Preparation method of carbonic rare earth-ferrum, cobalt and silicon compound with NaZn1 structure
A technology of iron-cobalt-silicon and compound, which is applied in the field of preparation of carbon-containing rare earth-iron-cobalt-silicon compound, which can solve the problems of uneven composition, fast cooling speed, difficulty in obtaining bulk materials, etc., and achieve shortened annealing time and stable performance reliable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
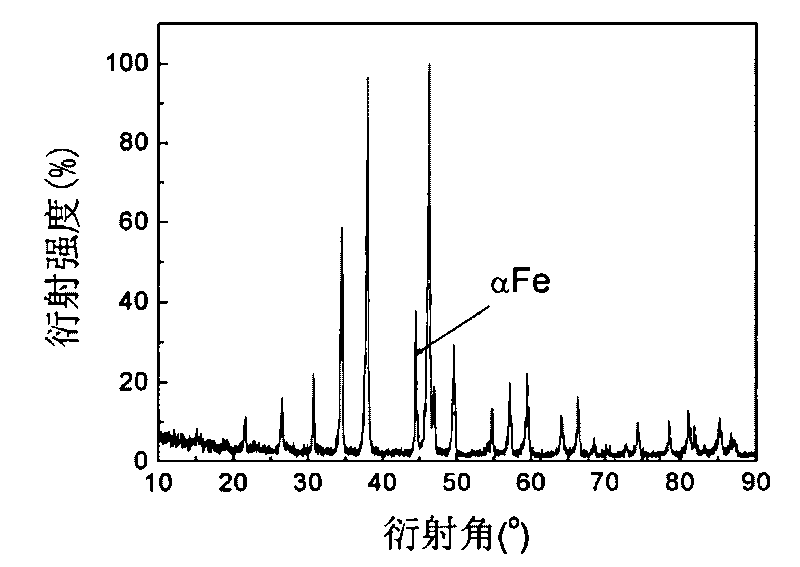
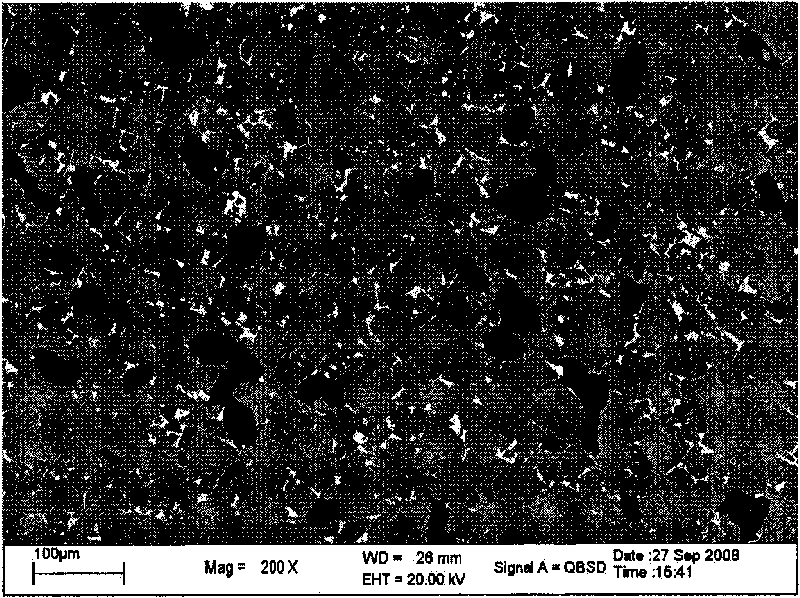
[0052] Raw materials with the same composition as Comparative Example 1 are distributed according to the chemical composition, the rare earth metal is added in excess of 10% atomic percentage, and the Si element is added in excess of 1% atomic percentage; put it into a vacuum induction furnace and evacuate to 2×10 -1 Above Pa, argon gas with a pressure of -0.05MPa is introduced, the melting temperature is controlled at 150°C above the melting point, and the melting time is controlled at 15 minutes. In the 30mm cylindrical mold, a master alloy with uniform composition was obtained. The metallographic diagram of the master alloy is shown in Figure 4 , composed of dendrites, the backscattering pattern of the sample is shown in Figure 5 , it can be known that the dendrite is α-Fe phase, and the interdendrite is non-NaZn 13 The rare earth-containing phase of the structure, no 1:13 phase is formed. The compound obtained by smelting was annealed at 1080°C for 2 days, and then di...
Embodiment 2
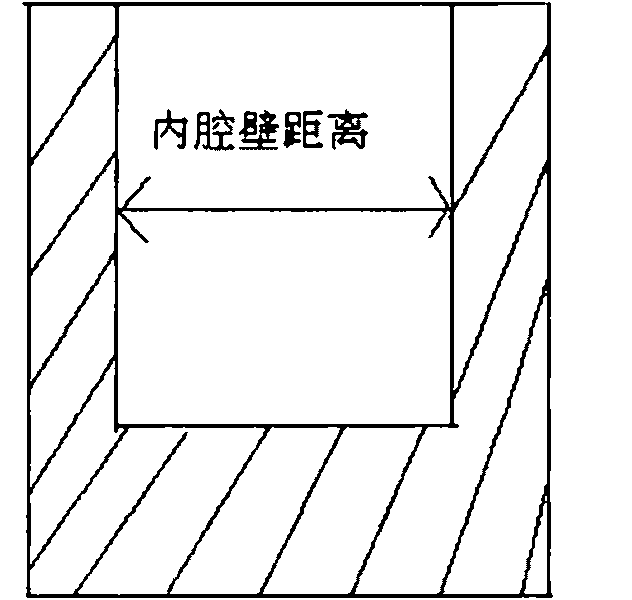
[0058] Raw materials such as La, Pr, Fe, Si, Co, C, etc. are classified according to chemical composition La 0.6 PR 0.4 Fe1 0.8 co 0.7 Si 1.5 C0.3 Ratio, the rare earth metal La is added in excess of 10% atomic percentage, the rare earth metal Pr is excessively added in 5% atomic percentage, and the Si element is added in excess of 1% atomic percentage; put it into a vacuum induction furnace and evacuate to 2×10 -1 Above Pa, argon gas with a pressure of -0.05MPa is introduced, the melting temperature is controlled at 200°C above the melting point, and the melting time is controlled at 10 minutes. The distance between the inner walls was 5 mm, resulting in a homogeneous compound. The compound obtained after smelting was annealed at 1100°C for 2 days, and then directly put into ice water for rapid quenching. Using SQUID to measure the change of magnetization curve with temperature, such as Figure 9 shown. The magnetization curve of this material is devoid of hysteresis a...
Embodiment 3
[0061] La, Fe, Si, Co, C and other raw materials are classified according to chemical composition La 0.9 Ce 0.1 Fe 10.7 co 0.9 Si 1.4 C 0.4 Ratio, the rare earth metal La is added in excess of 10% atomic percentage, the rare earth metal Ce is added in excess of 7% atomic percentage, and the Si element is added in excess of 1% atomic percentage; put it into a vacuum induction furnace and evacuate to 2×10 -1 Above Pa, argon gas with a pressure of -0.02MPa is introduced, the melting temperature is controlled at 200°C above the melting point, and the melting time is controlled at 10 minutes. After melting, it is poured into a copper cylindrical mold with a diameter of 20mm and a wall thickness of 5mm. , to obtain a homogeneous compound. The compound obtained by smelting was annealed at 1080° C. for 3 hours, 6 hours, 12 hours, and 2 days in sequence, and then directly put into ice water for rapid quenching. The metallographic photos of the samples obtained at each annealing t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com