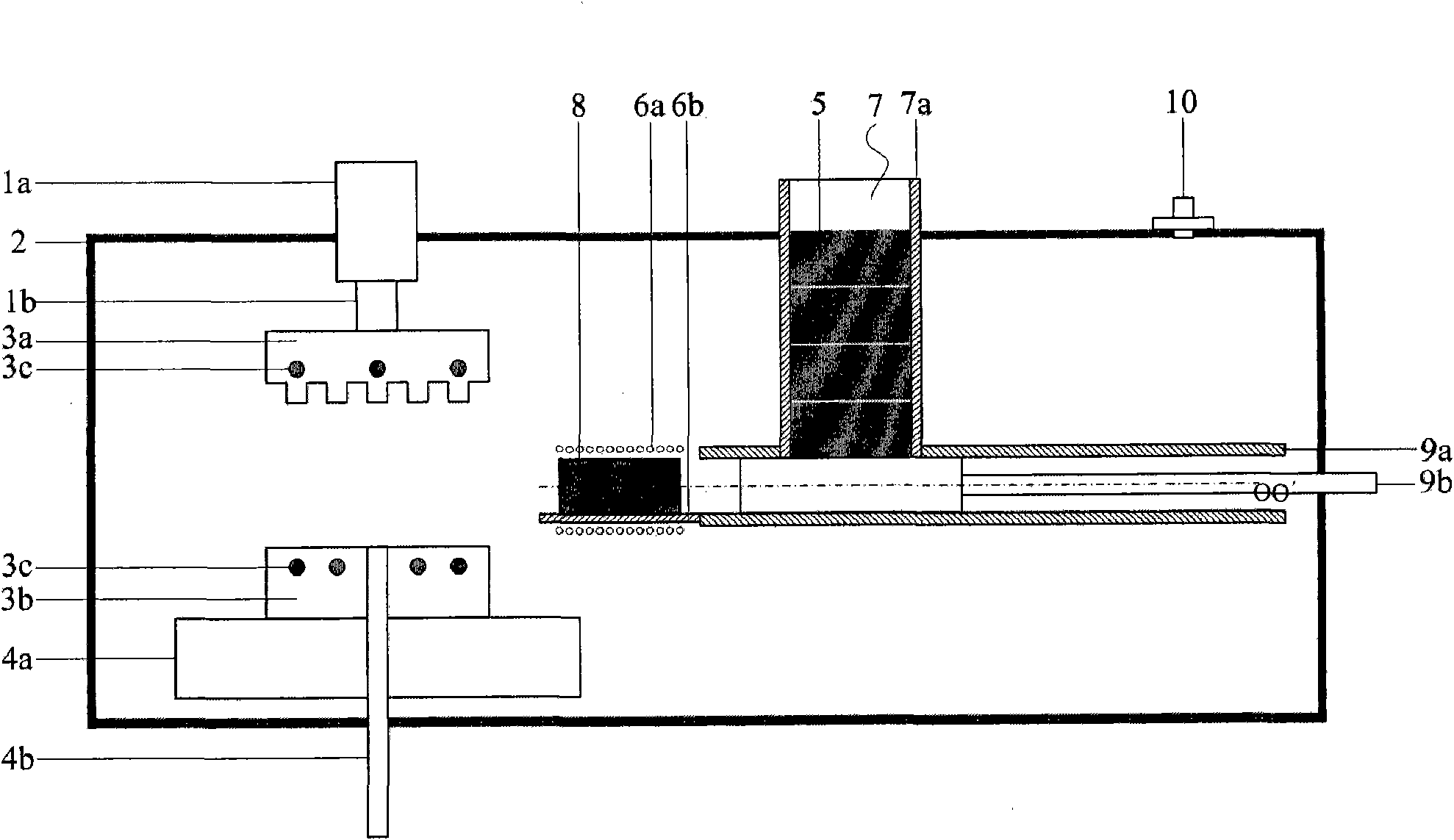
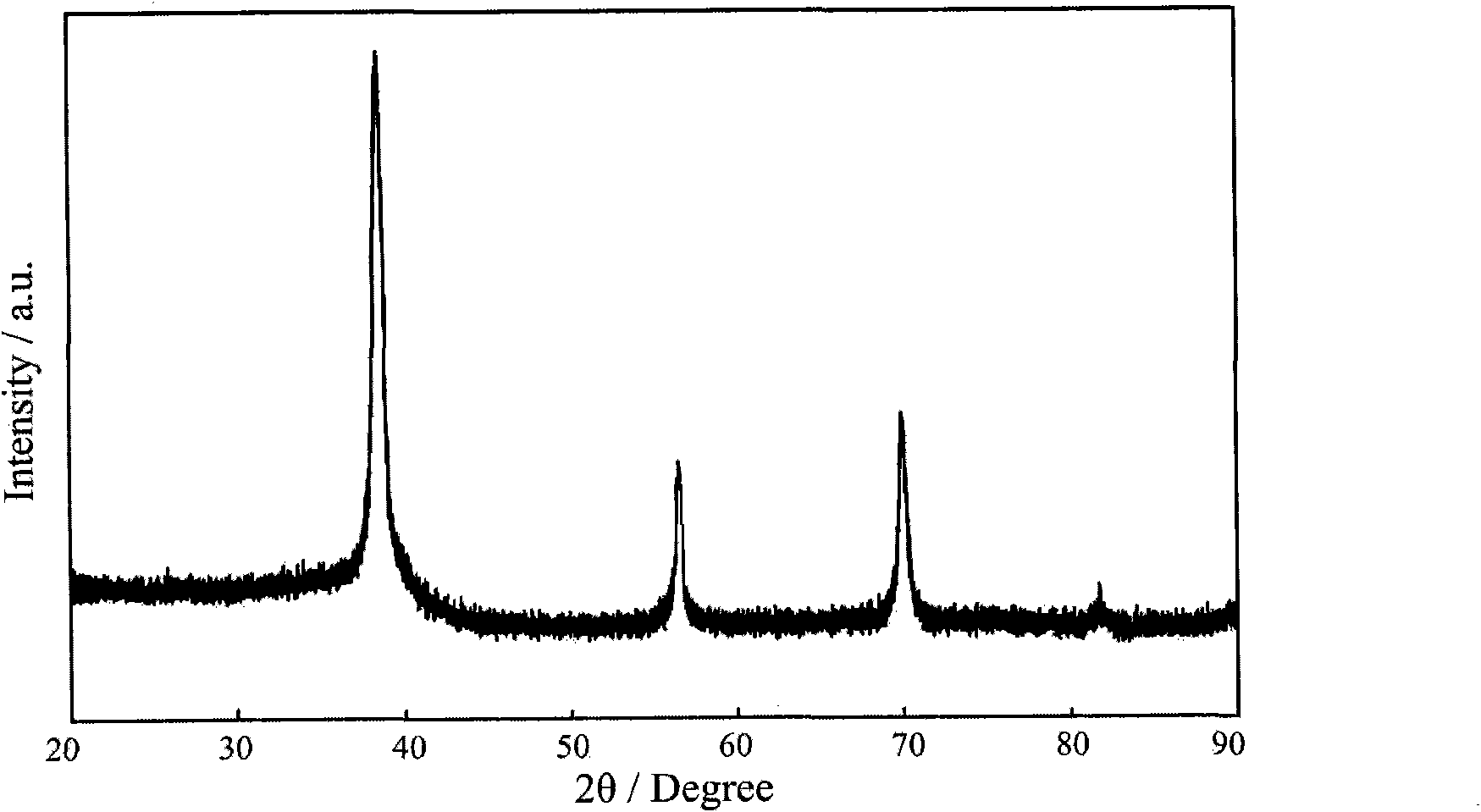
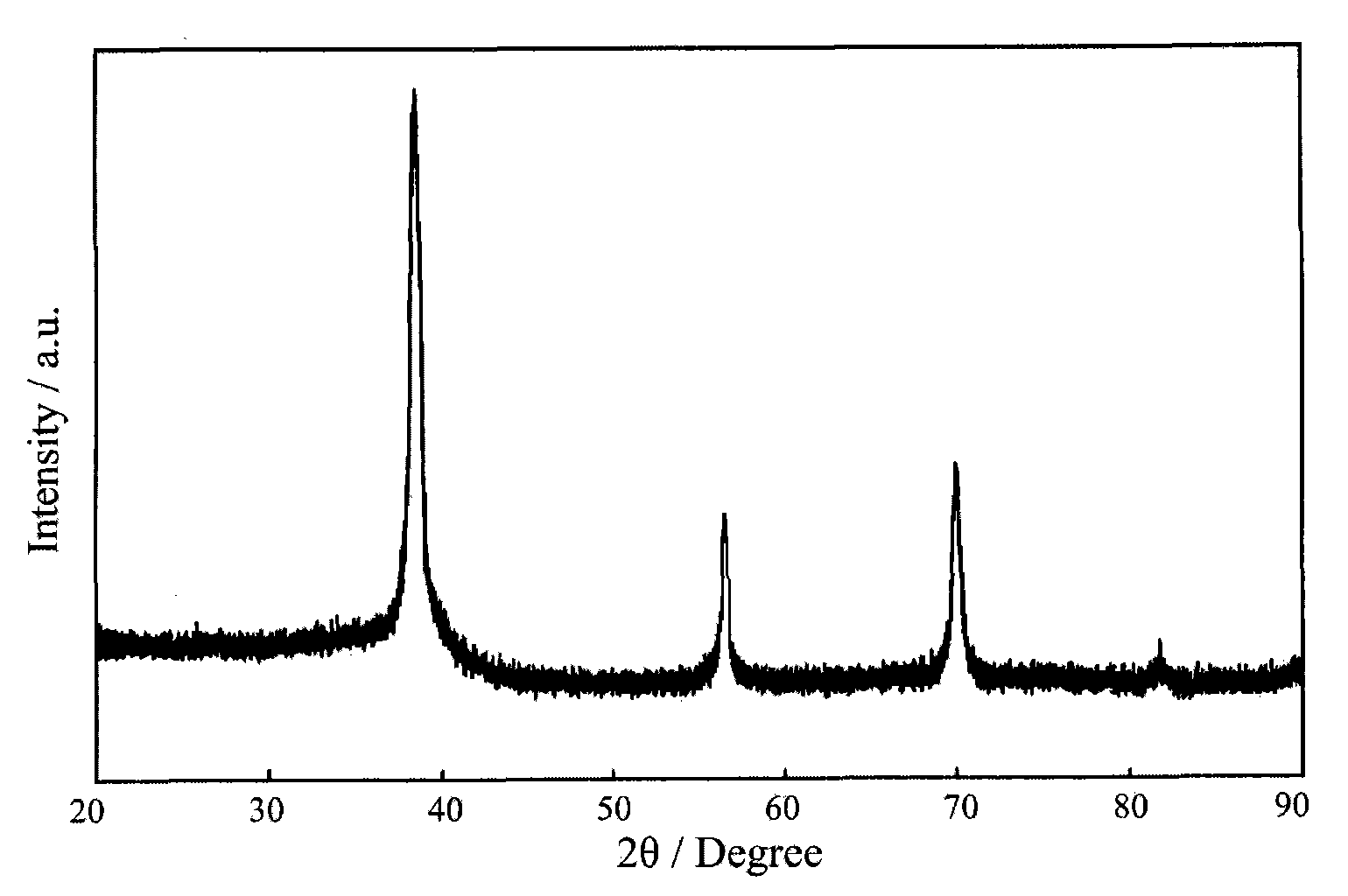
Forming method of block-shaped amorphous composite material
An amorphous composite material and block technology, applied in the field of amorphous alloy forming, can solve problems such as uneven distribution, low processing efficiency, slow deformation rate, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0026] Example: Open die forging a corrugated plate of bulk amorphous composite material, with a wall thickness of 1.5mm. The material is Ti 51.6 Zr 31.6 V 9.8 Cu 4.9 be 2.1 The alloy will precipitate a plastic second phase during the solidification process, and the matrix has a strong ability to form amorphous. The initial ingot is prepared by a water-cooled copper mold rapid cooling method. Using the above method and equipment, the corrugated plate forming steps are as follows:
[0027] (1) Clean up the components of the equipment, adjust the induction heating part 6, plunger 9b, movable mold 3a and ejector pin 4b to a reasonable position, and put the initial ingot into the pre-exhaust secondary chamber.
[0028] (2) Vacuumize the working cavity 2 and the auxiliary pre-exhaust chamber through the vacuum system, when the vacuum degree of the two reaches 3×10 -3 When it is above MPa, close the vacuum system, and fill the two with argon gas of about 1 atmosphere through t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com