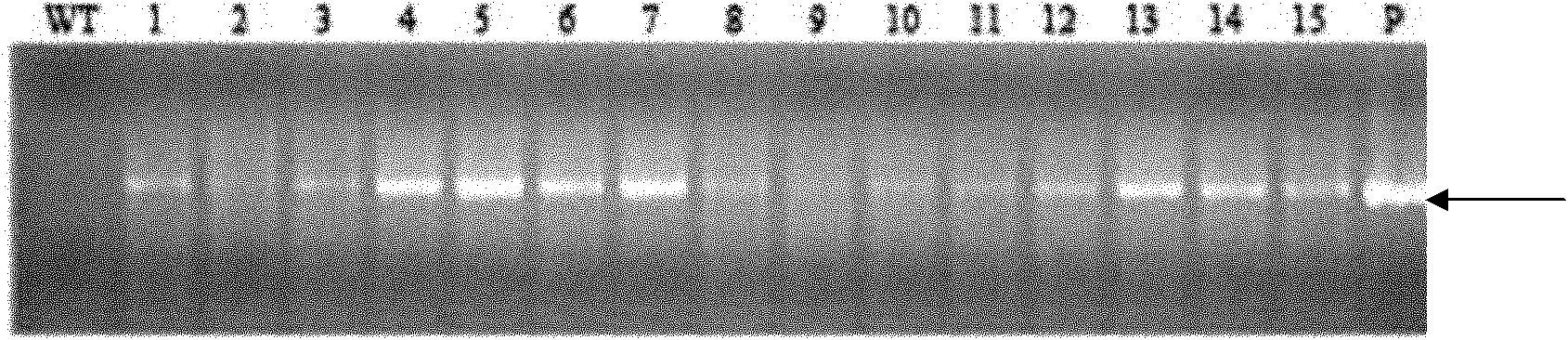Specific promoter and method for culturing disease-resistant transgenic plant
A promoter, coding gene technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, angiosperms/flowering plants, plant products, etc., can solve the problems of plant dwarfing, yield decline, growth retardation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1, the cloning of tissue-specific promoter RSS1P
[0042] A pair of specific primers (RSS1P-F1 and RSS1P-R1) were designed according to the 5' end sequence of the existing rice sucrose synthase gene, and the target sequence was the upstream sequence (1715bp) of the 5' end non-coding region.
[0043] RSS1P-F1: 5'-CTCCTTTCATTTTCAGTGCAAATGTG-3';
[0044] RSS1P-R1: 5'-CCAATGGTGGTCAGAGACG AG-3'.
[0045] Genomic DNA was extracted from the young leaves of rice variety "Nipponbare" according to the improved CTAB method.
[0046] Using genomic DNA as a template, specific primers (RSS1P-F1 / RSS1P-P1) were used for PCR amplification to obtain PCR amplification products. Taq plus DNA polymerase (Takara) was used for PCR amplification; the reaction parameters were: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; 30 cycles of 94°C for 1 min, 58°C for 1 min, and 72°C for 3 min; and extension at 72°C for 10 min. The PCR product was recovered and purified by low-melting point agarose ...
