Method of labelling interferons with peg
A labeling method, interferon technology, applied in the direction of interferon, cytokines/lymphokines/interferons, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as the influence of protein folding activity, and achieve the effect of enhancing activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0135] Example 1: Generation of Pyruvyl PEG
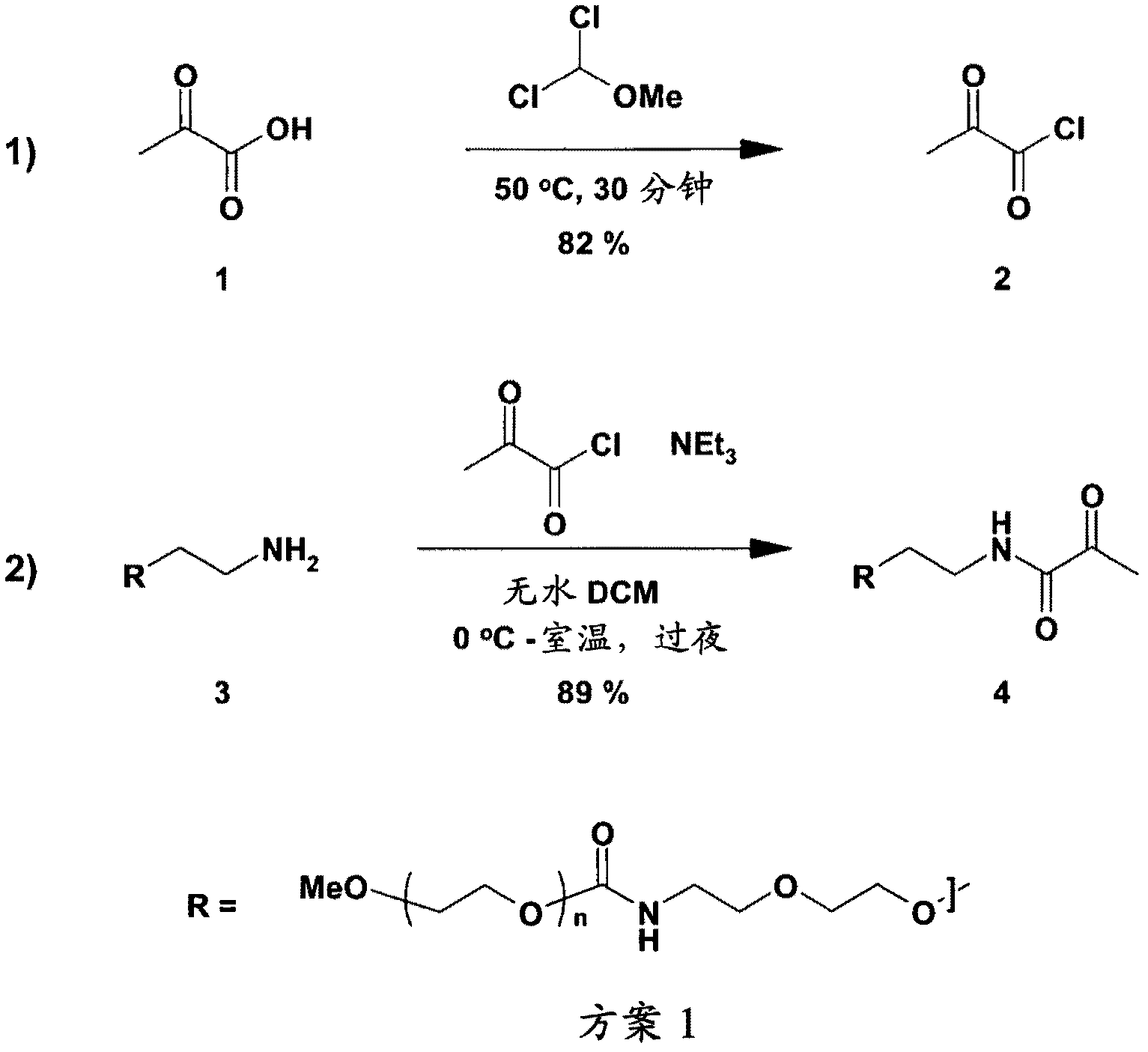
[0136] Such as figure 1 As shown in Scheme 1, a 10 kDa PEG target compound (4) containing an N-terminal pyruvyl functional group was prepared. This was achieved by overnight acylation of a commercially available PEG amine (3) with preformed pyruvic chloride (2). PEG amine was obtained from Nektar {MeO-PEG-NH2Nektar / 2M2U0101 / PT03F24].
[0137] The acid chloride (2) is formed by treating pyruvate (1) with α,α-dichloromethyl methyl ether. Briefly, pyruvic acid (5 g) was charged under nitrogen to a 50 ml 3-neck RB flask equipped with a reflux condenser, dropping funnel and connected to a dreschel bottle containing 2N NaOH(aq). α,α-Dichloromethyl methyl ether (5.16 ml) was added dropwise, the reaction mixture was heated to 50 °C for 30 minutes, the methyl formate by-product was removed by evaporation under reduced pressure, and in 82% yield (4.96 g) The crude acid chloride was obtained as a yellow oil.
[0138] The crude acid ch...
