Processing for recovering low-grade molybdenum oxide concentrate through wet process
A low-grade, molybdenum oxide technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve problems such as difficult utilization of molybdenum oxide ore
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
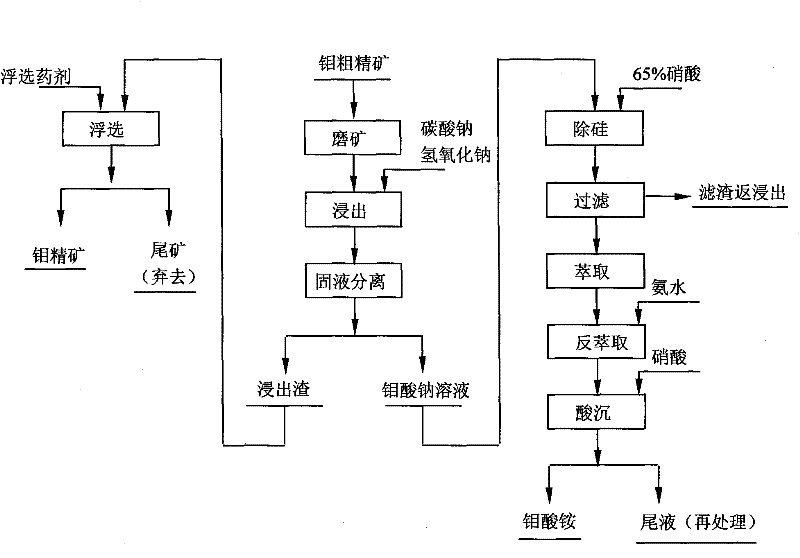
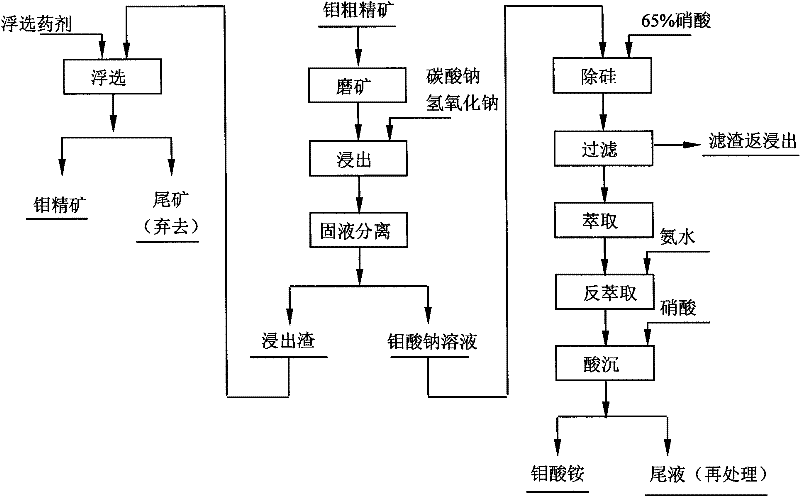
[0015] The process of wet recovery of low-grade molybdenum oxide concentrate, such as figure 1 As shown, the steps include:
[0016] 1) Molybdenum coarse concentrate is ground to make the fineness reach -200 mesh and the content is not less than 90%, and then add leaching agents sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide, so that sodium carbonate accounts for 10% of the total weight of dry ore and agents, hydrogen Sodium oxide accounts for 5%; adjust the pulp concentration to 30%, and then put the pulp into the reaction kettle for leaching for 2 hours at a leaching temperature of 80°C; the leached pulp is filtered and washed by a filter press to achieve solid-liquid separation and obtain molybdic acid Sodium solution and leach residue.
[0017] 2) Use the flotation process of one rough, five fine and one sweep to flotation the leached slag to produce molybdenum concentrate. The flotation reagents required for each ton of leached slag are: 10g of sodium cyanide, 300g of water glass...
Embodiment 2
[0020] The process of wet recovery of low-grade molybdenum oxide concentrate, such as figure 1 As shown, the steps include:
[0021] 1) The molybdenum coarse concentrate is ground to make the fineness reach -200 mesh and the content is not less than 90%, and then add the leaching agent sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide, so that the sodium carbonate accounts for 20% of the total weight of the dry ore and the agent, hydrogen Sodium oxide accounts for 1%; adjust the pulp concentration to 50%, then put the pulp into the reaction kettle for leaching for 1 hour, and the leaching temperature is 100°C; the leached pulp is filtered and washed by a filter press to achieve solid-liquid separation and obtain molybdic acid Sodium solution and leach residue.
[0022] 2) Use the flotation process of one rough, five fine and one sweep to flotation the leached slag to produce molybdenum concentrate. The flotation reagents required for each ton of leached slag are: 30g of sodium cyanide, 6...
Embodiment 3
[0025] The process of wet recovery of low-grade molybdenum oxide concentrate, such as figure 1 As shown, the steps include:
[0026] 1) The molybdenum coarse concentrate is ground to make the fineness reach -200 mesh and the content is not less than 90%, and then add the leaching agent sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide, so that the sodium carbonate accounts for 15% of the total weight of the dry ore and the agent, hydrogen Sodium oxide accounts for 3%; adjust the pulp concentration to 40%, and then put the pulp into the reaction kettle for leaching for 1.5 hours at a leaching temperature of 90°C; the leached pulp is filtered and washed by a filter press to achieve solid-liquid separation and obtain molybdenum Sodium acid solution and leaching residue.
[0027] 2) Use the flotation process of one rough, five fine and one sweep to flotation the leaching slag to produce molybdenum concentrate. The flotation reagents required for each ton of leaching slag are: 20g of sodium c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com