Microorganism detoxification, and solidification and hazard-free treatment method for metal substrate sludge
A technology of toxic metals and microorganisms, applied in the field of environmental engineering, can solve problems such as complicated procedures, low efficiency, and high energy consumption, and achieve the effects of less process equipment, good application prospects, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
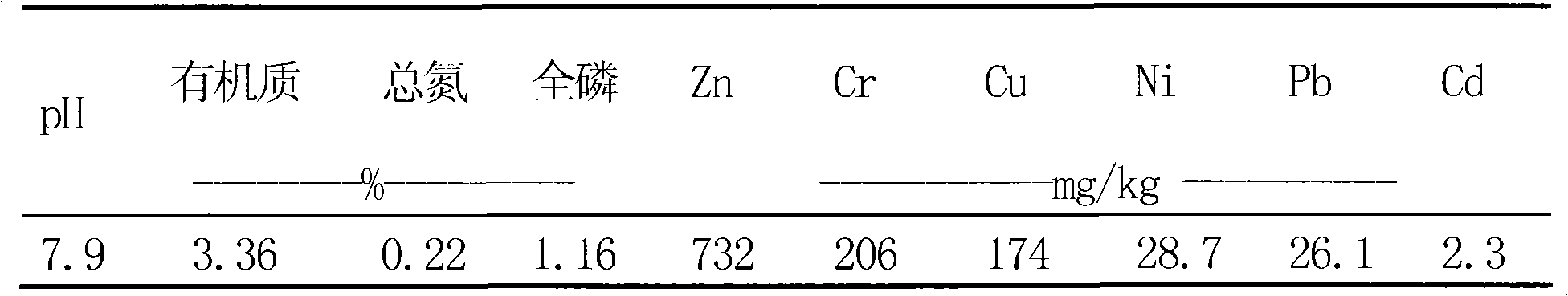
[0018] The samples were collected from the sediment of a toxic metal-polluted river in Shandong Province. The basic properties are shown in Table 1. The bottom sludge is black and smelly, heavily polluted by Zn, Cr and Cu. After sampling, the stones, gravel, and animal and plant residues in the mud samples were removed, and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
[0019] Table 1 Basic properties of sediment
[0020]
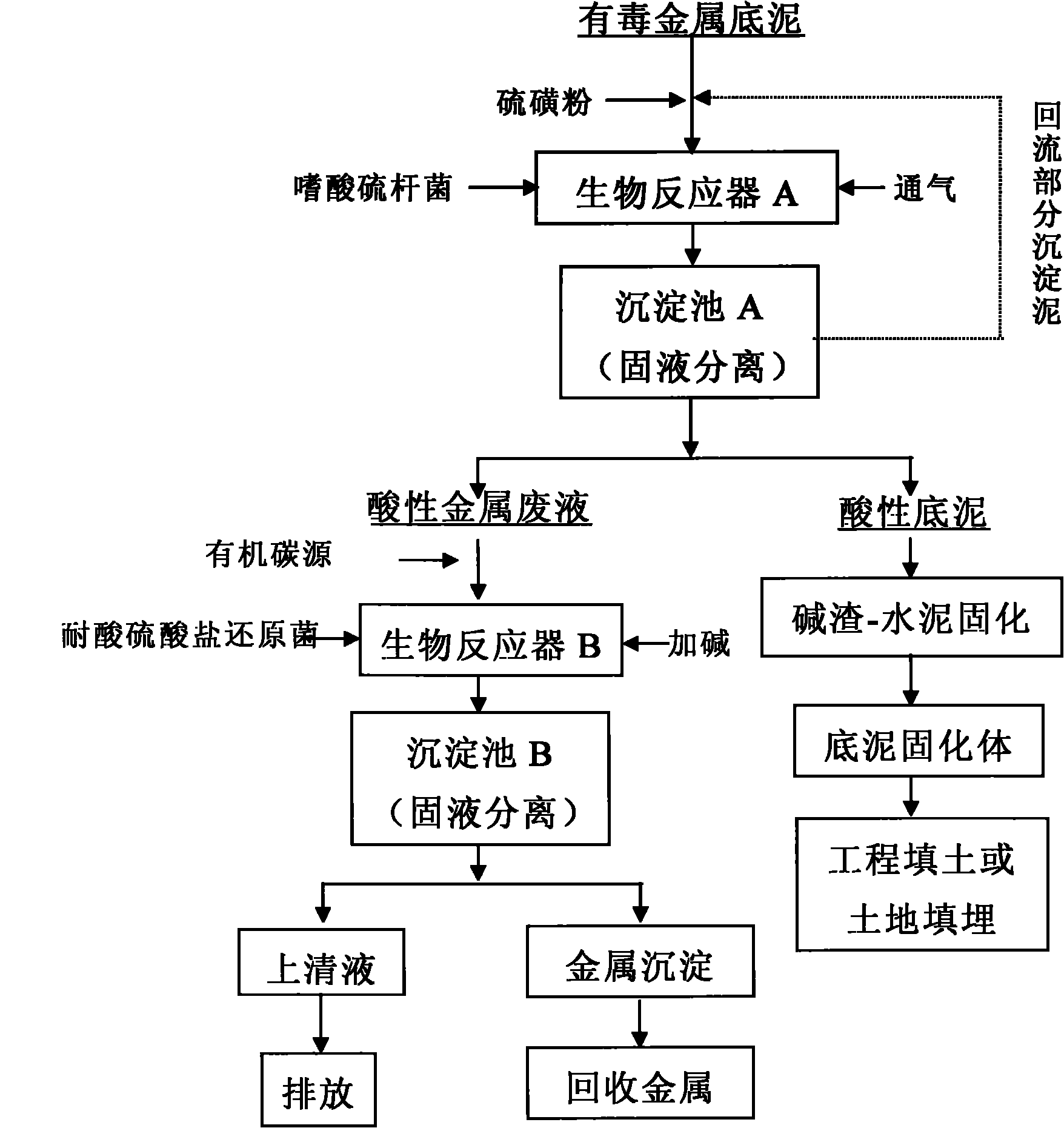
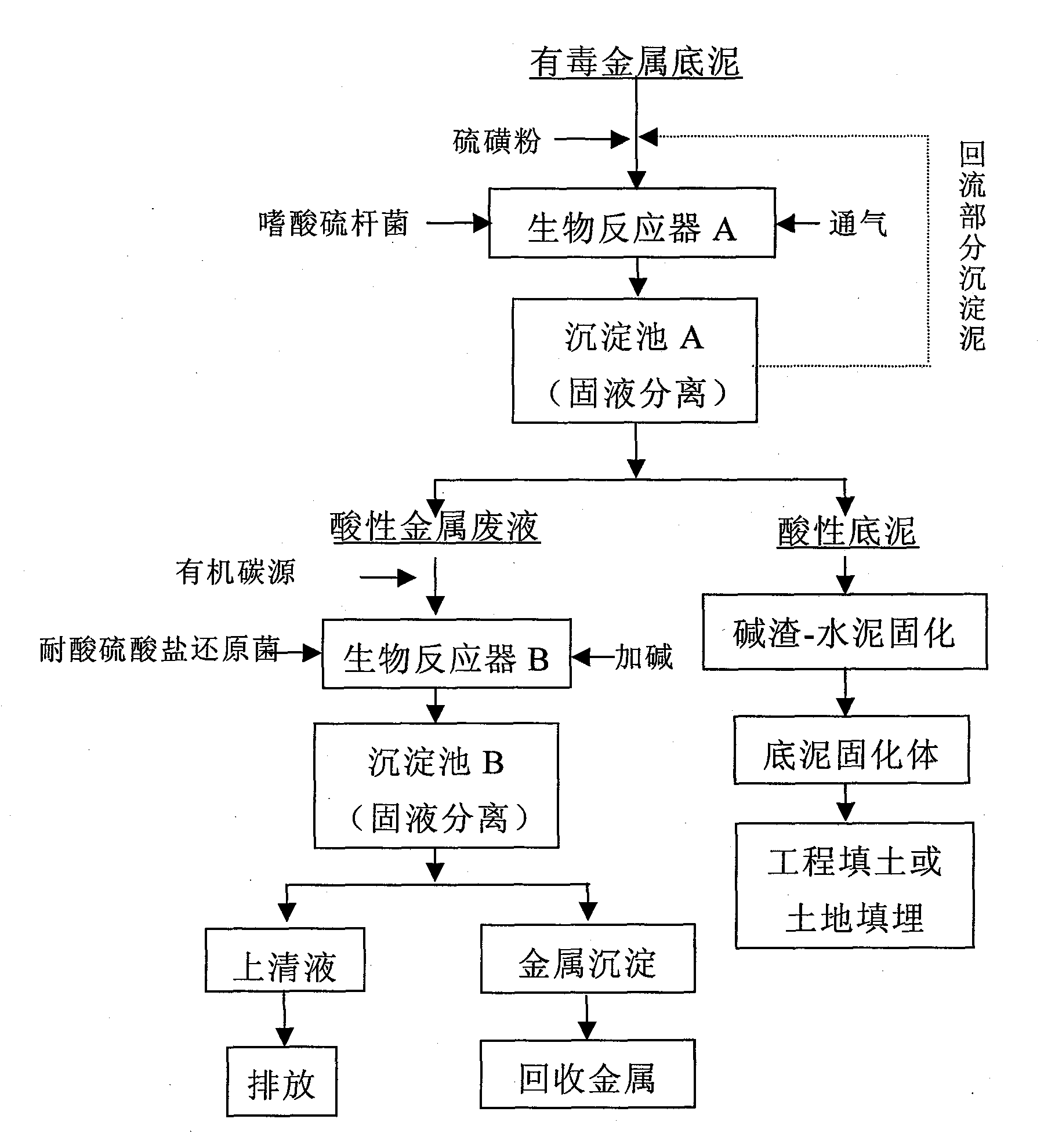
[0021]Step 1: Pump the bottom sludge with a solid content of 10% into the bioreactor A, add 3g / L sulfur powder, and at the same time insert the 8% inoculum of Thiobacillus acidophilus FD97 bacteria solution, and cultivate it with