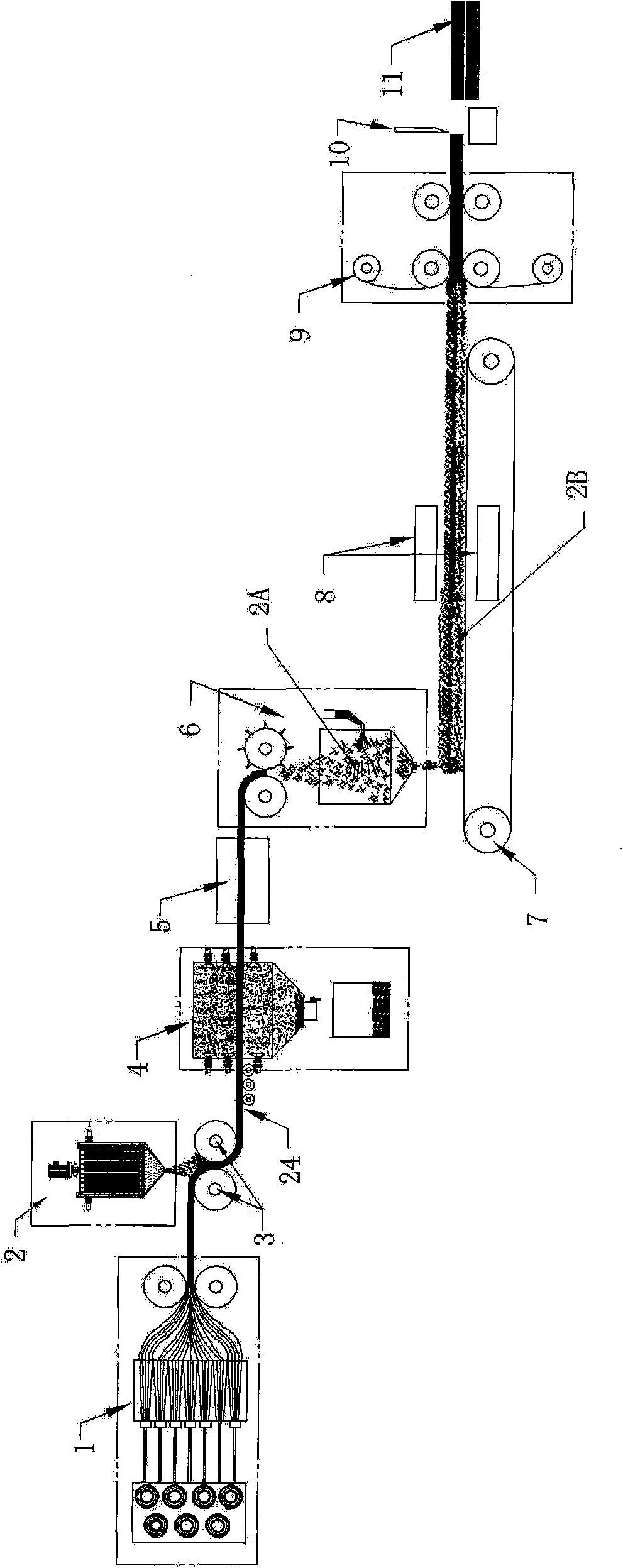
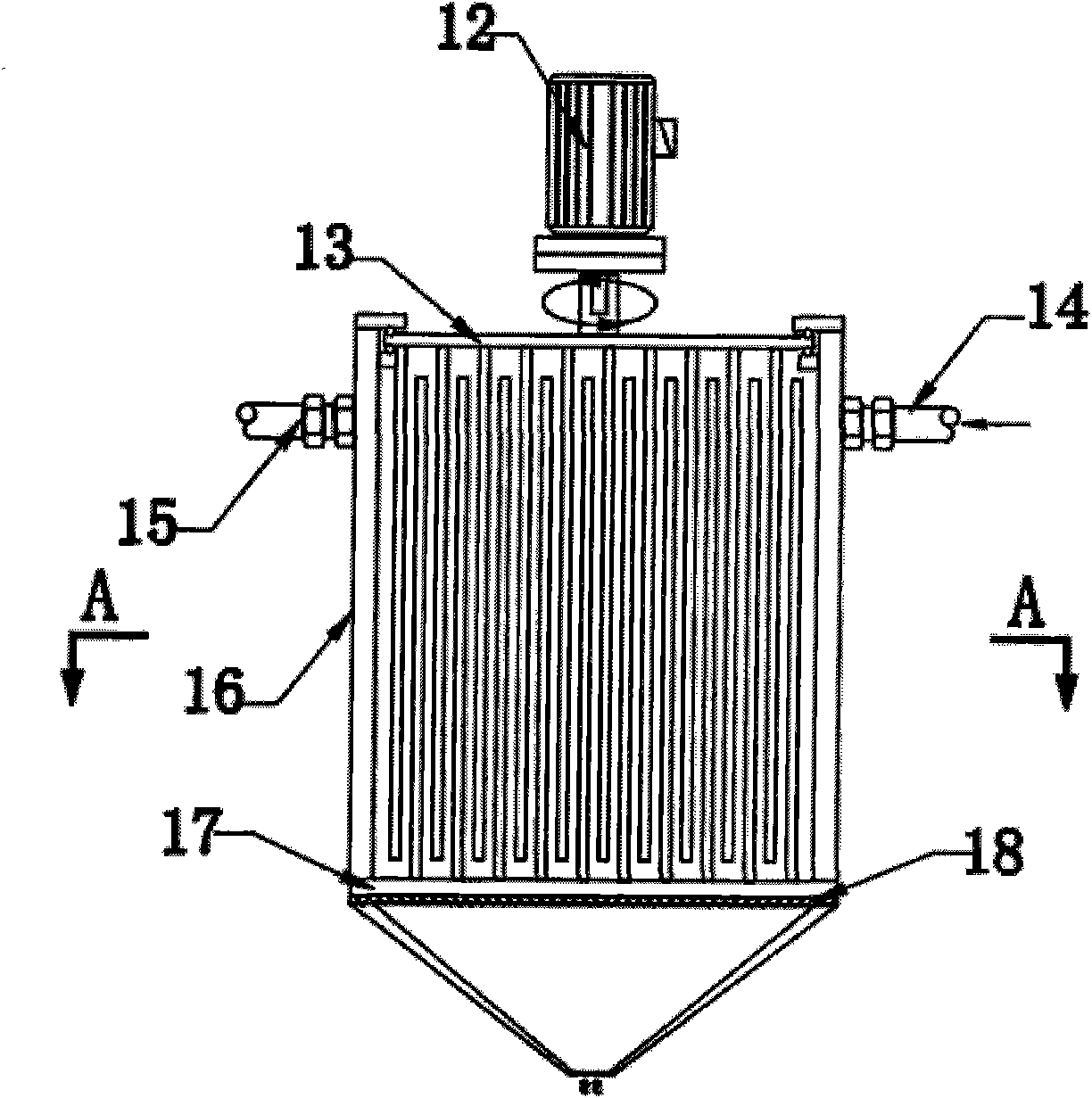
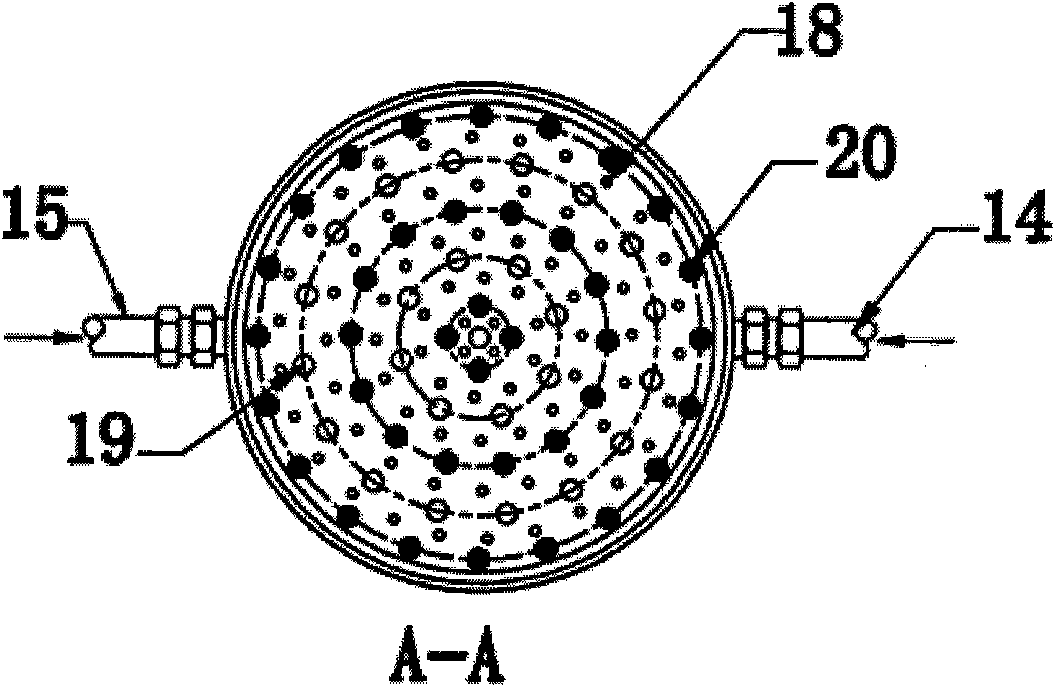
Method for manufacturing glass fibre reinforced thermoplastic sheet
A technology that enhances thermoplasticity and glass fiber. It is applied in the field of interior parts of automobiles and other vehicles. It can solve the problems of weakening the strength of the board, large differences in specific gravity, and poor uniformity of the base mat, so as to increase the flame retardant effect and improve the adhesion. , the effect of reducing the content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Materials: 200kg of alkali-free glass fiber (untwisted roving, density 2.35g / cm3, diameter 12μm), 150#PP powder 100kg (density 0.91g / cm3, 60 mesh to 120 mesh), polyethylene (PE) powder 20kg (density 0.95g / cm3, 60 mesh to 120 mesh);
[0047] Wetting-related auxiliary agents: stearic acid 35%, diluent 64.5%, silane coupling agent (KH550) 0.5%.
[0048] Dynamic powder adhesion aid: 150# polypropylene (PP) powder 20kg (diameter 0.1nm ~ 50μm), flame retardant (nitrogen phosphorus combination agent) 5kg, stabilizer 0.5kg.
[0049] Slitting air mixing aids: flame retardant (nitrogen and phosphorus combination agent) 10kg, stabilizer 1.5kg, dispersant 3.0kg, lubricant 10Kg, bulking agent 6kg;
