Genetically engineered strain and method for producing dihydroxyacetone by using the same
A technology of dihydroxyacetone and genetic engineering bacteria, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of dihydroxyacetone efficiency to be further improved, intolerance to high concentration of glycerin, etc., and achieve the effect of sufficient supply and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
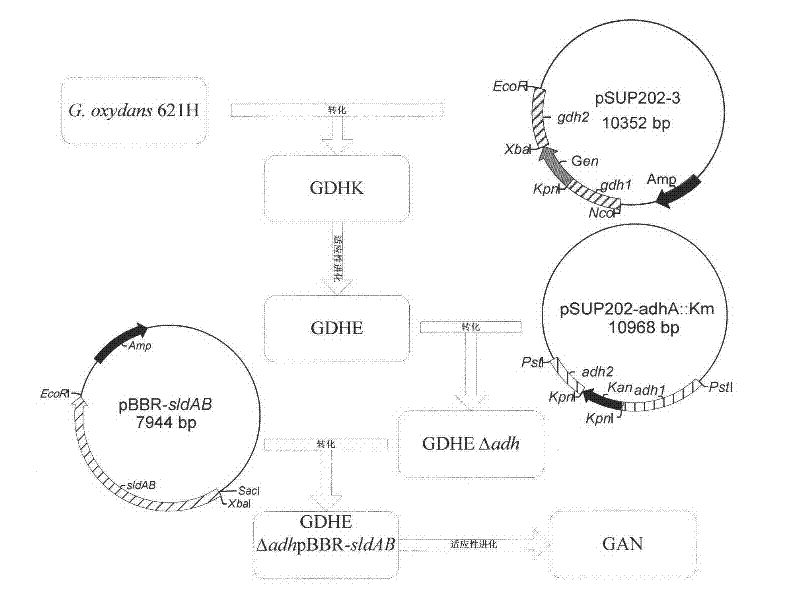
[0060] In order to introduce the prepared recombinant vector into Gluconobacter oxidans, any known method reported so far can be used. For example, the sldAB gene is carried by the Escherichia coli-fungus shuttle vector to prepare the Escherichia coli transformant, and with the help of the helper bacteria, the zygote is obtained by three-parent conjugation with Gluconobacter oxydans. Also can use electrotransformation method, as with 1% inoculum size of Gluconobacter oxydans acceptor bacterium seed, in 100ml sorbitol culture medium (sorbitol 80g / L, yeast powder 20g / L, KH PO 1.5g / L, ( NH4)2SO4 1.5g / L and MgSO4·7H2O 0.5g / L), 30°C, 220rpm, cultivated for 18h, then centrifuged, washed with sterile 10% glycerol, centrifuged, repeated 3 times, and finally suspended in 1ml 10% glycerol , it is advisable to make the cell concentration reach 1010cells / ml, aliquot 50μl, and store at -80℃. Use the Gene-Pulser (Bio-Rad, MicroPulserTM, U.S.A.) electrotransformer to transform, mix 50 μl of...
Embodiment approach
[0065] A preferred embodiment of the DHA high-yield strain construction method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0066] 1. Construct madh gene knockout strain GDHEΔadh. Refer to the literature, use the plasmid pSUP202 as the carrier, connect the adh1 gene, the kana resistance gene, and the adh2 gene in sequence to obtain the plasmid pSUP202-3-adhA::Km (Wei, L.J., X.P.Yang, et al.Characterization of Enzymes in the Oxidation of 1,2-Propanediol to d-(-)-Lactic Acid by Gluconobacter oxydans DSM 2003. Molecular Biotechnology. 2010, 46(1):26-33.). Escherichia coli containing the single-gene knockout vector pSUP202-3-adhA::Km was used as the donor, Gluconobacter oxidans GDHE was used as the acceptor, and Escherichia coli containing the plasmid pRK2013 was used as the helper bacteria to carry out three-parent conjugation, and the obtained zygote was It is the madh gene knockout strain GDHEΔadh.
[0067] 2. Construct the Escherichia coli transformant containin...
Embodiment 1
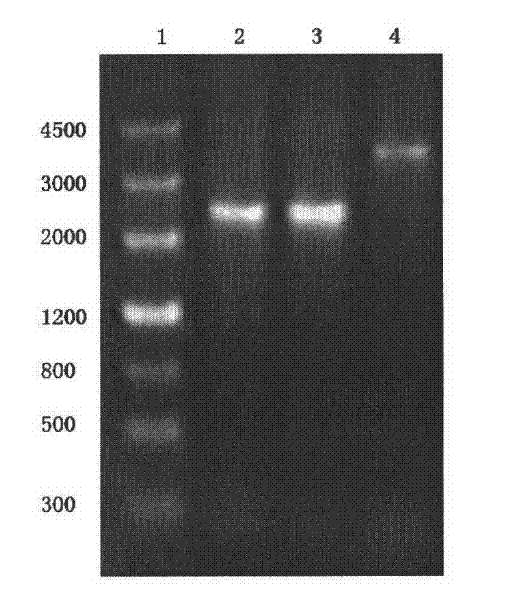
[0074] Example 1 Construction of Knockout Strain GDHEΔadh
[0075] The membrane-bound alcohol dehydrogenase (madh) gene in the genome of Gluconobacter oxidans GDHE was knocked out by homology exchange. Membrane-bound alcohol dehydrogenase can oxidize ethanol to acetaldehyde, which is further oxidized to acetate by membrane-bound acetaldehyde dehydrogenase. details as follows:
[0076] 1.1 Construction of knockout vector pSUP202-3-adhA::Km
[0077] Refer to the literature, use the plasmid pSUP202 as the carrier, connect the adh1 gene, the kana resistance gene, and the adh2 gene in sequence to obtain the plasmid pSUP202-3-adhA::Km (Wei, L.J., X.P.Yang, et al.Characterization of Enzymes in the Oxidation of 1,2-Propanediol to d-(-)-Lactic Acid by Gluconobacter oxydans DSM 2003. Molecular Biotechnology. 2010, 46(1):26-33.).
[0078] 1.2 Introducing the knockout vector into the cells of Gluconobacter oxidans to complete gene knockout
[0079] ①Establishment of donor bacteria: Tr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com