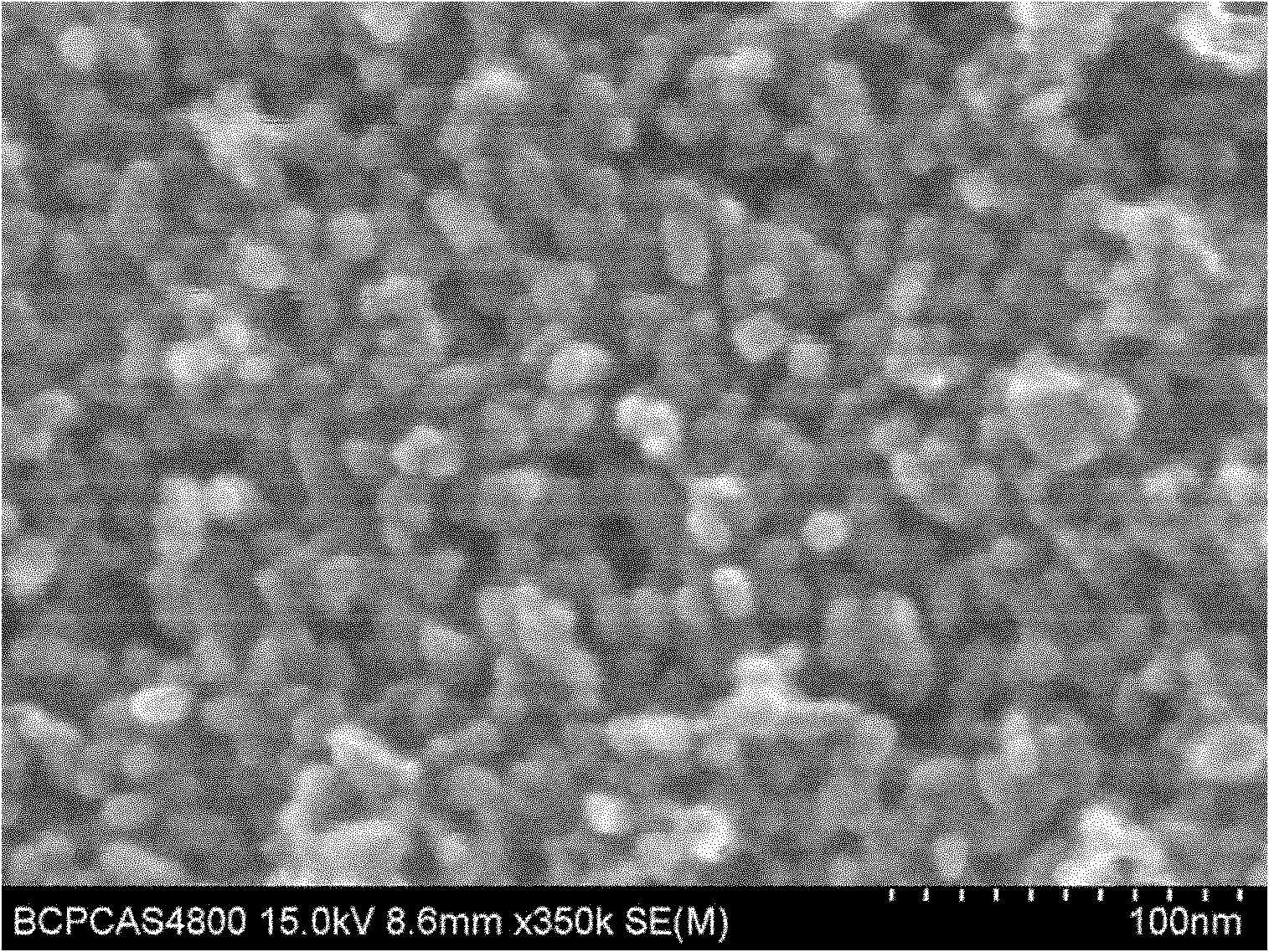
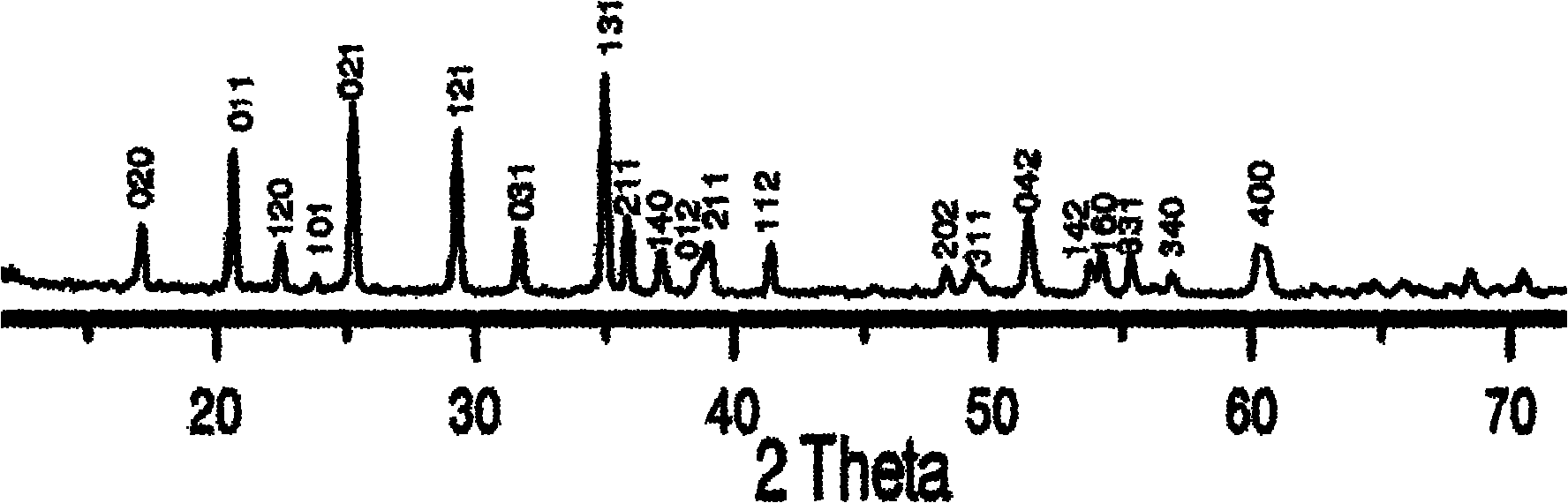
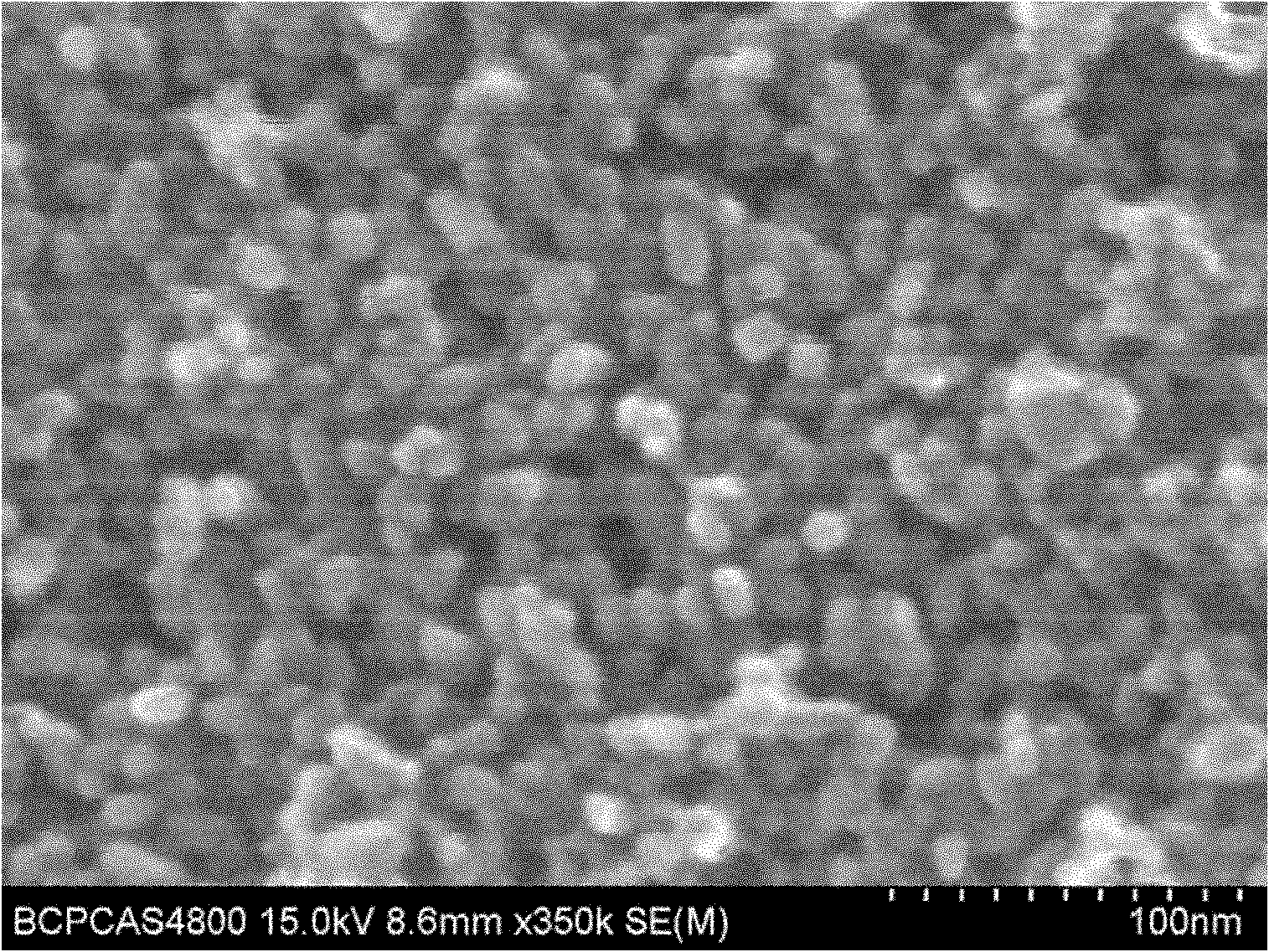
Method for preparing lithium iron phosphate-doped nano powder for lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery, lithium iron phosphate technology, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of powder agglomeration, high requirements for reaction atmosphere, poor reaction uniformity, etc. Uniform phase and small particle size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] 1) Synthesis of reaction precursors
[0022] Phosphoric acid, ferrous acetate and lithium hydroxide are formulated into a 0.4mol / L precursor solution according to the P:Fe:Li molar ratio of 1::1:1 (the solvent is water, and the following solvents all use water) ;
[0023] 2) Preparation of dopant source precursor solution
[0024] Prepare titanyl sulfate into a 0.5mol / L solution as the dopant source precursor;
[0025] 3) Mix the above doping source precursor solution and precursor solution according to the ratio of titanyl sulfate and ferrous ion molar ratio of 0.01:1, then put them in a hydrothermal reaction kettle, blow the inside of