Preparation of acrylic ester copolymer emulsion for pressure-sensitive adhesive
A pressure-sensitive adhesive, acrylate technology, applied in the direction of ester copolymer adhesives, adhesive types, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to simultaneously achieve initial tack, peeling and holding properties, initial tack and peeling properties. It can reduce the amount of residual glue, improve the initial adhesion, and improve the adhesion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
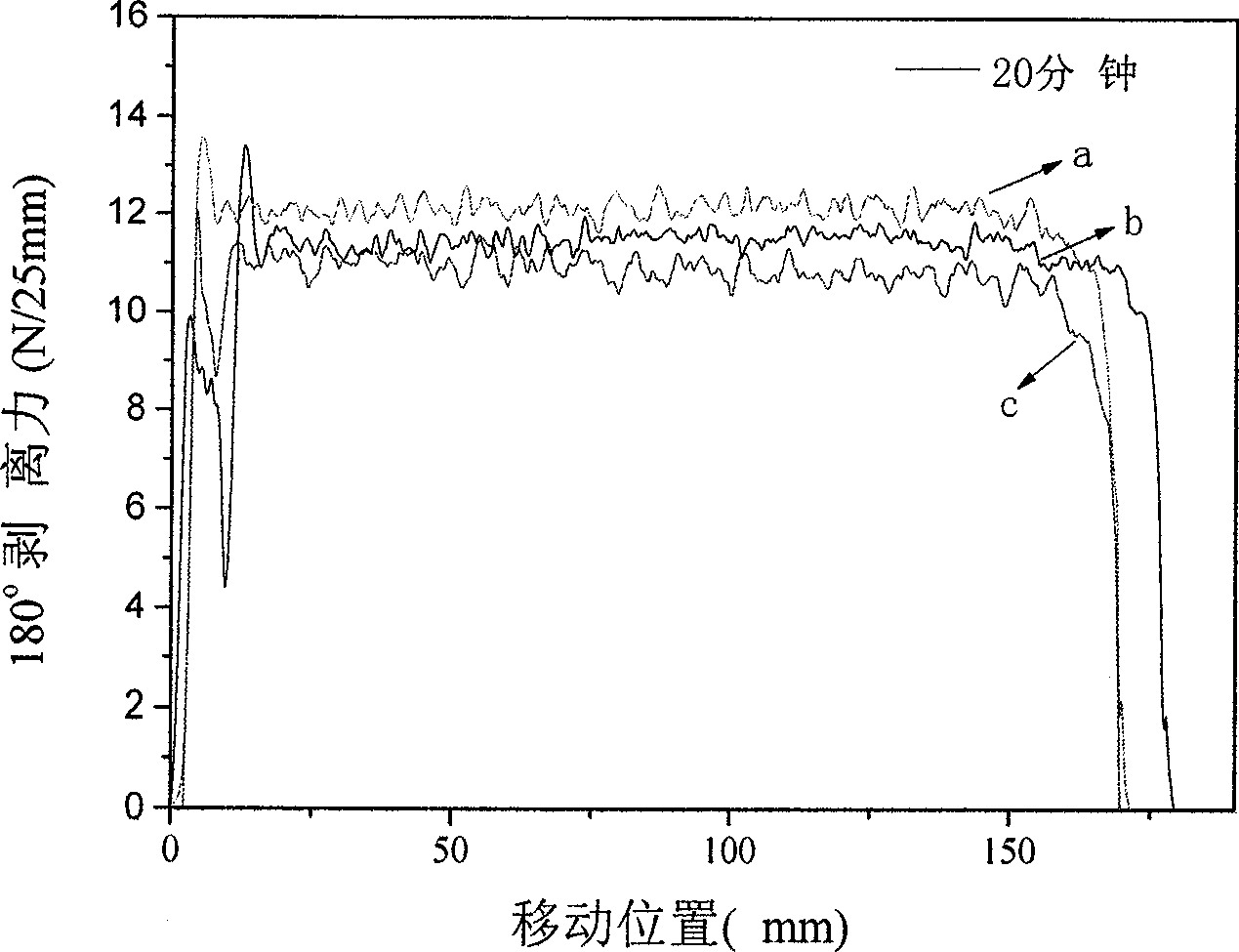
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The preparation of silica-acrylate copolymer emulsion comprises the following steps:
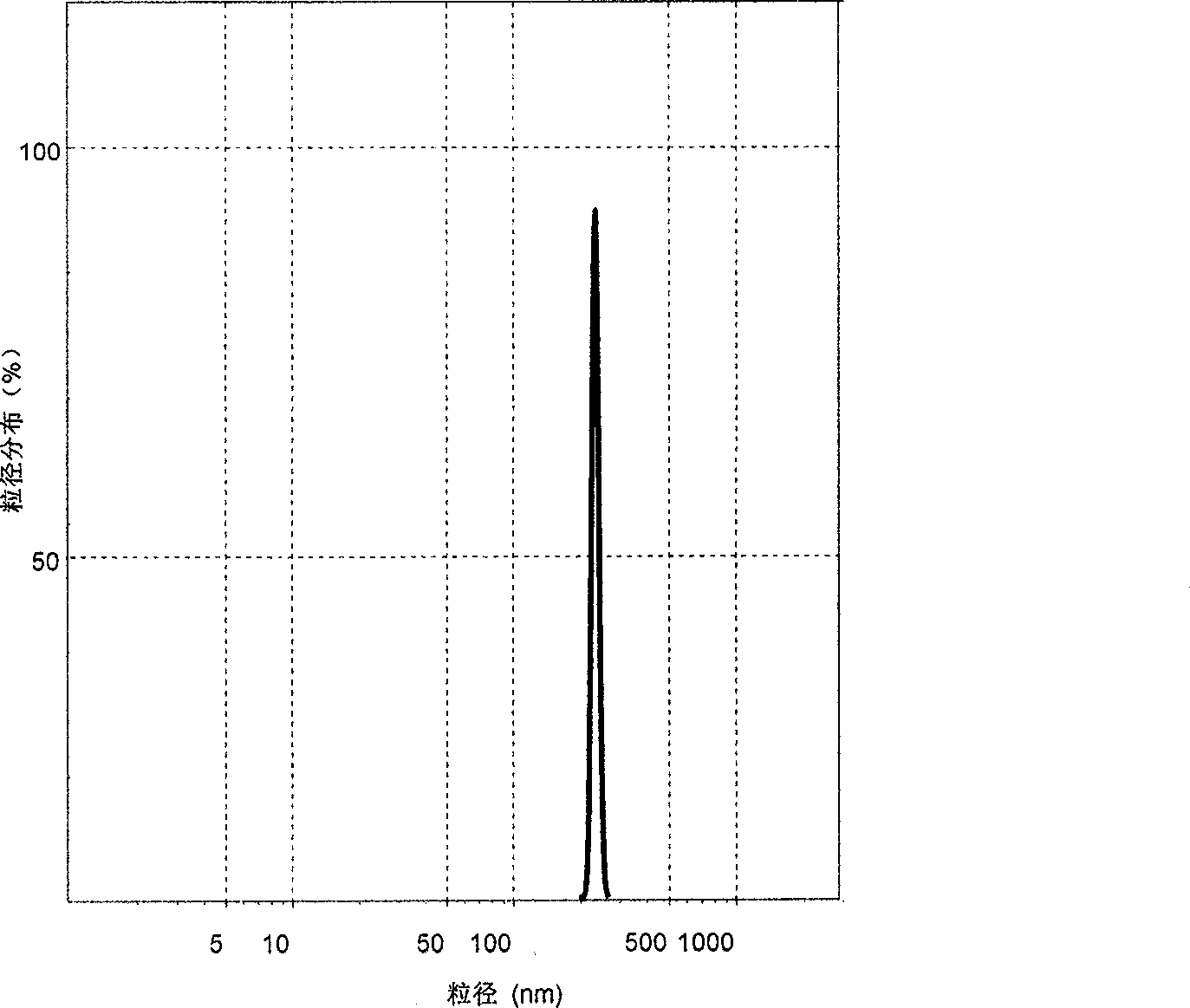
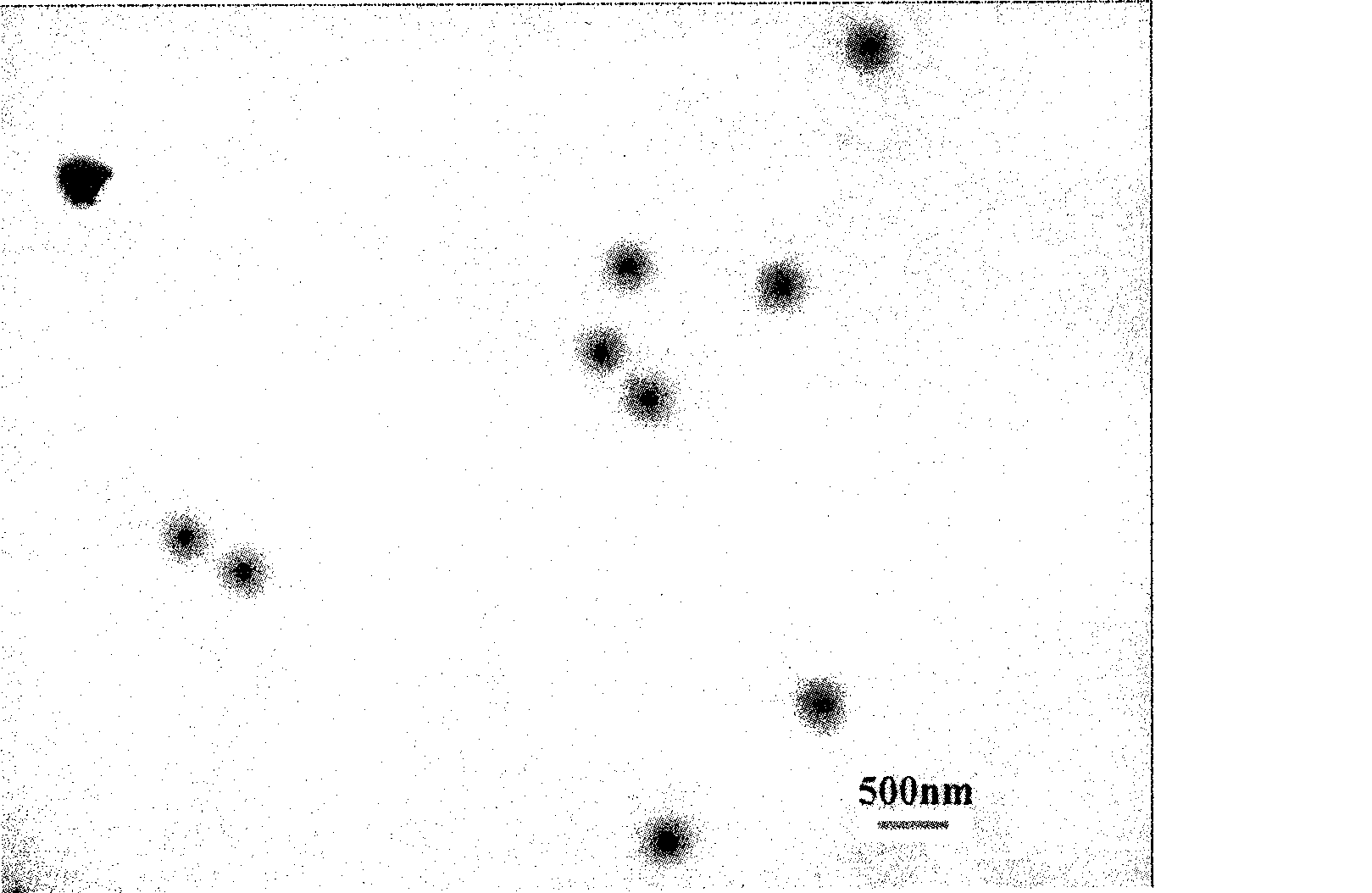
[0028]①Preparation of seed emulsion: at 83°C, in a polymerization vessel, dissolve 0.23g of emulsifier di-isooctyl sulfonate sodium succinate in 200g of water evenly, add 4.96g of silica hydrosol and stir for 10 minutes, then add 36.6g mass ratio is 1.64% initiator potassium persulfate solution, then incubated for 15 to 25 minutes; the nano silicon dioxide of this emulsion is silicon dioxide hydrosol, which can be a commercially available silicon dioxide hydrosol product or as a polishing The silicon dioxide hydrosol that is filtered through a 300-mesh sieve after use has a solid content of 42% to 45% and a particle size of 40 to 95nm.