Embodiment 2
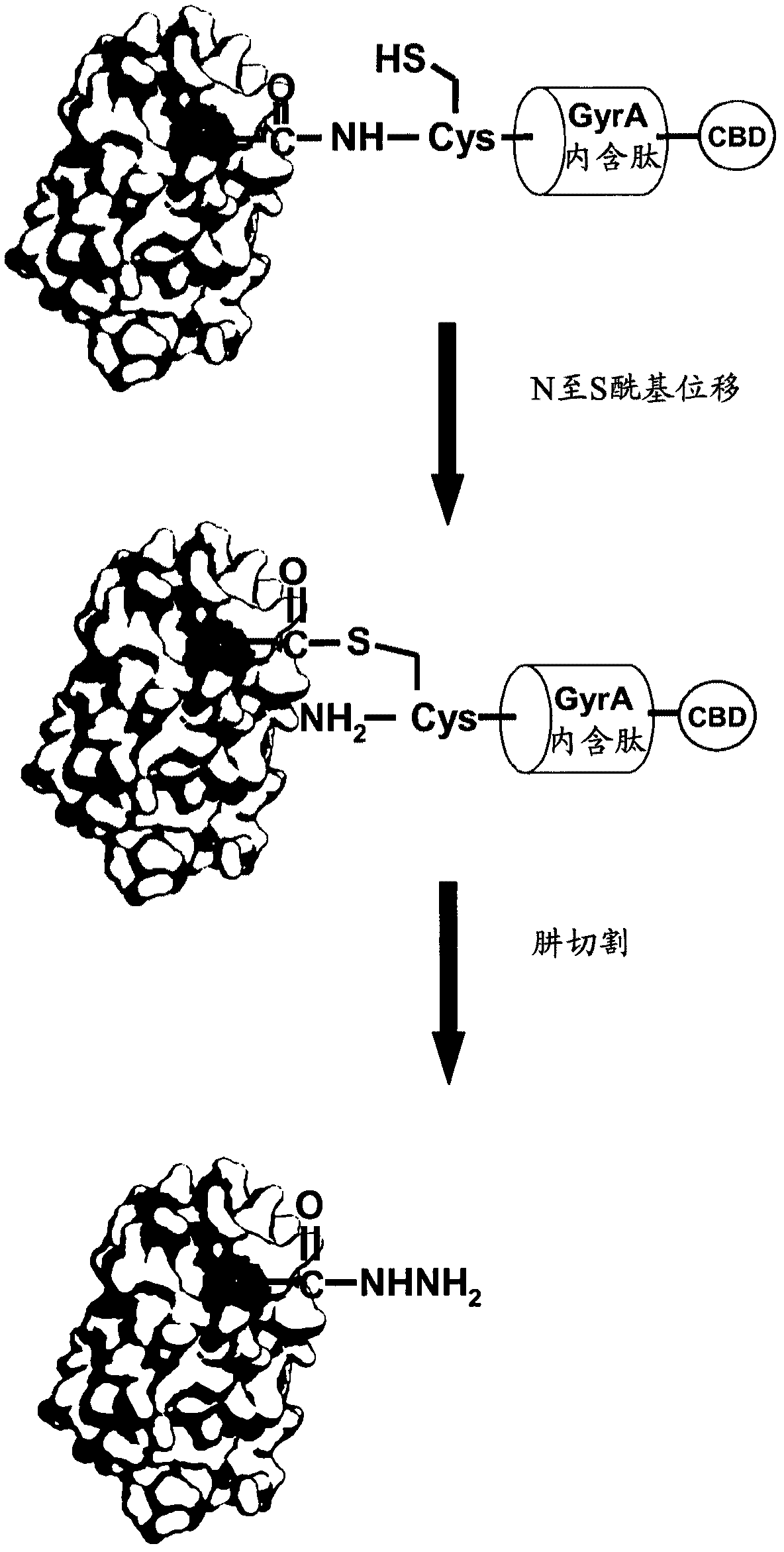
[0140] Example 2: Generation of site-specific C-terminal PEGylated IFNα2b hydrazide
Embodiment 21
[0141] Example 2.1: Cloning, expression and purification of soluble IFNα2b hydrazide
[0142] IFNα2b cDNA (IMAGE clone 30915269) was purchased from Gene Service Ltd. The IFNα2b coding sequence was amplified by PCR using the following primers:
[0143] The forward primer was designed to include an NdeI site immediately before the 5' IFNα2b sequence:
[0144] 5'-GGTGGTCATATGTGTGATCTGCCTCAAACCC-3'
[0145] A reverse primer was designed to eliminate the stop codon at the end of the IFNα2b coding sequence and replace it with a glycine codon that was immediately followed by a SapI site:
[0146] 5'-GGTGGTTGCTCTTCCGCACCCTTCCTTACTTCTTAAACTTTCTTGC-3'
[0147] The resulting PCR product was cloned into the NdeI SapI site of the pTXB1 vector (NEB). The pTXB1 IFNα2b GLY construct encodes a fusion protein whereby IFNα2b is linked via glycine to the N-terminus of the GyrA intein which in turn is fused to the N-terminus of the chitin binding domain (CBD). It was transformed into E. col...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com