the kettle with high-purity nitrogen for 3 minutes, and then add 8MPa initial pressure, then react at 100°C for 20 hours, take it out after natural cooling, and then dry it after centrifugal washing to obtain a well-crystallized doped lithium iron phosphate nanopowder.
Embodiment 2
[0027] The first step is to synthesize the precursor solution: the phosphorus source compound (ammonium dihydrogen phosphate: phosphoric acid = 1: 1), ferrous chloride and lithium carbonate are formulated according to the ratio of P: Fe: Li molar ratio of 1: 1: 1 1.4mol / L precursor solution;
[0028] The second step is the preparation of the doping source precursor solution: nickel phosphate is prepared into a 1mol / L solution as the doping source precursor solution, and the doping source is nickel phosphate;
[0029] The third step is to mix the dopant source precursor solution with the precursor solution in a molar ratio of 0.1:1 and then place it in a hydrothermal reaction kettle. Blow the inside of the kettle with high-purity nitrogen for 3 minutes and then add an initial pressure of 4 MPa, and then After reacting at 180°C for 8 hours, take it out after natural cooling, then centrifuge, wash and dry to obtain a well-crystallized doped lithium iron phosphate nanopowder.
[...
Embodiment 3
[0032] The first step, synthetic precursor solution: phosphorus source compound (by diammonium hydrogen phosphate: phosphoric acid is mixed as 1: 1 in molar ratio): ferrous sulfate: lithium source compound (by lithium chloride and lithium acetate in molar ratio 1:1 mixing) according to the ratio of P:Fe:Li molar ratio of 1::1:1 to prepare a 2.4mol / L precursor solution (the solvent is water, and the following solvents all use water);
[0033] The second step is the preparation of the doping source precursor solution: the doping source is prepared into a 0.8mol / L solution, and the doping source is nickel phosphate,
[0034] Step 3: Mix the dopant source precursor solution with the precursor solution at a molar ratio of 0.08:1 and place it in a hydrothermal reaction kettle. Blow the inside of the kettle with high-purity nitrogen for 3 minutes and add an initial pressure of 2 MPa. After reacting at 220°C for 5 hours, take it out after natural cooling, then centrifuge, wash and dry...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com