[0050] According to the design and process requirements of the board, the ratio of glass fiber, polypropylene (PP) powder and related additives in the board is 55:40:5, and the width of the board is 1800mm.
[0051] The alkali-free glass fiber rolls are unwound and spun to form uniform...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The process parameters remain unchanged, only the dynamic powder adhesion flame retardant is canceled, and the length of the glass fiber is 130mm for splitting and air mixing.
[0059] Materials: 200kg of alkali-free glass fiber (untwisted roving, density 2.35g / cm3, diameter 12μm), 150#PP powder 100kg (density 0.91g / cm3, 60 mesh to 120 mesh), polyethylene (PE) powder 20kg (density 0.95g / cm3, 60 mesh to 120 mesh);
[0060] Wetting-related auxiliary agents: stearic acid 35%, diluent 64.5%, silane coupling agent (KH550) 0.5%.
[0061] Dynamic powder adhesion aid: 150# polypropylene (PP) powder 20kg (diameter 0.1nm ~ 50μm), stabilizer 0.5kg.
[0062] Slitting air mixing aids: flame retardant (nitrogen and phosphorus combination agent) 10kg, stabilizer 1.5kg, dispersant 3.0kg, lubricant 10Kg, bulking agent 6kg;
[0063] According to the design and process requirements of the board, the ratio of glass fiber, polypropylene (PP) powder and related additives in the board is 55...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The production process parameters remain unchanged, only the ratio of glass fiber to polypropylene (PP) and related additives in the board is adjusted to 60:35:5, and the length of the glass fiber is 90mm for splitting and air mixing.
[0072] Materials: 200kg of alkali-free glass fiber (untwisted roving, density 2.35g / cm3, diameter 12μm), 150#PP powder 100kg (density 0.91g / cm3, 60 mesh to 120 mesh), polyethylene (PE) powder 20kg (density 0.95g / cm3, 60 mesh to 120 mesh);
[0073] Wetting-related auxiliary agents: stearic acid 35%, diluent 64.5%, silane coupling agent (KH550) 0.5%.
[0074] Dynamic powder adhesion aid: 150# polypropylene (PP) powder 20kg (diameter 0.1nm ~ 50μm), flame retardant (nitrogen phosphorus combination agent) 5kg, stabilizer 0.5kg.
[0075] Slitting air mixing aids: flame retardant (nitrogen and phosphorus combination agent) 10kg, stabilizer 1.5kg, dispersant 3.0kg, lubricant 10Kg, bulking agent 6kg;
[0076]According to the design and process ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com