ventilation at room temperature for 12 days. The pH of the bottom sludge in bioreactor A is reduced to 2.5, and then, the bottom sludge in bioreactor A is pumped into sedimentation tank A for solid-liquid sedimentation separation, and 10% of the bottom sludge in the sedimentation tank is returned to bioreactor A again, Add the bottom mud ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The sample is the dredged sediment of a certain river in Guangdong. The pH of the sediment is 8.3, and the organic matter content is 18%. The only toxic metal in the sediment is Zn, which is 388mg / kg.
[0032] The specific implementation method is the same as example 1: the bottom mud was treated for 13 days (inoculum size 5%, sulfur powder addition 2g / L) through acidophilic thiobacillus in the bioreactor A, and the bottom mud pH was down to 3.0. After precipitation, 5% of Settling mud is refluxed, and with example 1 step cycle treatment, 95% of settling mud is dehydrated, and residual Zn content is reduced to 85mg / kg in the dehydration; The acidic metal waste liquid that dehydration produces adds 8.0g / L sodium lactate, adjusts pH with magnesium oxide After reaching 4.0, put it into bioreactor B, add acid-resistant sulfate-reducing bacteria at the same time according to the inoculation amount of 15%, anaerobic treatment, after stabilization, the pH of the effluent rises ...
Embodiment 3
[0034] The bottom mud sample is the same as the bottom mud in Example 1.
[0035] The specific implementation method is the same as example 1: in the bioreactor A, pump the bottom mud with a solid content rate of 15%, add 4g / L sulfur powder, add acidic Thiobacillus acidophilus FD97 bacterium liquid by 10% inoculum simultaneously, aeration culture 15d, Bottom mud pH is reduced to 2.6, is driven into sedimentation tank A and settled, and 10% of settled mud returns to flow into reactor A and is treated with example 1 method cycle, and 90% of settled mud is dehydrated, and residual Zn, Cr and Cu content in decementing, through The detections were 97, 121 and 58mg / kg respectively, and the pH of the waste liquid produced by dehydration was 2.2, Zn 2+ 、Cu 2+ and Cr 3+ Contents were 93, 10.7 and 16mg / L, SO 4 2- The content is 7960mg / L; add 7.0g / L ethanol to the above waste liquid, adjust the pH to 3.8 with quicklime, pour it into bioreactor B, and add acid-resistant sulfate-reduci...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com