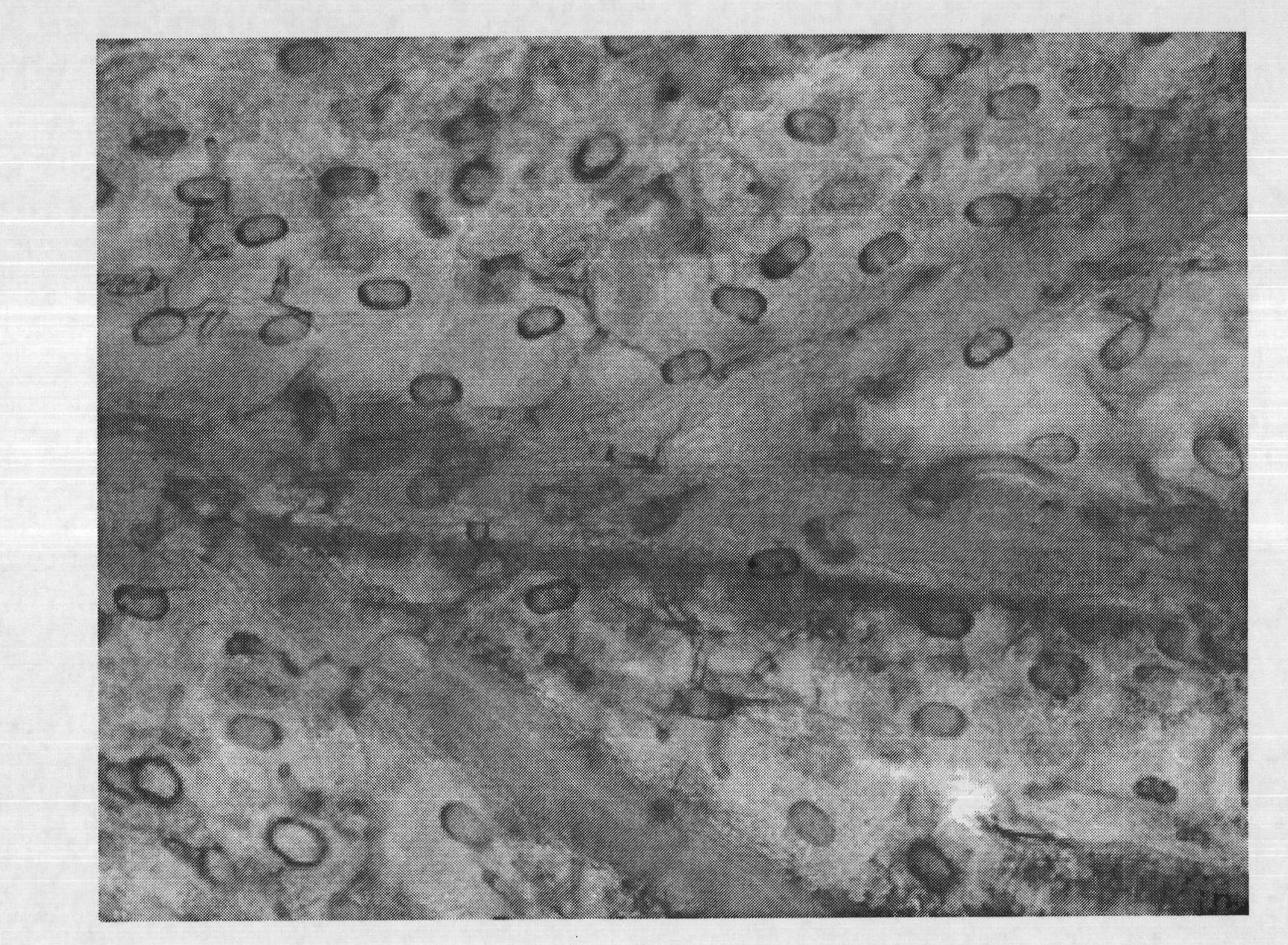
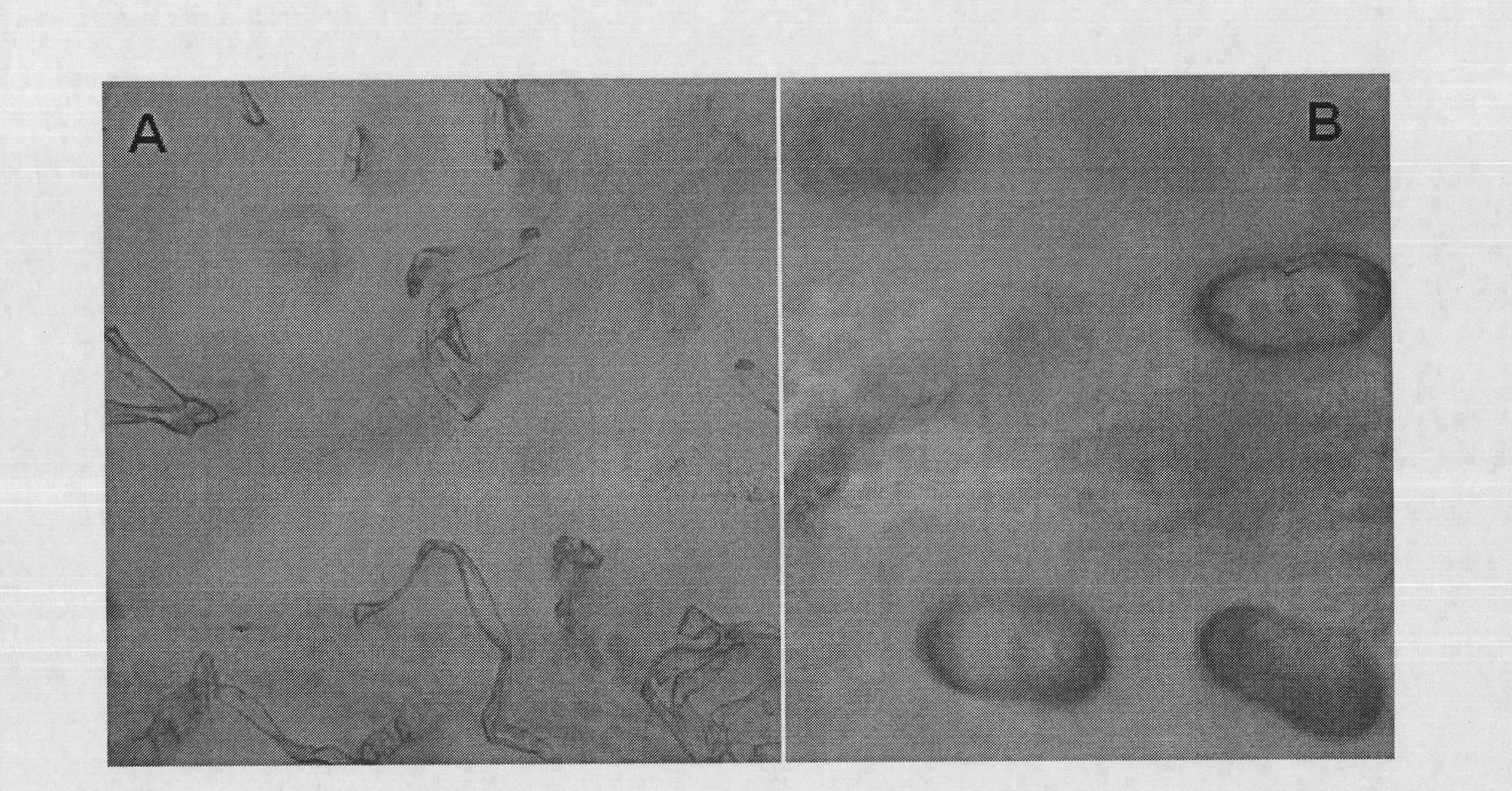
Observation and density measurement method for glandular hairs on Artemisia annua leaf surfaces
A technology for measuring the density of Artemisia annua leaves, applied in the field of life sciences, can solve the problems of difficult observation with glandular hairs, damage to the structure of glandular hairs, and distortion of the number and density of glandular hairs, so as to reduce the cost and time of measurement and achieve good repeatability , reagent and non-toxic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
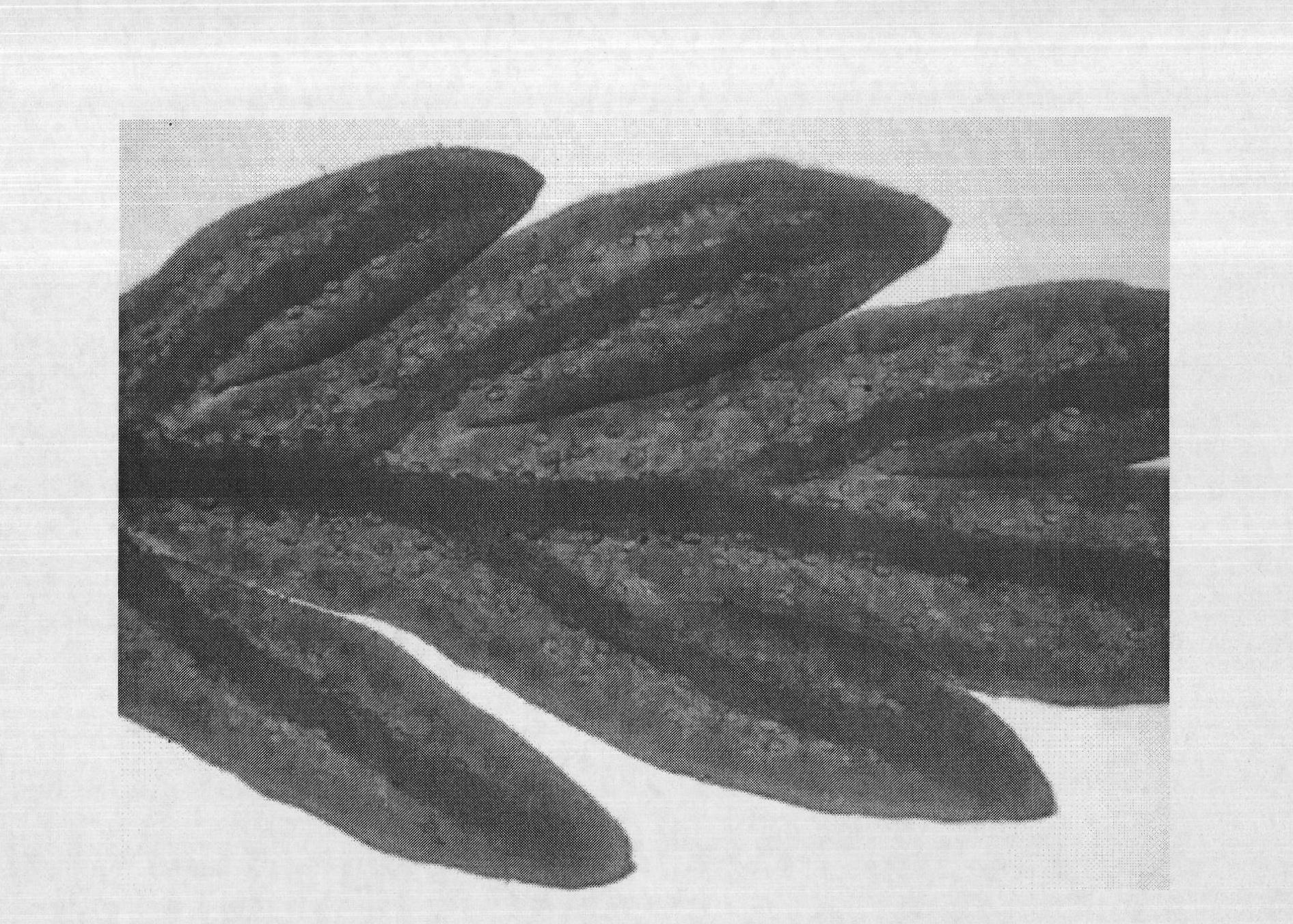
[0035] Randomly select 96 plants of Artemisia annua that grow healthy and have a growth age of 3 months, and take the first leaf that has just fully expanded from the top of the main stem to be complete and vigorously growing (mainly referring to the leaves that have just fully expanded and have no pests and diseases, etc.) Artemisia annua leaves were washed once with distilled water if necessary, and 1 square centimeter each was placed in the small wells of a 96-plate in turn, and 198 μL of petroleum ether, 1.7 μL of absolute ethanol and 0.3 μL of glacial acetic acid reagent were added to each Well, incubate at room temperature for 7 min.
