Zinc-rich yeast with high biomass, breeding selection method and application thereof
A high-biomass, zinc-rich yeast technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, applications, etc., can solve the large difference in zinc ion absorption and transformation ability, unfavorable industrial production, and zinc resistance. problem, to achieve the effect of broad practical application prospects, strong practicability, and simple methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Example 1, Breeding of high biomass zinc-rich yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) F-090428X
[0017] The breeding of high biomass zinc-rich yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) (F-090428X) is divided into the following steps:
[0018] 1) According to the determination of the tolerance of yeast to zinc sulfate, the initial screening was carried out, and the tolerance of brewer's yeast on the wort solid medium containing 5000 μg / ml, 6000 μg / ml, 8000 μg / ml, and 10000 μg / ml of gradient zinc ion concentration was measured. For the growth situation, 2 strains were selected which grew well on the wort solid medium containing 10000 μg / ml zinc ions.
[0019] 2) Determination of the cell biomass and cell zinc content of a strain obtained from the primary screening cultured in wort liquid medium containing 10000 μg / ml zinc ions. Through domestication and screening, a strain (F-090415) with a dry cell zinc content of 35.5 mg / g and a dry cell weight of 9.2 g / L was obtained.
[0020] 3) I...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2, Optimal culture conditions of high biomass zinc-rich yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) F-090428X
[0023] 1) The culture conditions of high-biomass zinc-rich yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) F-090428X (including medium components, zinc salt concentration, medium pH value, aeration, Inoculum size and fermentation time, etc.) experiment, by culture condition experiment, determined optimal culture condition: wort+0.3% urea culture medium, total sugar content is 5%-20%, zinc salt (such as zinc sulfate) concentration in the culture medium 10000-15000 μg / ml, the pH of the culture medium is 4.5-5.5, the inoculum size is 10%-30%, and the culture is stirred at 28°C-30°C for 16-48h.
[0024] 2) Fermentation and cultivation of zinc-rich yeast with high biomass and high zinc content under optimized fermentation conditions: under optimized conditions, the dry cell weight per liter of culture medium can reach more than 12g, and the zinc content per gram of dry cells can rea...
Embodiment 3
[0025] Embodiment 3, the production of high biomass zinc-rich yeast
[0026] The production process of zinc-rich yeast products with high biomass and high zinc content includes:
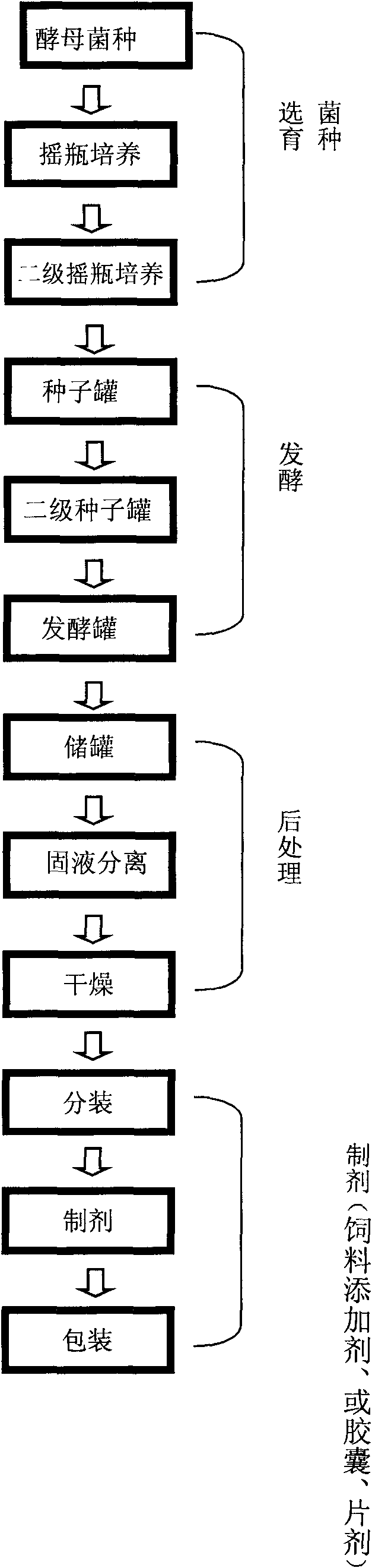
[0027] Inclined surface bacteria → first-level shake flask strain cultivation → second-level shake flask seed cultivation → seed tank → second-level liquid seed tank → fermentation tank → storage tank → solid-liquid separation → freeze-drying or spray drying → (or use plate and frame pressing Or centrifuge to collect zinc-enriched yeast cells → pulverize) → zinc-enriched with high biomass and high zinc-enriched content → sub-package → preparation (feed additive, or capsule, tablet, etc.) → packaging.
[0028] Below the production process is further described as follows:
[0029] (1) Bacteria culture on inclined plane
[0030] High-biomass zinc-rich yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) F-090428X was inoculated on the wort solid slant with a total sugar content of 16% and a zinc salt (such as zinc sulfate)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com