MicroRNA structure-based construction method and function verification of hepatic cell selective multi-target interfering plasmid vector
A technology of plasmid vectors and hepatocytes, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of reduced interference efficiency, no cell/tissue specificity, easy methylation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
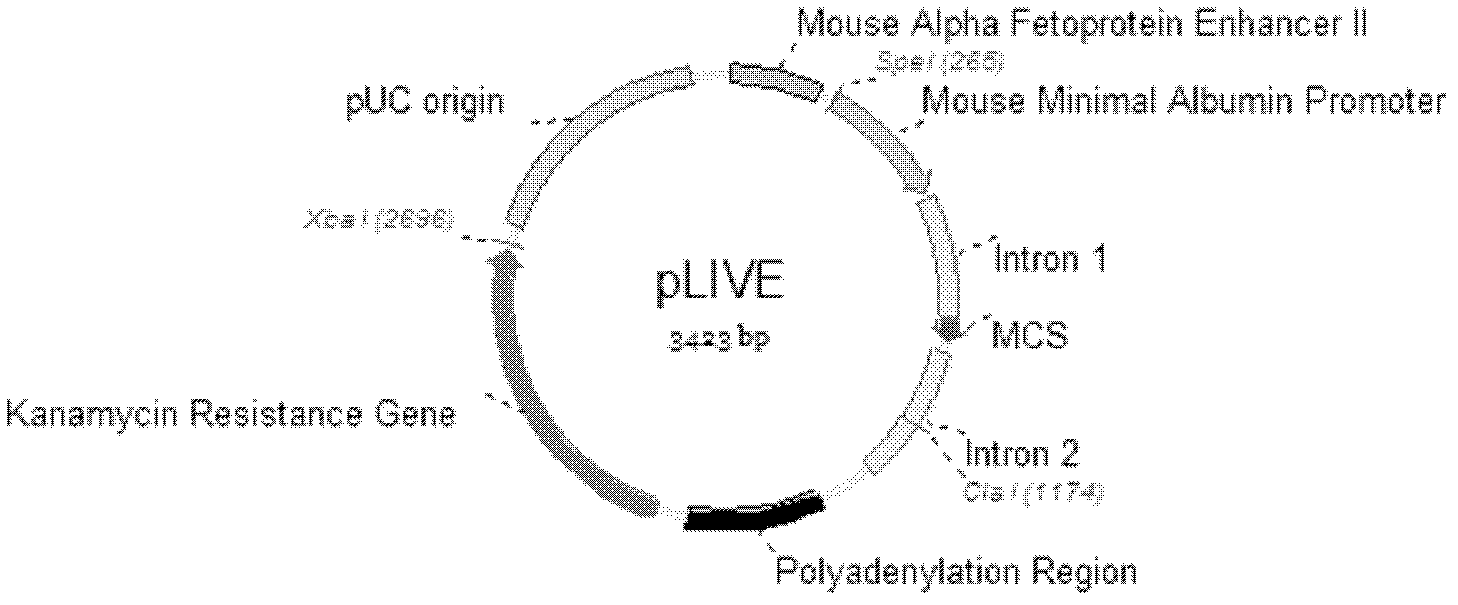
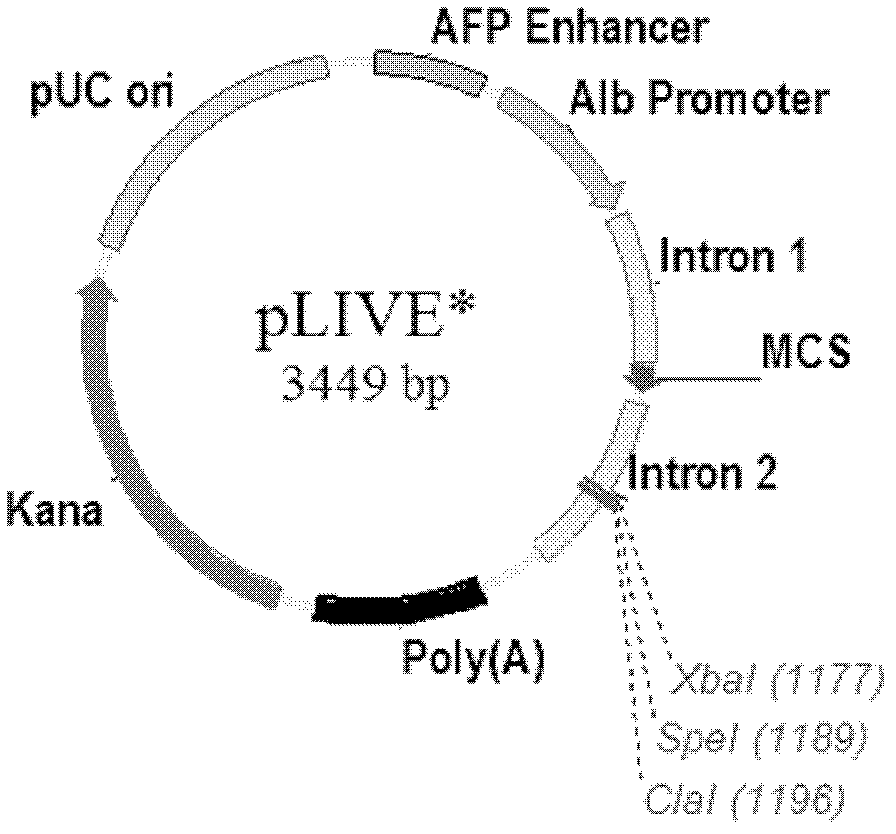
[0052] Example 1: Hepatocyte selective multi-target interference plasmid vector pLIVE-(shLuc155 based on microRNA structure mir -shLuc155 mir -shEGFP131 mir -shEGFP425 mir ) construction
[0053] 1. Transformation of pLIVE plasmid (Mirus company)
[0054] (1) Remove Xba I, Spe I restriction endonuclease sites:
[0055] The Xba I and Spe I sites in the pLIVE initial plasmid were removed by filling in the 5' protruding ends and self-ligating. First, 2 μg of the pLIVE initial plasmid was cut with Spe I enzyme (purchased from Fermentas, Cat.#FD1254), and the digested product was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis, and the linear pLIVE plasmid was recovered, and Klenow Fragment (purchased from Fermentas, Cat.# EP0052) to fill in the 5' protruding end, and then use T4 ligase (purchased from Fermentas, Cat. #EL0011) to ligate the linear plasmid to form a circular shape, and the newly generated sequence after ligation does not contain a Spe I site. The ligation product was ...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Example 2: Functional identification of hepatocyte-selective single-target, dual-target, and multi-target interference plasmid vectors targeting reporter genes Luciferase and EGFP
[0101] 1. The constructed liver cell selective single-target interference plasmid pLIVE-shLuc155 mir , dual-target interference plasmid pLIVE-(shLuc155 mir -shLuc155 mir ) was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α and amplified, the cells were collected by centrifugation, and the medium was prepared to extract and purify the plasmid, and the OD was determined 260 Plasmid concentration, sequencing confirmed that the plasmid sequence was correct.
[0102] 2. Introducing hepatocyte-selective single-target interference plasmid pLIVE-shLuc155 mir , dual-target interference plasmid pLIVE-(shLuc155 mir -shLuc155 mir ) and the Luciferase expression plasmid pGL3-CMV (purchased from Promega, Cat. #E1751, inserted into the CMV promoter) at a ratio of 3:1, co-transfected with liposome lipofectamin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com