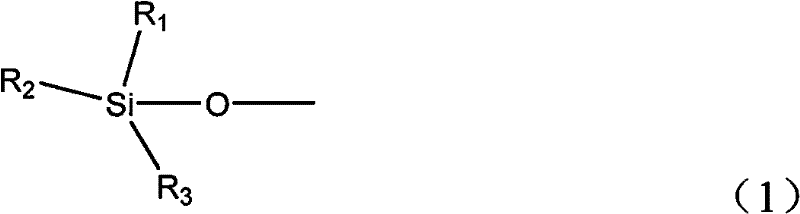Method for removing alkine and dialkene from pyrolysis gas through selective hydrogenation
A technology for selective hydrogenation and cracking of gas, applied in chemical instruments and methods, processing of gas mixtures, treatment of hydrocarbon oil, etc., can solve problems such as the influence of catalyst hydrogenation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Take a toothed spherical Pd-Au-Ca / Al with a diameter of 2.0mm 2 o 3 Catalyst 15 grams (produced by Beijing Research Institute of Chemical Industry, volume 35ml, the mass percentage content of Pd, Au, Ca is respectively 0.1%, 0.1%, 0.5%, and the balance is Al 2 o 3 , the catalyst loses 1.2wt% when the temperature rises to 500° C. on the thermogravimetric analyzer), and the catalyst is loaded into a fixed-bed reactor (diameter 15 mm, length 400 mm, with two temperature display control points). After the reactor temperature is stabilized at 110°C, nitrogen containing 2vol% trimethylmethoxysilane is passed into the reactor, the flow rate is controlled at 150ml / min, and the temperature is raised to 150°C after maintaining 110°C for 1 hour, and the temperature is stable After keeping for 0.5 hours, the nitrogen gas containing trimethylmethoxysilane was stopped, and argon gas was added to lower the temperature to obtain the catalyst Cat-1.
[0063] Comparison of Pd-Au-Ca / Al...
Embodiment 2
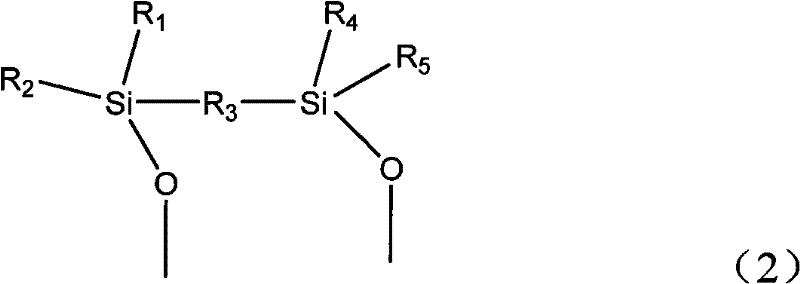
[0068] Take a spherical Pd-F-Cu-K / SiO with a diameter of 3mm 2 Catalyst 25 grams (produced by Beijing Research Institute of Chemical Industry, volume 53ml, the mass percentage content of Pd, F, Cu and K is respectively 0.08%, 0.4%, 1.0% and 0.5%, the balance is SiO 2, weight loss 1.1wt% when the temperature rose to 500°C on the thermogravimetric analyzer), the catalyst was packed into a 500ml three-necked bottle, the three-necked bottle was placed in the oil bath, one of the three-necked bottles was connected to the cooling coil, one was connected to the thermometer, and Connect to the feed port. First, 150ml of p-xylene was poured into the three-necked flask, and after the temperature of the reactor was stabilized at 110°C, 8ml of trimethylchlorosilane was passed into the reactor. After maintaining 110°C for 1 hour, the temperature was raised to 140°C. After the temperature was stabilized, the temperature was maintained for 1 hour and then lowered. The catalyst was taken out...
Embodiment 3
[0074] The catalysts of Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 were respectively applied to the mixed-phase hydrogenation reaction of cracked gas. The raw cracked gas came from Sinopec Yanshan Petrochemical Company and was taken from the outlet of the fifth-stage compressor. The composition is shown in Table 1.
[0075] Table 1 cracked gas composition (mol%)
[0076]
[0077] The mixed-phase hydrogenation reactor uses pyrolysis gasoline as the flushing phase, and the liquid space velocity is 5h -1 , wherein pyrolysis gasoline is hydrogenated and saturated, with a boiling point of 82°C to 178°C and a water content of 500ppm (mol).
[0078] The hydrogenation reactor is a 15ml isothermal fixed bed, and the catalyst is 5.0g. The process conditions of the hydrogenation reaction are shown in Table 2. In the hydrogenation reaction, 1ml of water vapor was pulsed in at 100h to investigate the water fluctuation resistance of the catalyst. After 700 h of reaction, the amount of carbon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com