Method for extracting metallic elements of ferrum, magnesium and calcium from molybdenum milltailings
A technology of metal elements and tailings, which is applied in the fields of magnesium, calcium, and metal element iron extraction, can solve the problems of low iron recovery rate, low magnetic iron content, and inability to comprehensively utilize it, achieving less waste liquid discharge, simplified operation, The effect of reducing the amount of waste liquid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
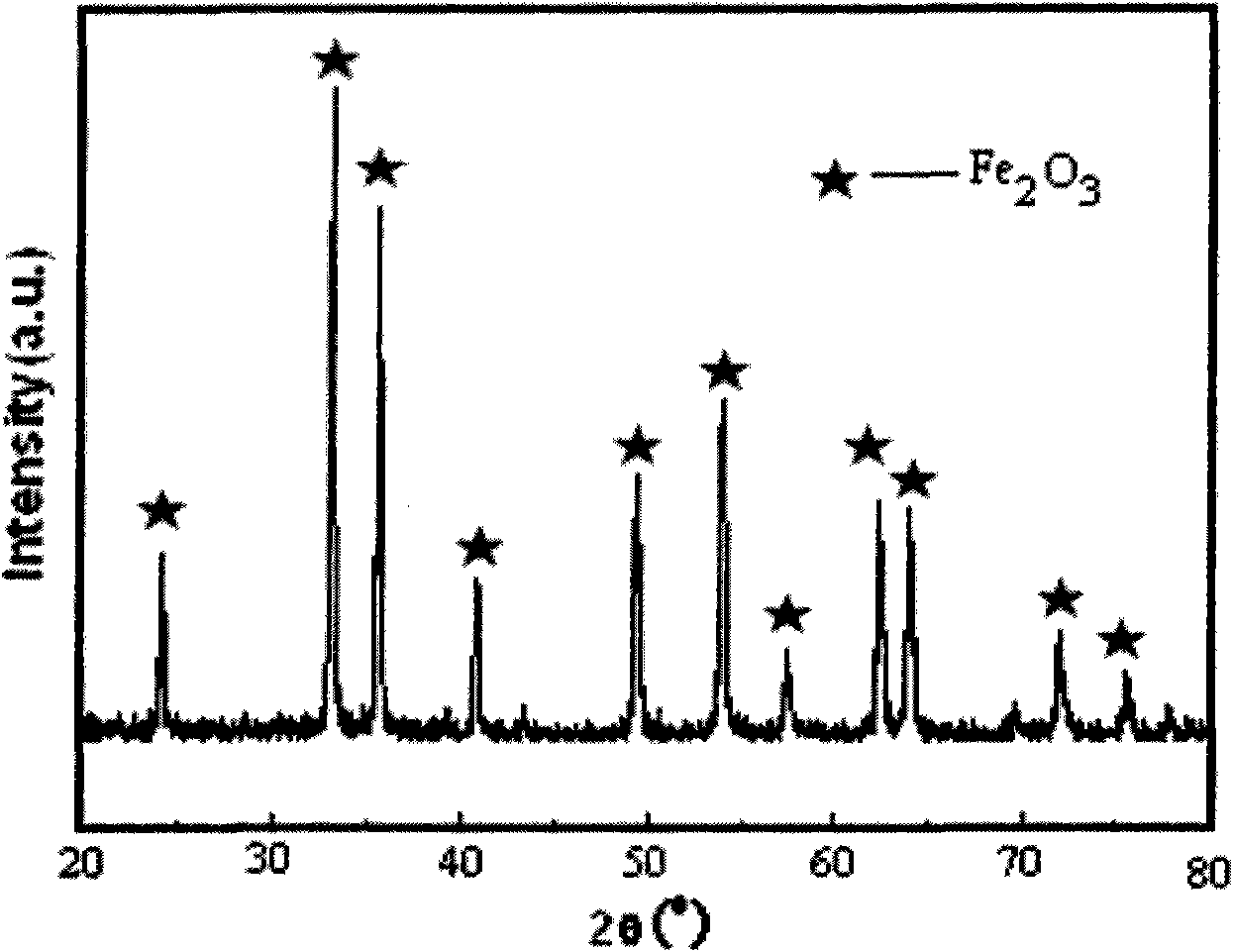
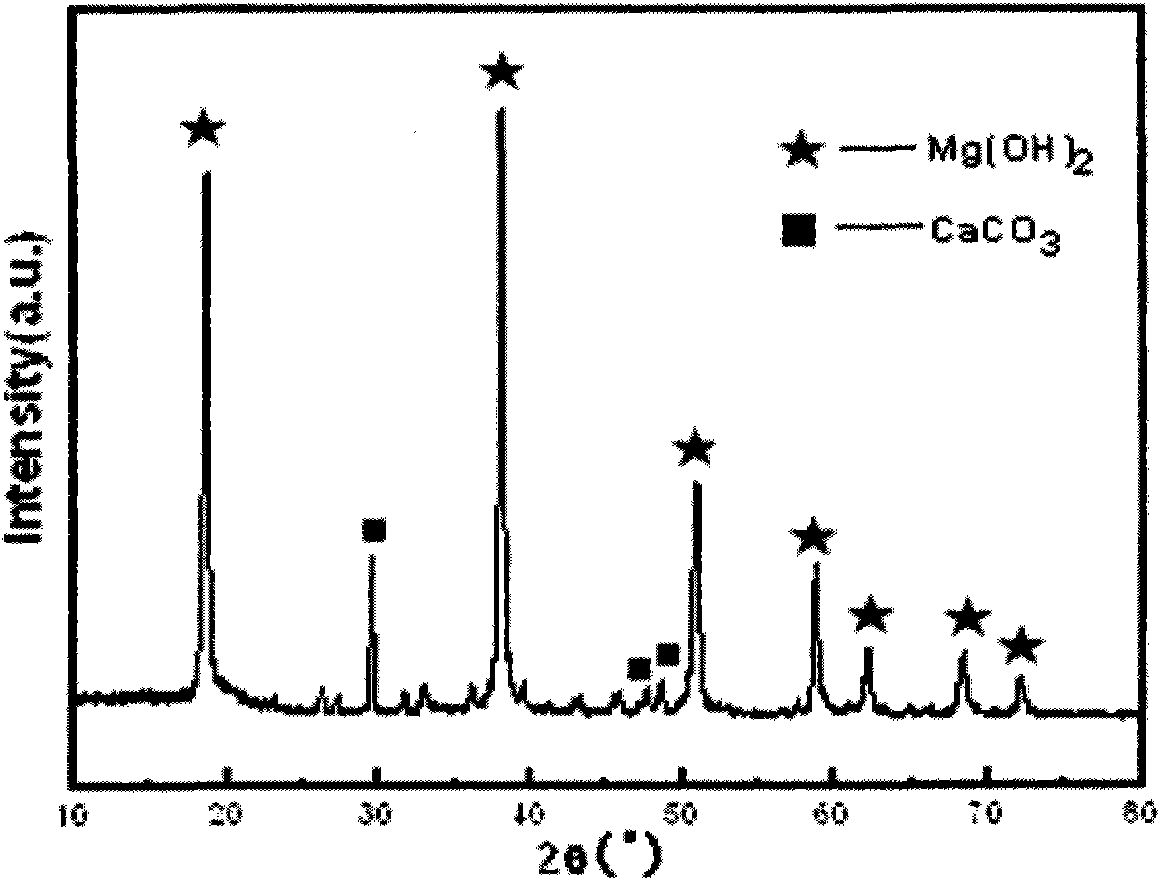
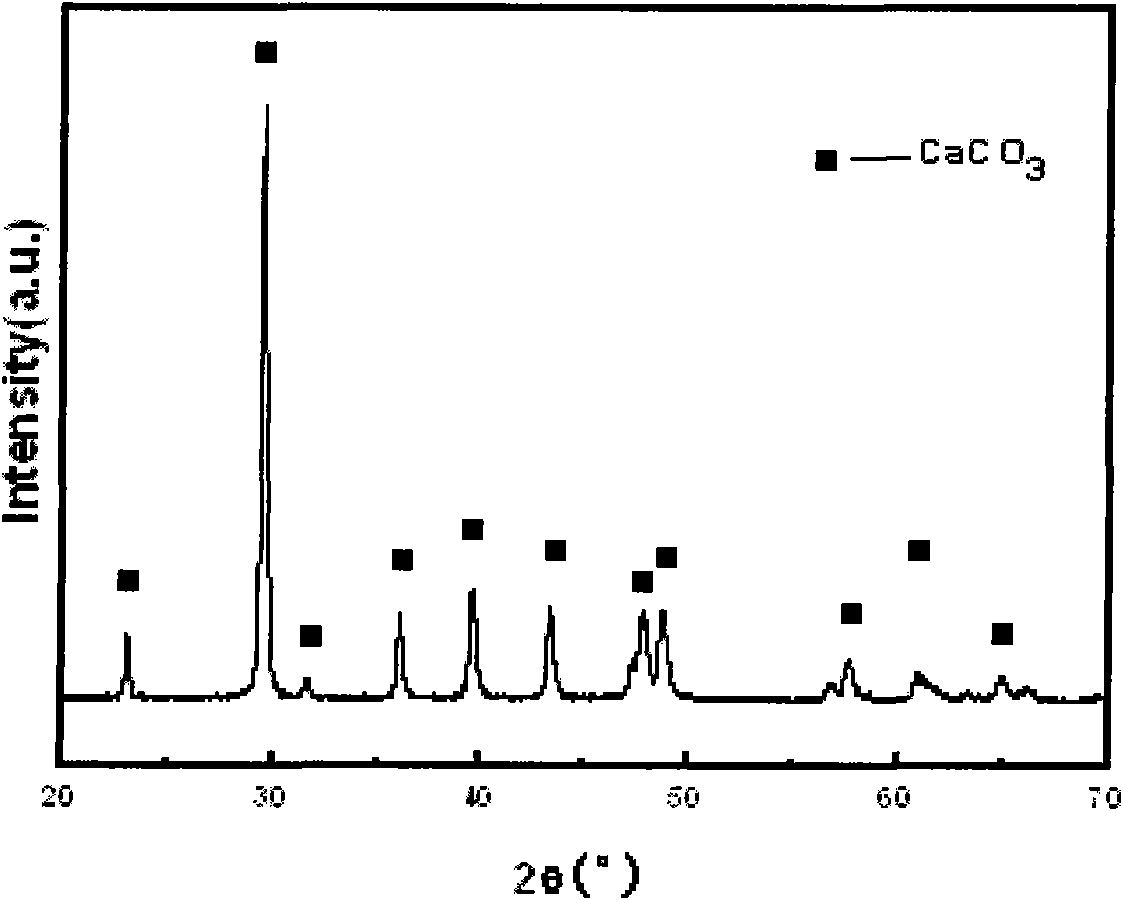
[0027] Pass the molybdenum beneficiation tailings whose main components are Si 22.79wt.%, Ca 16.21wt.%, Fe 9.117wt.%, Mg8.87wt.%, S 1.412wt.%, Al 1.289wt.% through a 40-mesh sieve, The sieved material is put into a ball mill tank for ball milling for 10 minutes, then passed through a 180-mesh sieve by a vibrating sieving machine, and the sieved material is taken. Mix 10wt.% hydrochloric acid with the undersize material at a liquid-solid ratio of 8:1, stir, then react in a water bath at 100°C for 4 hours, filter and wash to obtain acid dipping solution and filter residue. Hydrogen peroxide