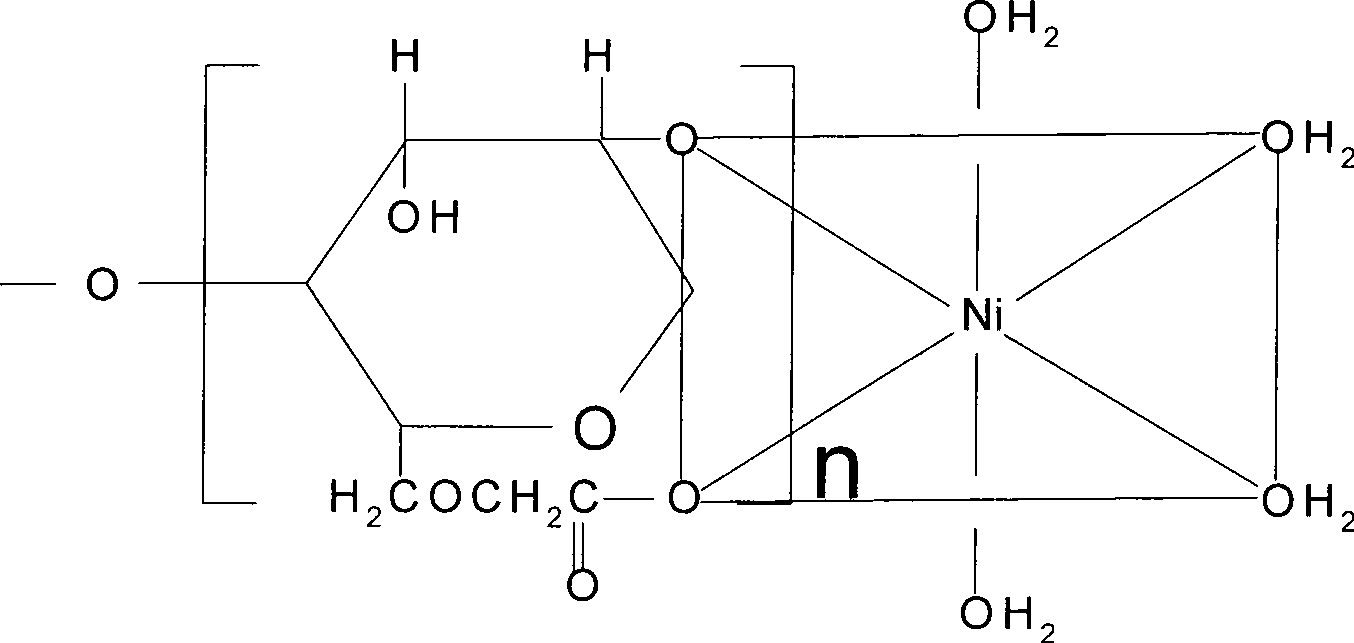
Palladium-free activation process for plastic substrate surface of nickel adsorbed sodium carboxymethylcellulose by chelating function
A technology of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and carboxymethyl cellulose is applied in liquid chemical plating, metal material coating process, coating and other directions to achieve the effects of simple and feasible process, cost reduction and high operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1 (see attached figure 2 ):
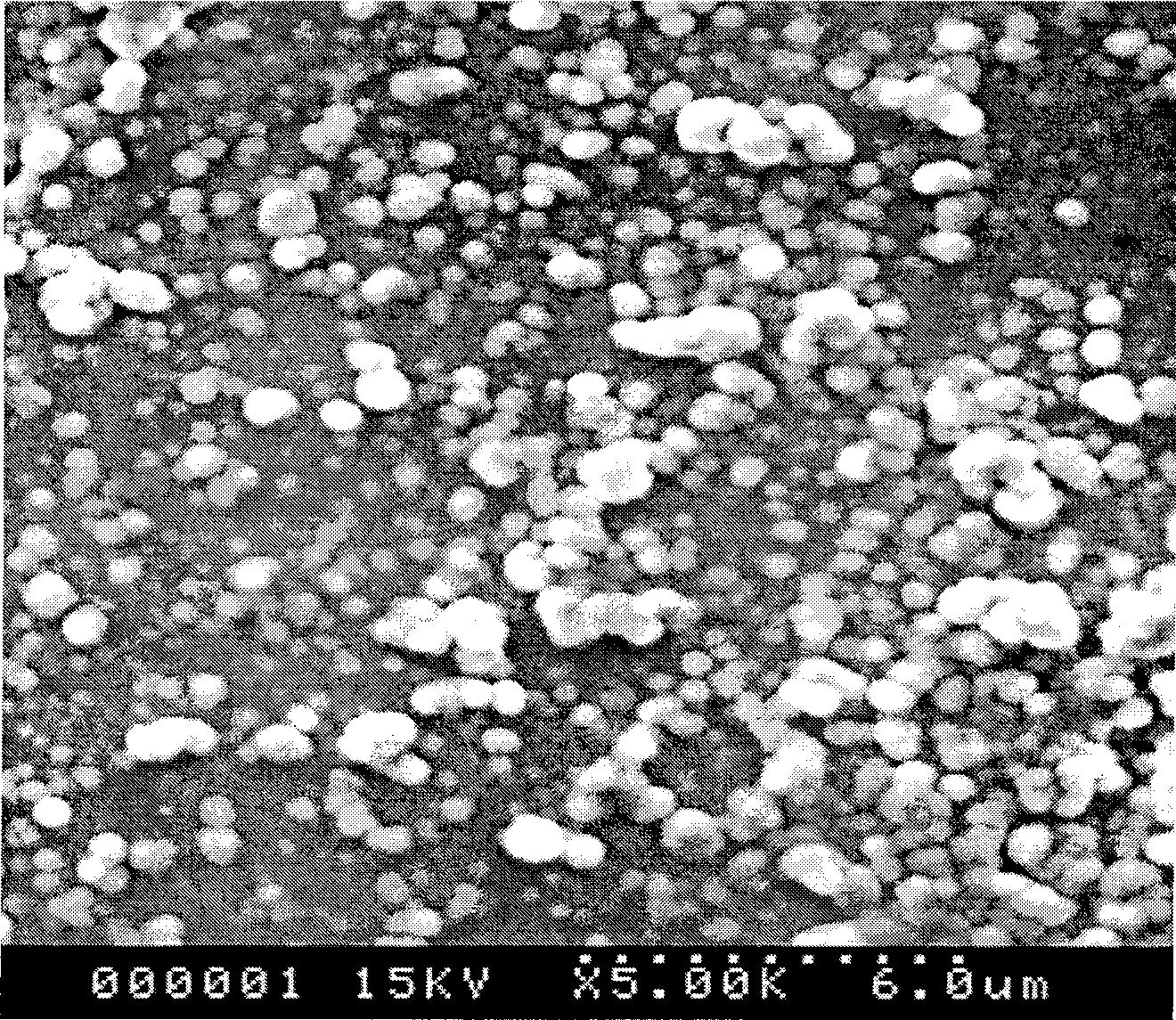
[0022] This test is a non-palladium activation method on the surface of the plastic substrate of carboxymethylcellulose sodium chelated and adsorbed nickel with PET plastic as the substrate, using 2 × 5cm 2 , a PET plastic sheet with a thickness of 100 μm is used as the base material, immersed in the above-mentioned 40°C degreasing solution for 15 minutes, washed with water, then immersed in the above-mentioned roughening solution at 55°C for 30 minutes, washed with water, and put in sodium carboxymethylcellulose (FH6, Extra-high type) 5g / L, nickel sulfate 10g / L prepared in the activation solution for 5min, temperature 40 ℃, washed with water, then reduced in 1g / L sodium borohydride solution at room temperature for 5min, washed with water, and finally put Plating in the electroless plating solution for 5 minutes, the brightness of the obtained coating is grade one, observed by metallographic microscope (see image 3 photo), th...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Using 2×5cm 2 , a PET film with a thickness of 100 μm was used as the substrate, and the pretreatment, activation and reduction treatments were completed under the same conditions as in Example 1. The difference is that the formula of the activation solution is 15g / L of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and 15g / L of nickel sulfate. Then electroless plating is carried out, and the brightness of the obtained coating is grade one. Through metallographic microscopic observation, the coating is flat, densely bonded and excellent in bonding force.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Adopt 8×6cm 2 , polyvinyl chloride plastic with a thickness of 0.3cm is used as the base material, and the pretreatment, activation and reduction treatment are completed under the same conditions as in Example 1. The brightness of the obtained coating is second-level. Through metallographic microscopic observation, the coating is smooth, densely bonded, and the bonding force is high. excellent.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com