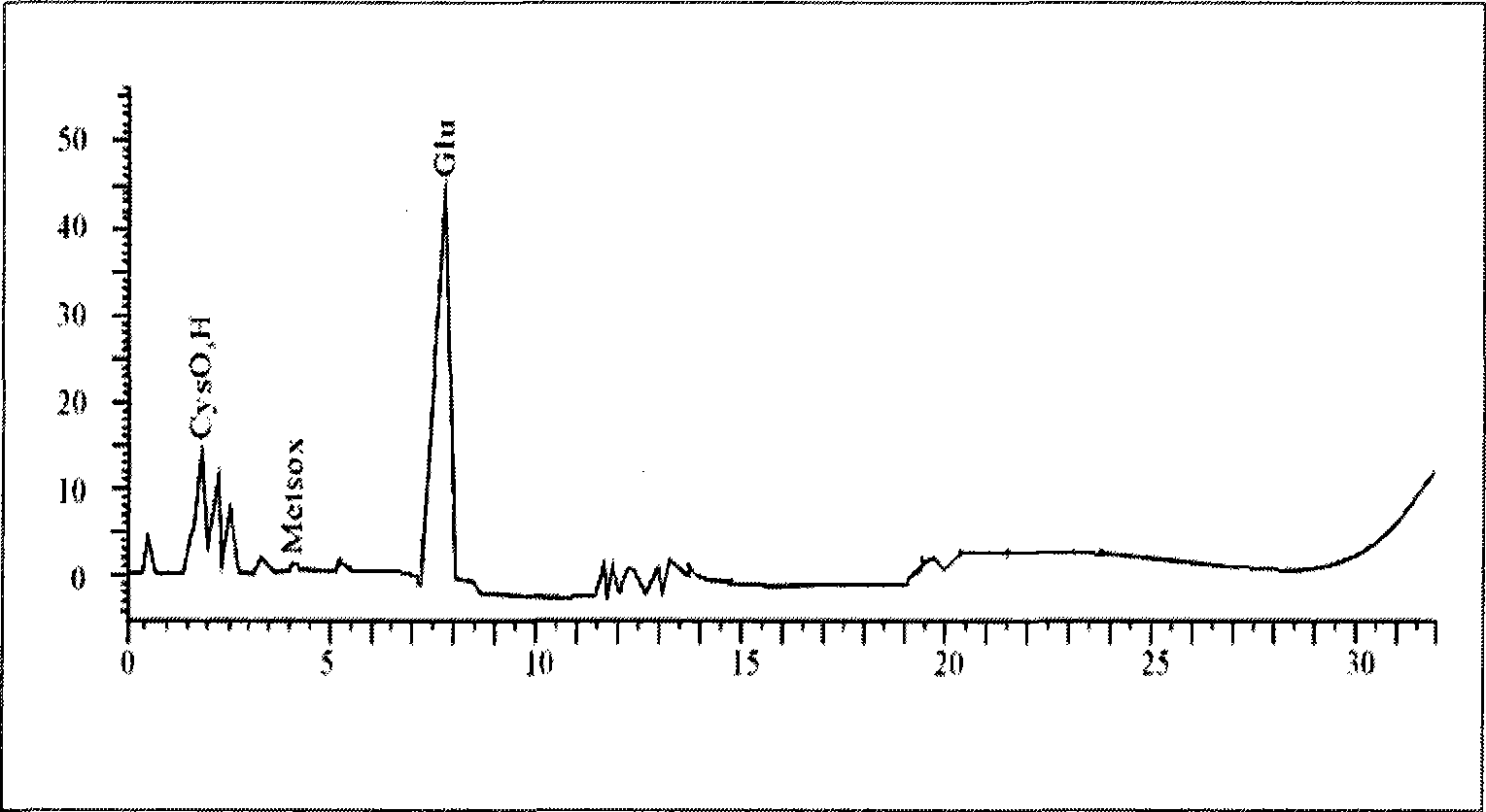
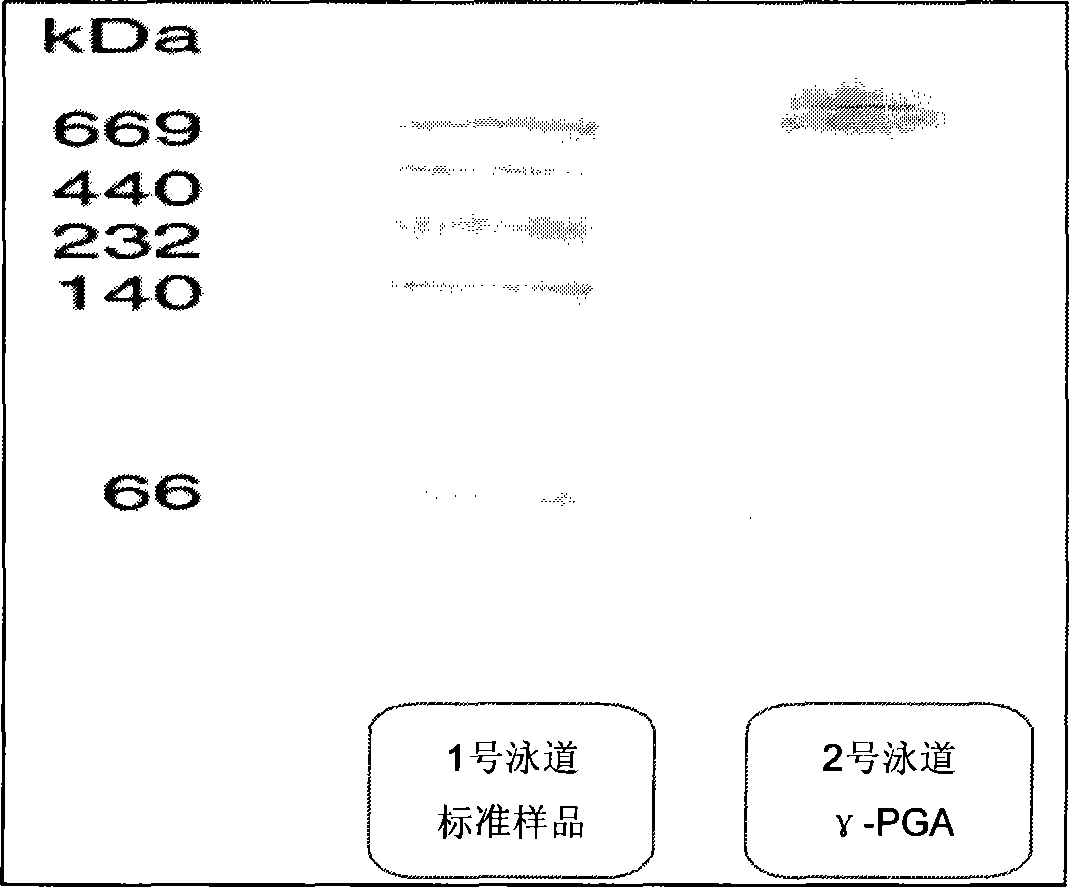
Method for preparing poly-gamma-glutamic acid by fermenting maize raw material Bacillus subtilis
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and glutamic acid, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of difficult removal of bacteria, large dosage, and difficulty of increasing polyglutamic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0070] 1. Seed culture preparation of slant seed medium: peptone 5.0g / L, beef extract 3.0g / L, sodium chloride 3.0g / L, agar 20.0g / L, pH value 7.4, sterilized at 121°C for 20min, cooled to room temperature, Inoculate and incubate at a constant temperature of 35°C for 24 hours.
[0071] Inoculate the seeds on the slant medium into the liquid seed medium, the liquid seed medium formula: peptone 5.0g / L, beef extract 3.0g / L, cornstarch 20.0g / L, glutenic acid 20.0g / L, NaCl3.0g / L, pH 7.4. Sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes, cool to room temperature, inoculate, and culture at 35°C, 200r / min shaker for 24 hours.
[0072] 2 Liquid fermentation Put the mature liquid seeds into the fermentation medium according to the inoculation amount of 8%. The fermentation medium formula: peptone 5.0g / L, beef extract 3.0g / L, corn starch 50.0g / L, gluten acid 50.0g / L L, sodium chloride 3.0g / L, KH 2 PO 40 1.0g / L, MgSO 4 0.5g / L, pH7.4. Sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes, cool to room temperature, inocul...
