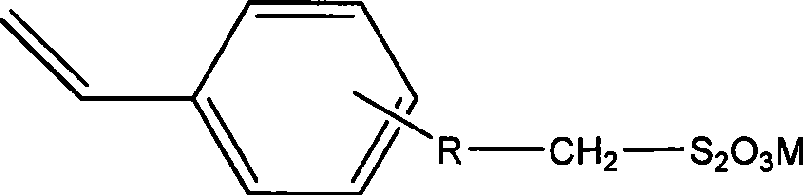
Sulfhydryl chain transfer hyperbranched polymerization process
A polymerization method and chain transfer technology, applied in the field of novel thiol chain transfer hyperbranched polymerization method, can solve the problems of complex and difficult structure of AB branched monomers, restricting the development of hyperbranched polymers, low monomer universality, etc. The branched monomers are simple and easy to obtain, have strong applicability, and control the degree of branching.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0023] 0.0253 g (0.1 mmol) (4-vinyl)-benzyl sodium thiosulfate, 0.0328 g (0.2 mmol) AIBN, and 2.0830 g (20 mmol) styrene were successively added to a 25 mL round bottom flask. Add 2 mL of DMSO as the reaction solvent. Close the polymerization system, and remove oxygen and other polymerization inhibitors in the system by freezing and pumping air with liquid nitrogen. Put it into a constant temperature oil bath at 70°C, react for 9 hours, and precipitate twice with a mixture of methanol and water (volume ratio 3:1), collect the solid and dry it in a vacuum oven at 40°C. The weight-average molecular weight of the product measured by GPC-MALLS is 5.10×10 4 , the molecular weight distribution is 1.569. The intrinsic viscosity is 26.5wmL / g. The alpha value was 0.540 ± 0.006. The glass transition temperature of the product was determined by differential scanning calorimetry to be 99.34°C.
Embodiment 3
[0025] 0.0506g (0.2mmol) (4-vinyl)-benzyl sodium thiosulfate, 0.0328g (0.2mmol) AIBN, and 2.0830g (20mmol) styrene were successively added to a 25mL round bottom flask. Then 2 mL of DMF was added as the reaction solvent. Close the polymerization system, and remove oxygen and other polymerization inhibitors in the system by freezing and pumping air with liquid nitrogen. Put it into a constant temperature oil bath at 70°C, react for 9 hours, and precipitate twice with a mixture of methanol and water (volume ratio 3:1), collect the solid and dry it in a vacuum oven at 40°C. The weight-average molecular weight of the product measured by GPC-MALLS is 6.57×10 4 , the molecular weight distribution is 1.781. The intrinsic viscosity is 27.5wmL / g. The alpha value was 0.580 ± 0.005. The glass transition temperature of the product was measured with a differential scanning calorimeter to be 99.17°C.
Embodiment 4
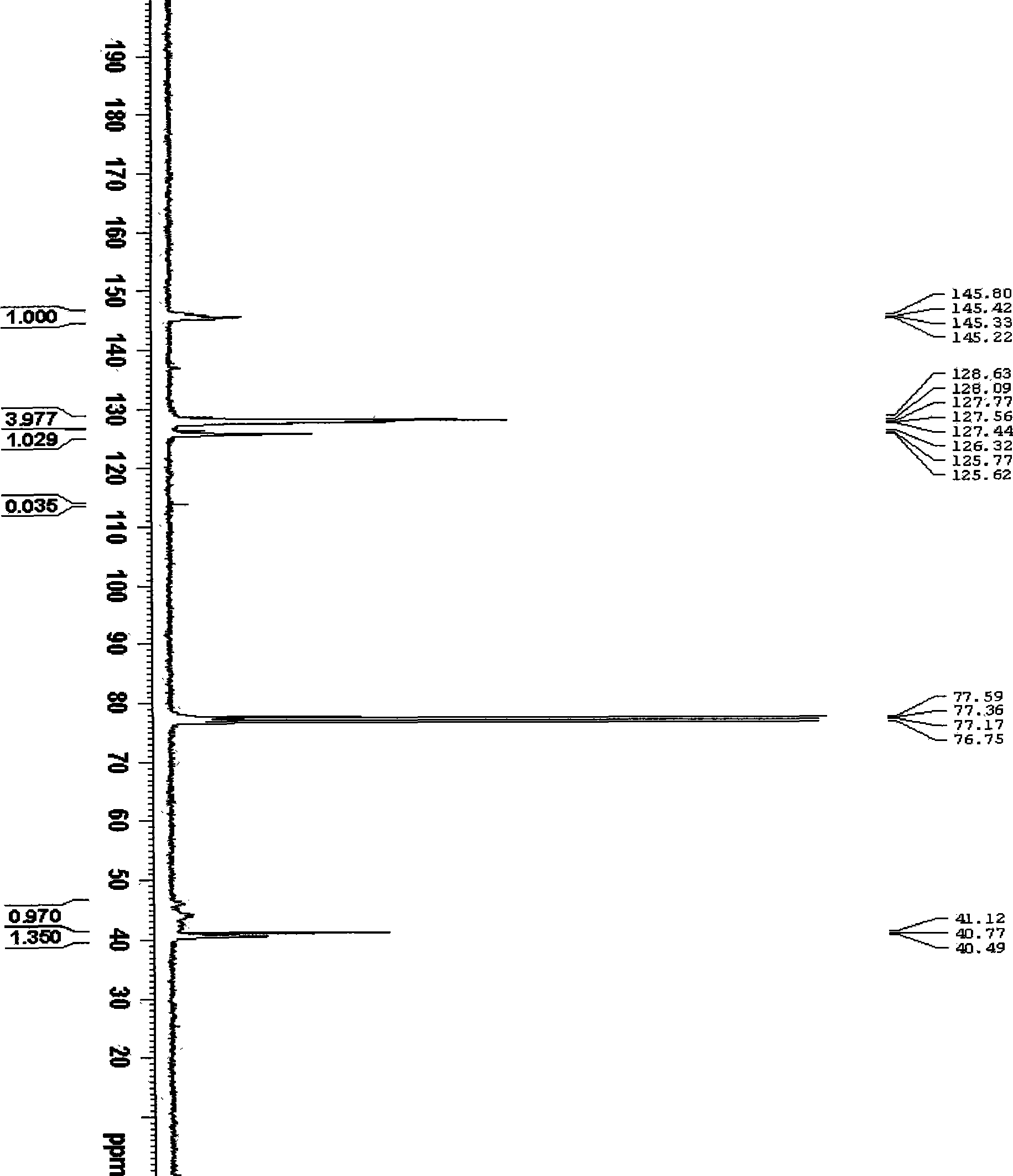
[0027] 0.0759g (0.3mmol) (4-vinyl)-benzyl sodium thiosulfate, 0.0328g (0.2mmol) AIBN, and 2.0830g (20mmol) styrene were successively added to a 25mL round bottom flask. Then 2 mL of DMF was added as the reaction solvent. Close the polymerization system, and remove oxygen and other polymerization inhibitors in the system by freezing and pumping air with liquid nitrogen. Put it into a constant temperature oil bath at 70°C, react for 9 hours, and precipitate twice with a mixture of methanol and water (volume ratio 3:1), collect the solid and dry it in a vacuum oven at 40°C. The weight-average molecular weight of the product measured by GPC-MALLS is 6.89×10 4 , the molecular weight distribution is 2.024. The intrinsic viscosity was 25.9wmL / g. The alpha value was 0.574 ± 0.006. The glass transition temperature of the product measured by differential scanning calorimetry was 94.88°C. hyperbranched polymer 13 C-NMR spectrum see figure 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com