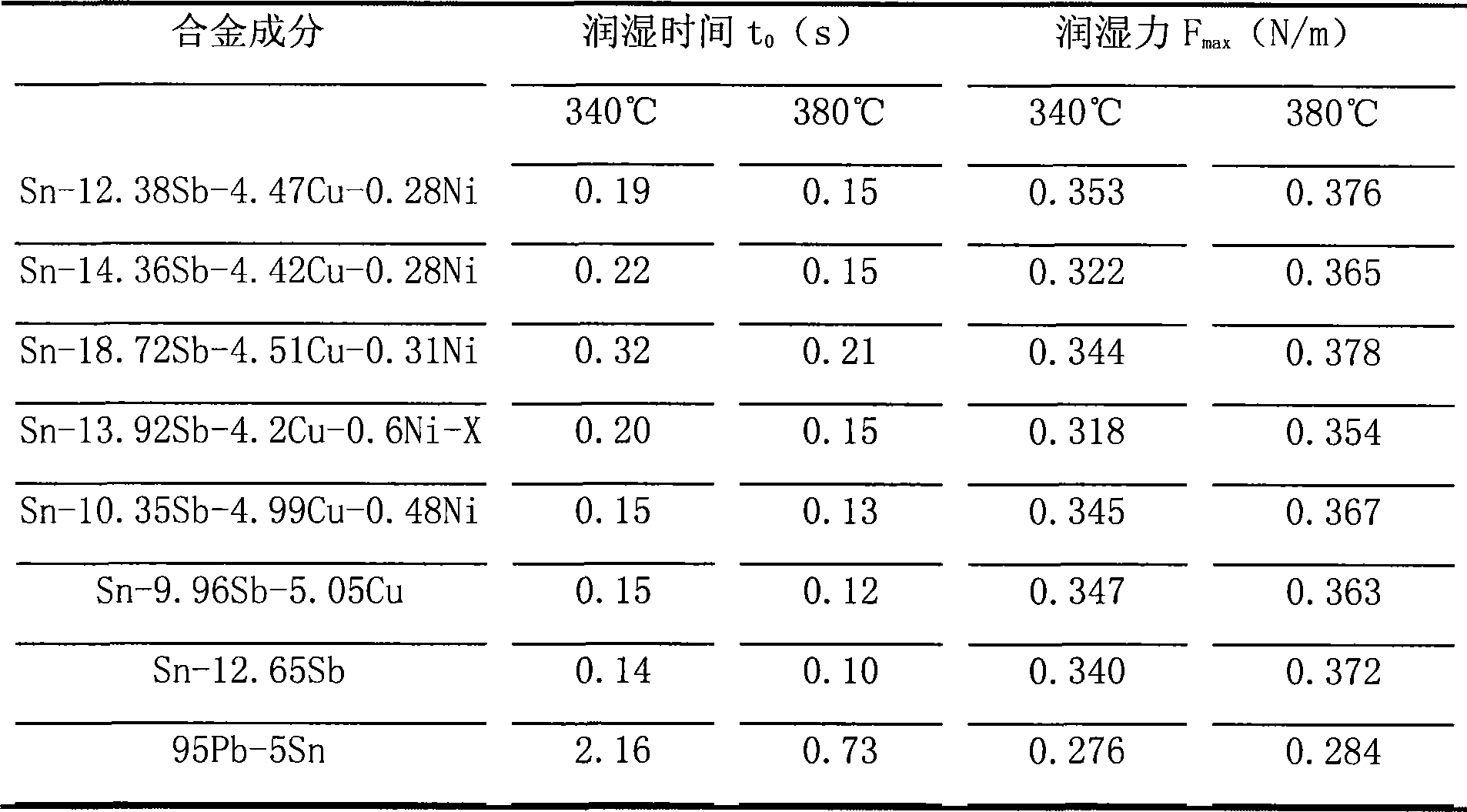
[0026] The alloy composition and its weight percentage are: 12.38% Sb, 4.47% Cu, 0.28% Ni, the rest is Sn and some usual impurity elements. Through DSC measurement, the melting point range of the alloy is 246.2~292.3°C, and the tensile strength is 68.2MPa, see Table 1 and Table 2 respectively.
[0027] The Cu wire with a diameter of 0.15 mm was immersed in the molten solder for reaction, and the corrosion rate of the alloy to the Cu matrix was investigated by measuring the diameter of the Cu wire after dipping for different times. The experimental results show that at a temperature of 400°C, the corrosion behavior of the alloy to Cu mainly occurs within 2s, the corrosion rate of Cu wire is 12.2%, and the diameter of Cu wire is basically stable after 2s, as shown in Table 1.
[0028] The preparation method of the present invention is as follows: it is to heat the prepared various alloy elements at 850-900° C. for 1-2 hours in a vacuum melting furnace or a non-vacuum melting fur...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The alloy composition and its weight percentage are: 14.36% Sb, 4.42% Cu, 0.28% Ni, the rest is Sn and some impurity elements usually. The melting point measured by DSC is: 249.5~295.4°C, and the tensile strength is 71.3MPa.
[0033] The corrosion behavior of the alloy to Cu mainly occurs within 2s, and the corrosion rate of the 0.15mm Cu wire is 12.2%, and the diameter of the Cu wire is basically stable after 2s.
Embodiment 3
[0035] The alloy is refined according to the following composition and weight percentage: Sb18.72%, Cu4.51%, Ni0.31%, and the rest is pure Sn and usual trace impurities. The melting point measured by DSC is 250.6~305.1°C, and the tensile strength is 83.1MPa.
[0036] The corrosion of Cu occurs within 1s at 400°C. At this time, the corrosion rate of 0.15mm Cu wire is 11.6%. The diameter of Cu wire increases between 1 and 2s, which is mainly due to the increase in the content of alloying elements. Finally, more uneven intermetallic compounds are formed during the interfacial reaction process, which affects the measurement results. A layer of gray oxide film is easily formed on the surface of the molten alloy.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com