example 2
[0075] 1 Seed culture Same as Example 1.
[0076] 2 Liquid fermentation Put the mature liquid seeds into the fermentation medium according to the inoculum amount of 8%. The fermentation medium formula: peptone 5.0g / L, beef extract 3.0g / L, corn dextrin 50.0g / L, glutenic acid 50.0g / L, sodium chloride 3.0g / L, KH 2 PO 40 1.0g / L, MgSO 4 0.5g / L, pH7.4. Sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes, cool to room temperature, inoculate, and culture at 35°C, 200r / min shaker for 72 hours.
[0077] 3 Extraction of γ-PGA Same as Example 1.
example 3
[0079] 1 Seed culture Same as Example 1.
[0080] 2. Liquid fermentation Put the mature liquid seeds into the fermentation medium according to the inoculum size of 8%. L, gluten acid 50.0g / L, sodium chloride 2.0g / L, KH 2 PO 40 1.0g / L, MgSO 4 0.5g / L, pH7.4. Sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes, cool to room temperature, inoculate, and culture at 35°C, 200r / min shaker for 72 hours.
[0081] Preparation of corn saccharification solution: Weigh 100g corn flour, add 300mL water, adjust pH to 7.6 with NaOH, heat to 100°C, add 10u α-amylase / g raw material, and stir for 15min. Cool to 62°C, adjust pH to 5.0 with HCl, add 120 u / g of glucoamylase, keep warm for 10 hours, filter to obtain corn saccharification solution, adjust pH to 7.4, and set aside.
[0082] 3 Extraction of γ-PGA Same as Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com