[0036] Take out the leaves on the glass slide, add a drop of double distilled water, gently cover the cover glass, and place it on the stage of the Motic B1 optical microscope. The part to be observed should be accurately moved to the bottom of the objective lens, and then press it with a press clamp. tight. The cover glass must be wiped cl...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Randomly select 10 Artemisia annua plants with healthy growth and a growth age of 6 months, and take the third fully expanded Artemisia annua leaf with complete leaves and vigorous growth from the top of the main stem, wash it once with distilled water if necessary, and take each 1 square centimeter was placed in a 1.5ml centrifuge tube in turn, and 980 μL of petroleum ether, 15 μL of absolute ethanol, and 5 μL of glacial acetic acid reagent were sequentially added to each centrifuge tube, and incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes.
[0042] According to the method of Example 1, take out the leaves on the glass slide, drop a drop of double distilled water, cover the cover glass, place it on the stage of the Motic B1 optical microscope, and use a 4× or 10× objective lens under the 10× eyepiece Observe, image, count the number of glandular trichomes, and finally calculate the density of glandular trichomes. The glandular hair density measured in this embodiment is 3...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Randomly select 10 Artemisia annua plants with healthy growth and a growth age of 9 months, and take the fifth Artemisia annua leaf with complete leaves and vigorous growth from the top of the main stem, wash it once with distilled water if necessary, and take each 1 square centimeter was placed in a 2ml centrifuge tube in turn, and 1900 μL of petroleum ether, 90 μL of absolute ethanol, and 10 μL of glacial acetic acid reagent were sequentially added to each centrifuge tube, and incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes.
[0046] According to the method of Example 1, take out the leaves on the glass slide, drop a drop of double distilled water, cover the cover glass, place it on the stage of the Motic B1 optical microscope, and use a 4× or 10× objective lens under the 10× eyepiece Observe, image, count the number of glandular trichomes, and finally calculate the density of glandular trichomes. The glandular trichome density measured in this embodiment is 45.9 per squ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com