was added dropwise to the pickling solution, and the Fe in the solution 2+ All oxidized to Fe 3+ , to obtain filtrate a; filtrate a was heated to 60 ° C, and the precipitant was added dropwise and stirred, and the pH was controlled to 4.0 until the precipitation was complete, filtered and washed to obtain crude Fe(OH) 3 Filter residue and filtrate b, crude Fe(OH) 3 Heat the filter residue ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Pass the molybdenum beneficiation tailings whose main components are Si 22.79wt.%, Ca 16.21wt.%, Fe 9.117wt.%, Mg8.87wt.%, S 1.412wt.%, Al 1.289wt.%. The sieved material is put into a ball mill tank for ball milling for 15 minutes, then passed through a 200-mesh sieve by a vibrating sieving machine, and the sieved material is taken. Mix 20 wt.% hydrochloric acid with the undersize material at a liquid-solid ratio of 6:1, stir, then react in a water bath at 90°C for 8 hours, filter and wash to obtain acid dipping solution and filter residue. Hydrogen peroxide was added dropwise to the pickling solution, and the Fe in the solution 2+ All oxidized to Fe 3+ , to obtain filtrate a; filtrate a was heated to 80 ° C, and the precipitant was added dropwise and stirred, and the pH was controlled to 3.8 until the precipitation was complete, filtered and washed to obtain crude Fe(OH) 3 Filter residue and filtrate b, crude Fe(OH) 3 Heat the filter residue with dilute hydrochloric...
Embodiment 3
[0033]The molybdenum beneficiation tailings whose main components are Si 22.79wt.%, Ca 16.21wt.%, Fe 9.117wt.%, Mg8.87wt.%, S 1.412wt.%, Al 1.289wt.% are passed through a 120-mesh sieve, The sieved material was put into a ball mill tank for ball milling for 20 minutes, then passed through a 240-mesh sieve by a vibrating sieving machine, and the sieved material was taken. Mix 30wt.% hydrochloric acid with the undersize material at a liquid-solid ratio of 4:1, stir, then react in a water bath at 80°C for 4 hours, filter, and wash to obtain acid dipping solution and filter residue. Hydrogen peroxide was added dropwise to the pickling solution, and the Fe in the solution 2+ All oxidized to Fe 3+ , to obtain filtrate a; filtrate a was heated to 40 ° C, and the precipitant was added dropwise and stirred, and the pH was controlled to 4.5 until the precipitation was complete, filtered and washed to obtain crude Fe(OH) 3 Filter residue and filtrate b, crude Fe(OH) 3 Heat the filter ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com