[0029] ②Pre-emulsification of the shell monomer: Divide 10.8g of methyl methacrylate into 6 parts according to n×0.72g, where n is 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, add 0.5g of acrylic acid to each part, and then Add 106.2g of butyl acrylate to form 6 parts of shell...
Embodiment 2~3
[0047] Preparation:
[0048] 1. the preparation of seed emulsion: with embodiment 1.
[0049] ② Pre-emulsification of the shell monomer: 10.8g methyl methacrylate according to n × 0.72g, n is 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0 (for Example 2) or n = 2.5, 2.5, 2.5 . 20g; then 1.6g of emulsifier diisooctyl sulfonate sodium succinate and 0.04g of tert-dodecyl mercaptan are mixed evenly and divided into 6 equal parts, and they are respectively combined with 6 parts of shell units corresponding to the above The mixture is uniformly mixed to form a pre-emulsion; the quality of methyl methacrylate in each part of pre-emulsion gradually decreases, that is, a negative gradient, and the quality of methyl methacrylate in each part of pre-emulsion is constant, that is, uniform. The change of MMA quality with time is shown in Table 2 during the gradient feeding of Examples 2-3.
[0050] ③Shell layer gradient feeding: at 83°C, the 6 parts of pre-emulsion (20.27g per part) prepared in the previous step are...
Embodiment 4~6
[0055] Preparation:
[0056] 1. the preparation of seed emulsion: with embodiment 1.
[0057] ② Pre-emulsification of the shell monomer: 21.6g methyl methacrylate according to n × 1.44g, n is 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (for Example 4) or n is 5, 4, 3 . Butyl ester is added thereto to form 6 parts of shell monomers, each part of shell monomer quality is 20g; then 1.6g emulsifier diisooctyl sulfonate sodium succinate and 0.04g tert-dodecyl mercaptan are mixed Divide into 6 equal parts after uniformity, and mix them with the corresponding 6 parts of the shell monomer above to form a pre-emulsion. The change of MMA quality with time is shown in Table 3 during the gradient feeding of Examples 4-6.
[0058] ③Shell layer gradient feeding: at 83°C, use the 6 parts of pre-emulsion (20.27g each) prepared in the previous step according to the above n as 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or n as 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0 or n=2.5, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5 Arrangement sequence every 30 minutes in the 241.79g seed emulsion...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com