Embodiment 2
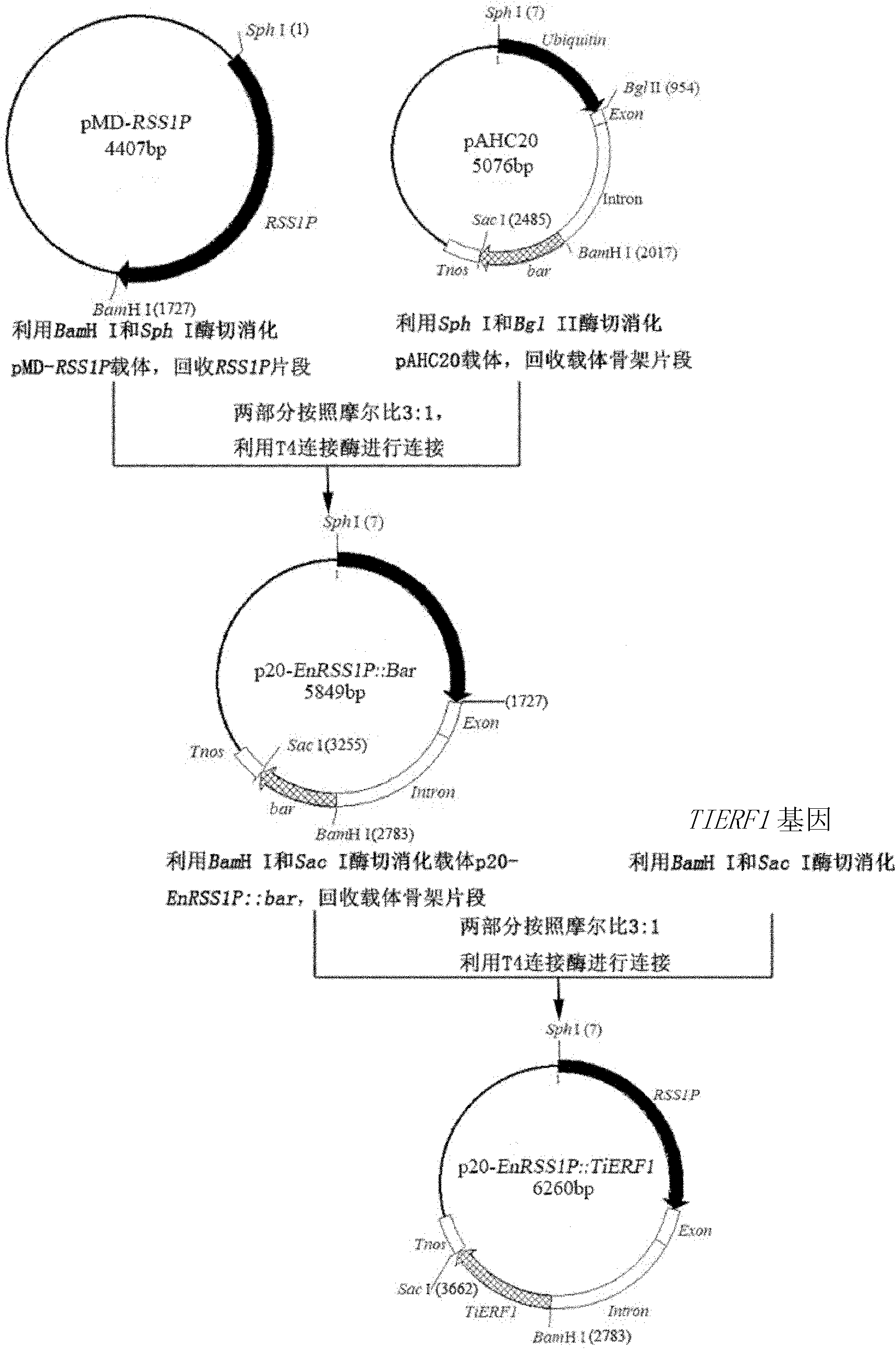
[0048] Example 2, Construction of recombinant expression vector (pA20-EnRSS1P::TiERF1) and acquisition of enhanced RSS1P (EnRSS1P)
[0049] 1. Construction of recombinant expression vector pA20-EnRSS1P::TiERF1
[0050] Such as figure 1 The recombinant expression vector pA20-EnRSS1P::TiERF1 was constructed as shown.
[0051] 1. According to the improved CTAB method (Murray M G, Thompson W F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 1980, 8(19): 4321-4325), the genomic DNA of the young leaves of the rice variety "Nipponbare" was extracted .
[0052] 2. Using the genomic DNA extracted in step 1 as a template, perform PCR amplification with a primer pair composed of RSS1P-F2 / RSS1P-R2 to obtain a PCR amplification product.
[0053] RSS1P-F2: 5′-AGA CTCCTTTCATTTTCAGTGCAAATG-3' (Sph I recognition sequence in the box);
[0054] RSS1P-R2: 5′-ATA CCAATGGTGGTCAGAGAC-3' (BamH I recognition sequence in box).
