Method for remediating pollution of nitrate nitrogen in underground water
A technology for nitrate nitrogen and groundwater, applied in water pollutants, contaminated groundwater/leachate treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in inflammability and explosion, low ammonia nitrogen generation ratio, and increased cost. Achieve low-cost and high-efficiency treatment effects, low ammonia nitrogen generation ratio, and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
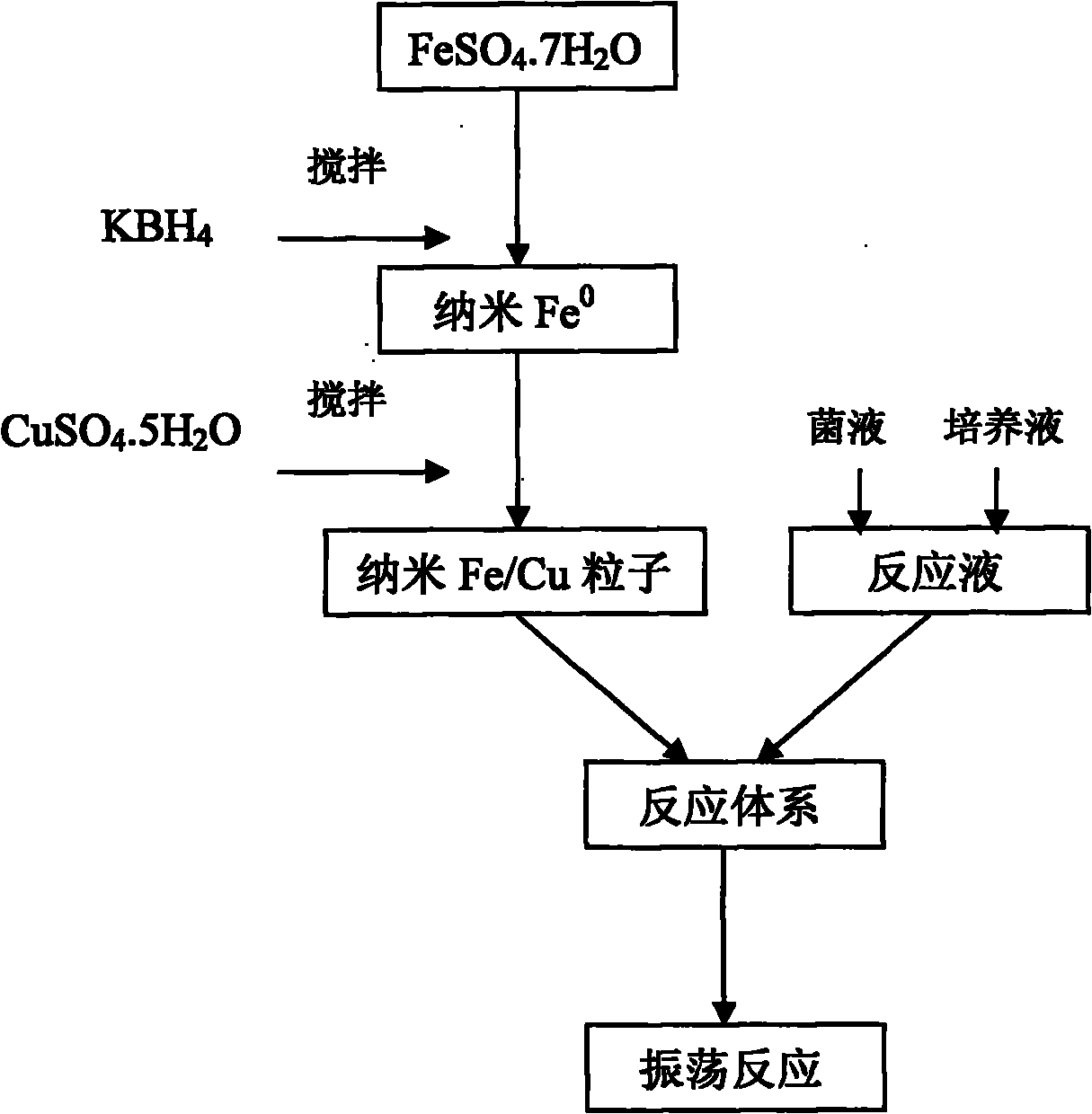
[0033] (1) Nano Fe 0 Particle preparation
[0034] FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was dissolved in ethanol-water system with PEG-4000 as dispersant, and argon gas was passed through to remove oxygen, and then KBH was added 4 Aqueous solution, stirring while adding dropwise, continue to stir and react for 40-60min after the dropwise addition, to obtain black nano-Fe 0 solution; nano-Fe was selected by magnetic separation 0 Particles, washed with deoxygenated deionized water;
[0035] (2) Preparation of Nano-Fe / Cu Particles
[0036] CuSO 4 ·5H 2 The aqueous solution of O was added to the nano-Fe 0 In the particles, continue to stir and react to prepare nano-Fe / Cu particles;
[0037] (3) Preparation of reaction solution
[0038] Adding deionized water to dilute the denitrifying bacteria liquid and the culture liquid to prepare the reaction liquid;
[0039] (4) Preparation of reaction system
[0040] Deoxidize the reaction solution and introduce it into the nano-Fe / Cu particles to pre...
