Nanofiber sheet, process for producing the same, and fiber-reinforced composite material
A technology of nanofibers and manufacturing methods, applied in the field of nanofiber non-woven fabrics and its manufacturing, can solve the problem of simultaneously achieving high transparency, low linear thermal expansion coefficient, high Young's modulus, and linear thermal expansion coefficient of fiber-reinforced composite materials Large size, poor heat resistance of nanofibers, etc., to achieve high strength, excellent heat resistance, and low specific gravity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0357] Degreasing of radiata pine-derived wood flour (longer diameter: 500 μm, longer diameter / shorter diameter ratio: 10, moisture content: 5% by weight) with a mixture of ethanol and benzene (ethanol:benzene = 1 volume:2 volume) For processing, put 10 g of the wood powder into a solution of 600 ml of distilled water, 4 g of sodium chlorite, and 0.8 ml of glacial acetic acid, and heat it for 1 hour in a hot water bath at 70° C. to 80° C. with stirring from time to time. After 1 hour, without cooling, 4 g of sodium chlorite and 0.8 ml of glacial acetic acid were added for repeated treatment. Do this 5 times.
[0358] This is followed by washing with about 5 L of cold water and about 500 ml of acetone.
[0359] Next, 10 g of the wood flour was immersed in a 5% by weight potassium hydroxide aqueous solution, left overnight at room temperature, and then recovered by suction filtration, and washed with about 2 L of water until neutral.
[0360] After such operation, the wood flo...
Embodiment 2
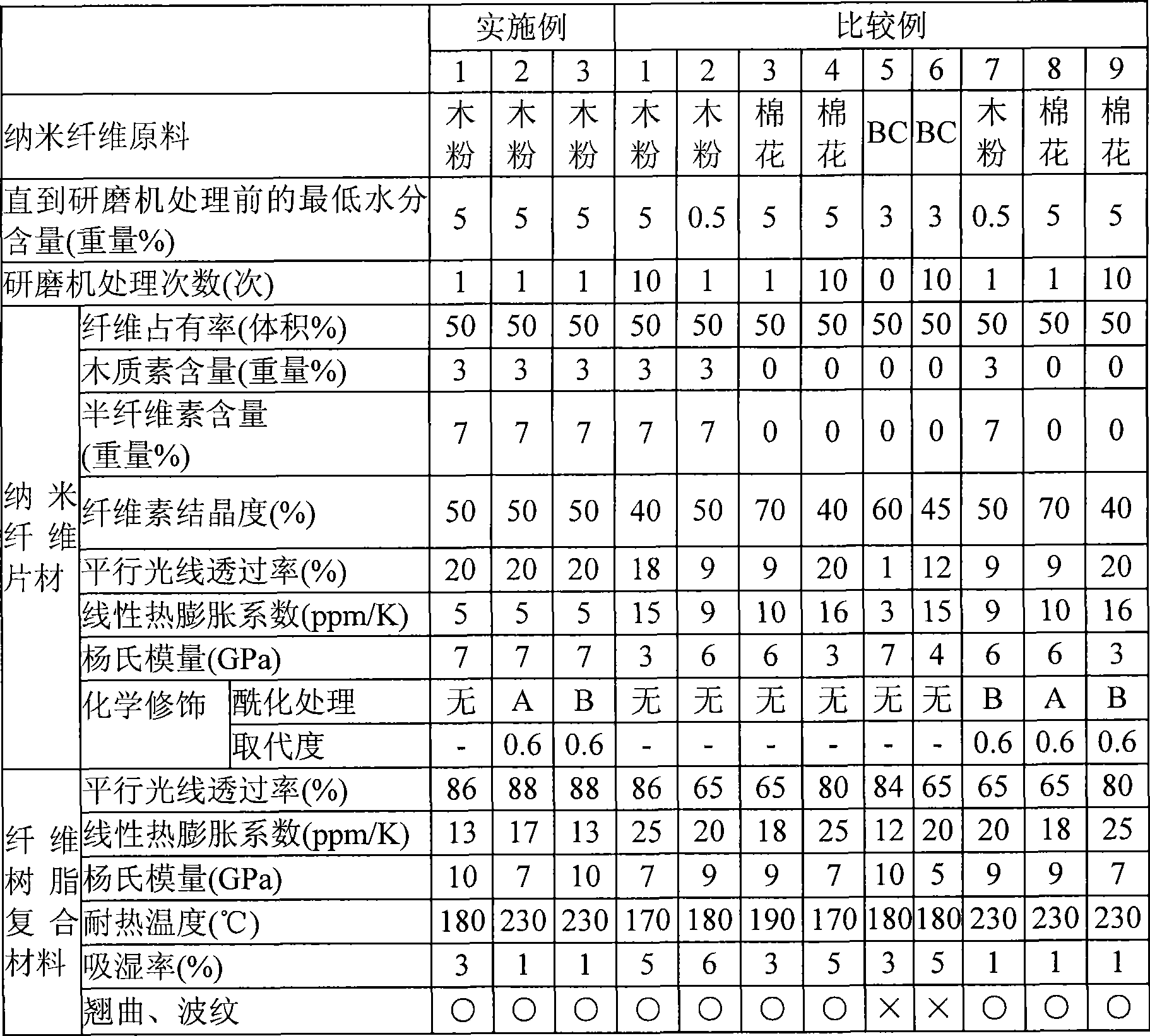
[0388] In Example 1, in the manufacture of the nanofiber sheet, the following acetylation treatment A was performed on the obtained water-containing nanofiber sheet, and the manufacture of the nanofiber sheet and the fiber For the manufacture of reinforced composite materials, the measurement results of various physical properties are listed in Table 2.
[0389]
[0390]1) Cold press the water-containing nanofiber sheet (10cm×10cm) at room temperature at 2MPa for 1 minute to remove water and form a sheet with a thickness of 1mm.
[0391] 2) The pressed nanofiber sheet was immersed in acetone to completely remove the water inside the nanofiber sheet. The obtained solvent-substituted nanofiber sheet was hot-pressed at 110° C. and 2 MPa for 3 minutes.
[0392] 3) 3 mL of butyric anhydride, 40 mL of acetic acid, 50 mL of toluene, and 0.2 mL of 60% by weight perchloric acid were added to a detachable flask to prepare a reaction solution.
[0393] 4) Dip the nanofiber sheet prod...
Embodiment 3
[0396] In Example 1, in the manufacture of the nanofiber sheet, the following acetylation treatment B was performed on the obtained water-containing nanofiber sheet, and the manufacture of the nanofiber sheet and the fiber For the manufacture of reinforced composite materials, the measurement results of various physical properties are listed in Table 2.
[0397]
[0398] 1) The water-containing nanofiber sheet (10cm×10cm) was hot-pressed at 120° C. and 2 MPa for 4 minutes to completely remove the water to form a dry nanofiber sheet with a thickness of 40 μm.
[0399] 2) 3 mL of butyric anhydride, 40 mL of acetic acid, 50 mL of toluene, and 0.2 mL of 60% by weight perchloric acid were added to a detachable flask to prepare a reaction solution.
[0400] 3) The nanofiber sheet produced in 2) was immersed in the reaction solution prepared in 3), and reacted at room temperature for 1 hour.
[0401] 4) After the reaction is terminated, the obtained acetylated nanofiber sheet is w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com