Method for treating poor-tin middling ore and recovering iron-making raw material
A technology for iron-making raw materials and ore materials, applied in the field of non-ferrous metallurgy, can solve problems such as affecting the quality of iron and steel, difficult to remove, harmful arsenic, etc., and achieve the effects of improving equipment production capacity, improving extraction rate, and saving energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
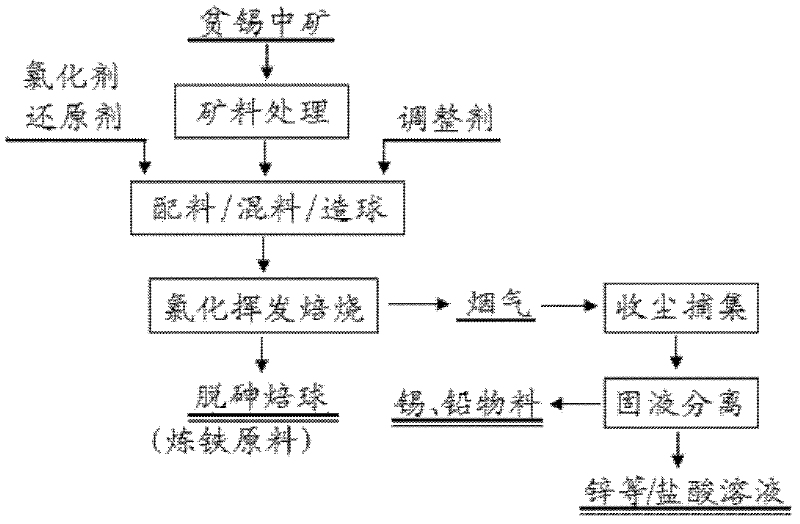
[0042] The tin ore is ground and passed through a 60-mesh sieve; add 7-8% CaCl of the tin ore 2 , 3-4% pulverized coal and 6-7% quartz powder (-60 mesh), mixed and pelletized; the ore pellets are put into the rotary kiln for chlorination and volatilization roasting; pulverized coal is used as fuel; the chlorination roasting temperature is 1050~ 1100℃, time 40~60min; control CO in furnace gas 2 / CO is 2.0; the flue gas is cooled, settled and wet dust collected to recover valuable metals. The baked balls are cooled and used as raw materials for ironmaking.
[0043] The volatilization rate (%) of each valuable element is: Sn 96.2; Pb 98.4; Zn 74.6; As 94.1. Baked balls contain 46.3% iron; other main impurities (%) are: Sn 0.060; Pb 0.033; Zn 0.205; As 0.051.
Embodiment 2
[0045] The tin ore is ground and passed through a 60-mesh sieve; add 4-5% CaCl of the tin ore 2 , 4-6% pulverized coal and 3-4% quartz powder (-60 mesh), mixed and pelletized; the ore pellets are put into the rotary kiln for chlorination and volatilization roasting; pulverized coal is used as fuel; the chlorination roasting temperature is 950~ 1000°C, time 70-80min; control CO in furnace gas 2 / CO is 1.2; the flue gas is cooled, settled and wet dust collected to recover valuable metals. The baked balls are cooled and used as raw materials for ironmaking.
[0046] The volatilization rate (%) of each valuable element is: Sn 94.5; Pb 97.1; Zn 72.3; As 92.4. The baked ball contains 47.1% iron; other main impurities (%) are: Sn 0.087; Pb 0.059; Zn 0.221; As 0.065.
Embodiment 3
[0048] The tin ore is ground and passed through a 60-mesh sieve; add 6-7% CaCl of the tin ore 2 , 4-5% pulverized coal and 5-6% quartz powder (-60 mesh), mixed and pelletized; the ore pellets are put into the rotary kiln for chlorination and volatilization roasting; pulverized coal is used as fuel; the chlorination roasting temperature is 1000~ 1050°C, time 60-70min; control CO in furnace gas 2 / CO is 2.8; the flue gas is cooled, settled and wet dust collected to recover valuable metals. The baked balls are cooled and used as raw materials for ironmaking.
[0049] The volatilization rate (%) of each valuable element is: Sn 95.5; Pb 98.0; Zn 73.8; As 93.7. Baked balls contain 46.3% iron; other main impurities (%) are: Sn 0.071; Pb 0.041; Zn 0.213; As 0.054.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com