Embodiment 1
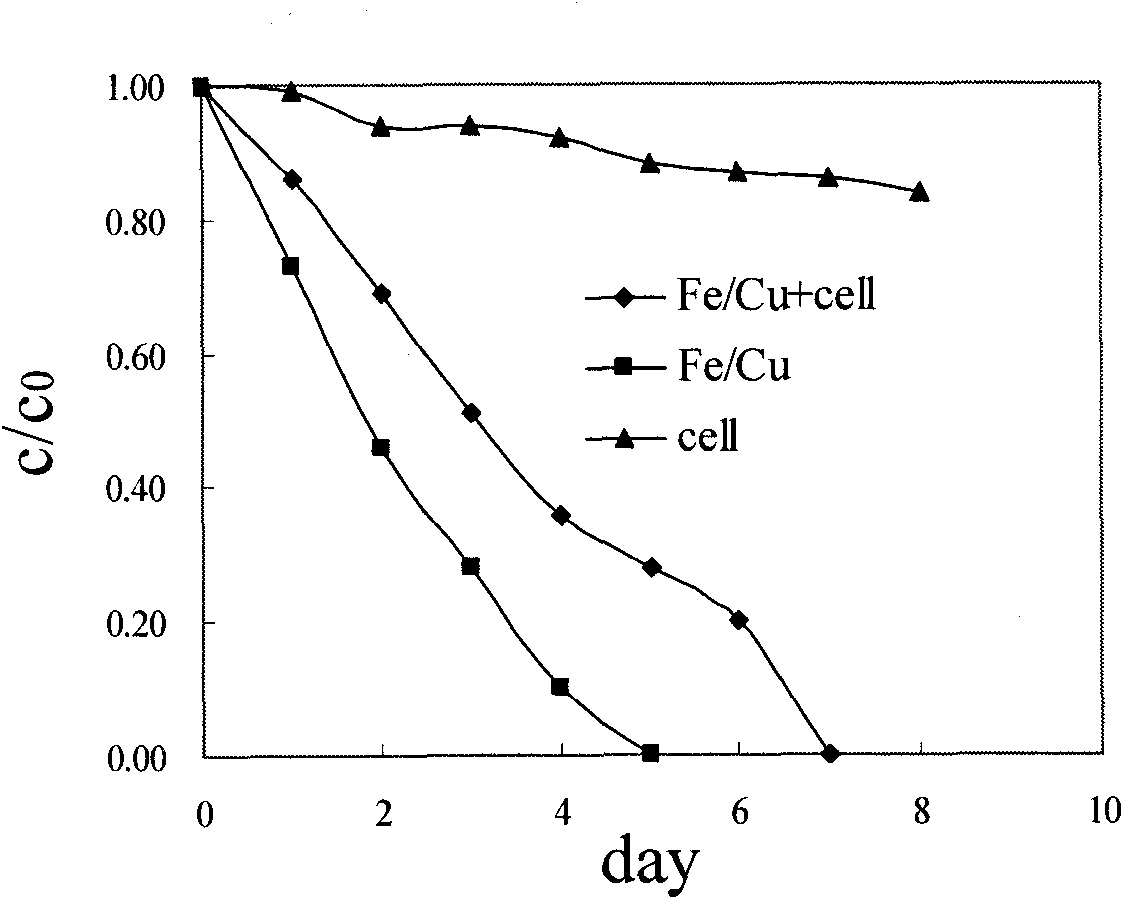
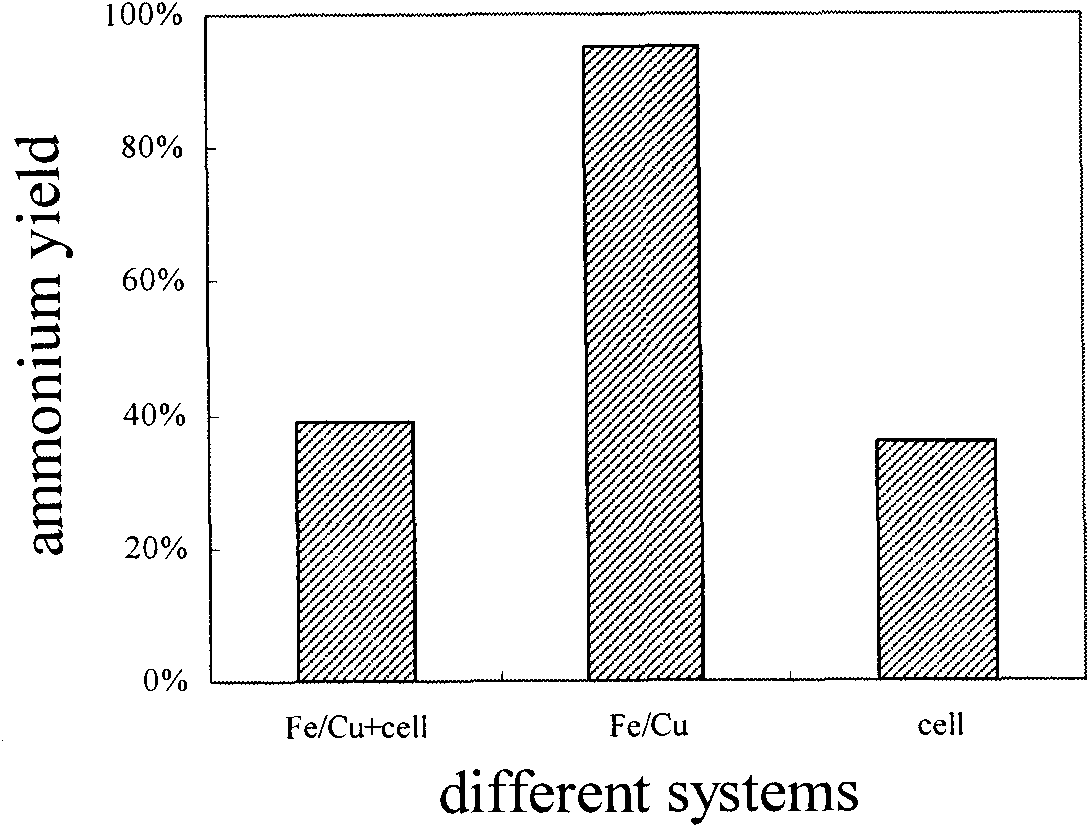
[0050]The method is used to remove nitrate nitrogen with a concentration of 30 mg / L in groundwater. Among them, the FeSO used in the preparation of nano-Fe / Cu particles 4 ·7H 2 O and KBH 4 The molar ratio of PEG-4000 and FeSO is 1:3 4 ·7H 2 The O mass ratio is 1:2, the ethanol-water volume ratio is 1:4, the stirring reaction time is 50min, the dosage of nano-Fe / Cu particles is 0.40g / L (Cu loading is 10%), and then the reaction Nitrifying bacteria solution (OD 420 =0.0027): culture solution: the volume ratio of deionized water is 5:2:13, carry out simple physical mixing, seal, adjust the solution pH=8.6, carry out oscillation reaction, its temperature is controlled at 30 ℃, and rotating speed is 140rpm. Regular sampling, analysis of reactant NO 3 - -N and product NH 4 + -N content changes with time. The analysis method is: NO 3 - -N: UV spectrophotometry; NH 4 + -N: Nessler's reagent spectrophotometry. Analysis results such as figure 2 and image 3 As shown, i...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The method is used to remove nitrate nitrogen with a concentration of 50 mg / L in groundwater. Among them, the FeSO used in the preparation of nano-Fe / Cu particles 4 ·7H 2 O and KBH 4 The molar ratio of PEG-4000 and FeSO is 1:5 4 ·7H 2 The mass ratio of O is 1:1, the volume ratio of ethanol to water is 2:5, the stirring reaction time is 40min, the dosage of nano-Fe / Cu particles is 0.57g / L (different Cu loading), and then denitrifying bacteria are added Bacterial solution (OD 420 =0.0046): the volume ratio of culture solution: deionized water is 7:2:13, simple physical mixing is carried out, sealed, the pH of the solution is adjusted to 7.5, and the oscillation reaction is carried out. The temperature is controlled at 30°C and the rotating speed is 150rpm. Regular sampling, analysis of reactant NO 3 - -N and product NH 4 + -N content changes with time. The analysis method is: NO 3 - -N: UV spectrophotometry; NH 4 + -N: Nessler's reagent spectrophotometry. A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com