[0055] 3. The PCR amplified product ...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Activity comparison of embodiment 3, RSS1P, EnRSS1P and Ubi promoter
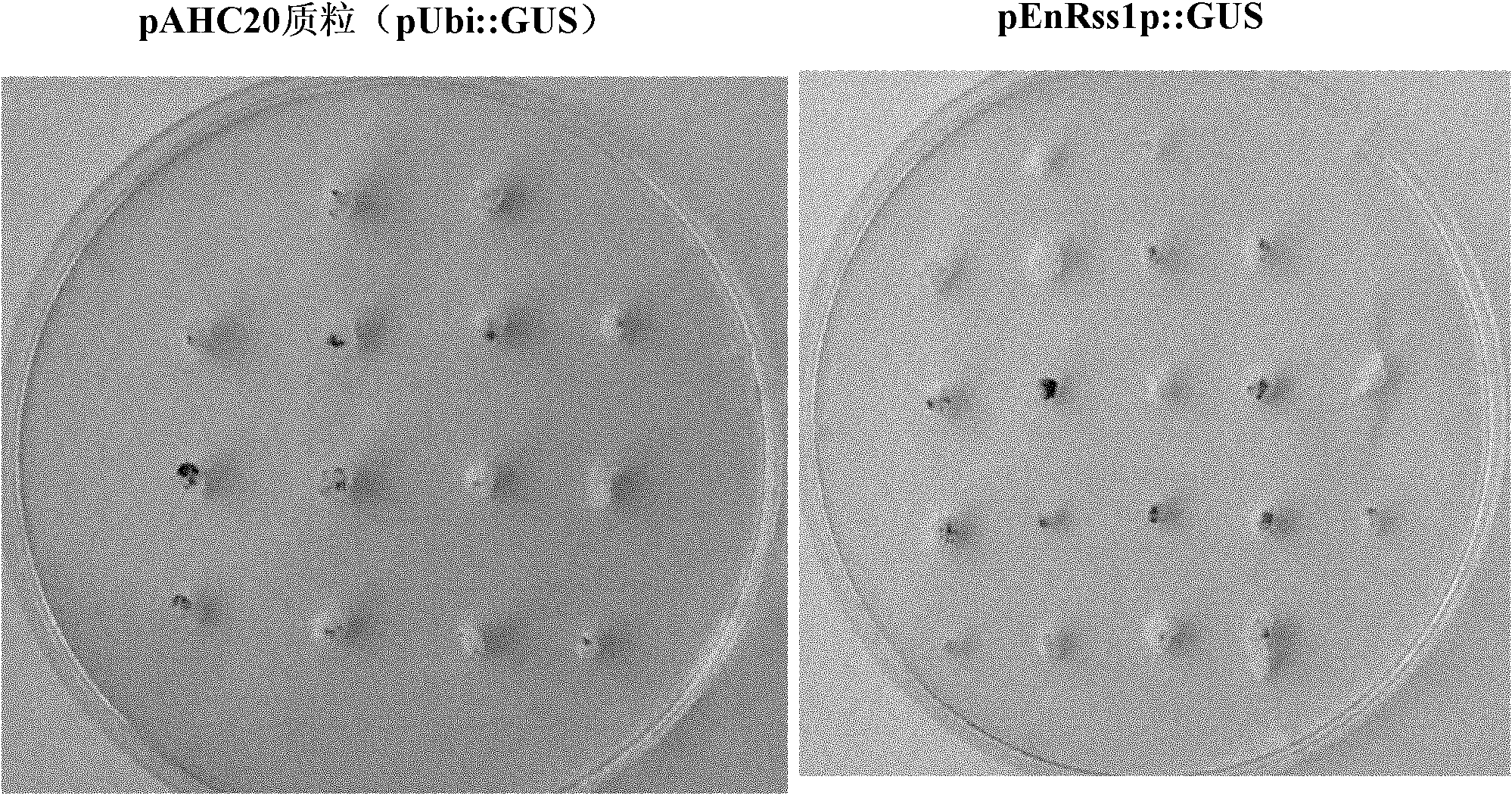
[0072] 1. Preparation of recombinant plasmids
[0073] The pAHC20 plasmid has a Ubi promoter-driven GUS gene expression cassette.
[0074] RSS1P shown in sequence 1 of the sequence listing was synthesized. RSS1P was inserted between the HindIII and BamH I sites of the pAHC20 vector plasmid to obtain recombinant plasmid A (pRss1p:GUS). In recombinant plasmid A, RSS1P promotes the expression of GUS gene.
[0075] Digest the pAHC20 vector with restriction endonuclease Bgl II and BamH I to recover a small fragment (UBI-INTRON fragment); digest the recombinant plasmid A with restriction enzyme BamH I to recover a large fragment (vector backbone); The large fragment and the small fragment were ligated to obtain recombinant plasmid B (pEnRss1p::GUS). In recombinant plasmid B, EnRSS1P promotes the expression of GUS gene.
[0076] 2. Transient expression experiment
[0077] Using Xu Huijun et al. (Xu H-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com