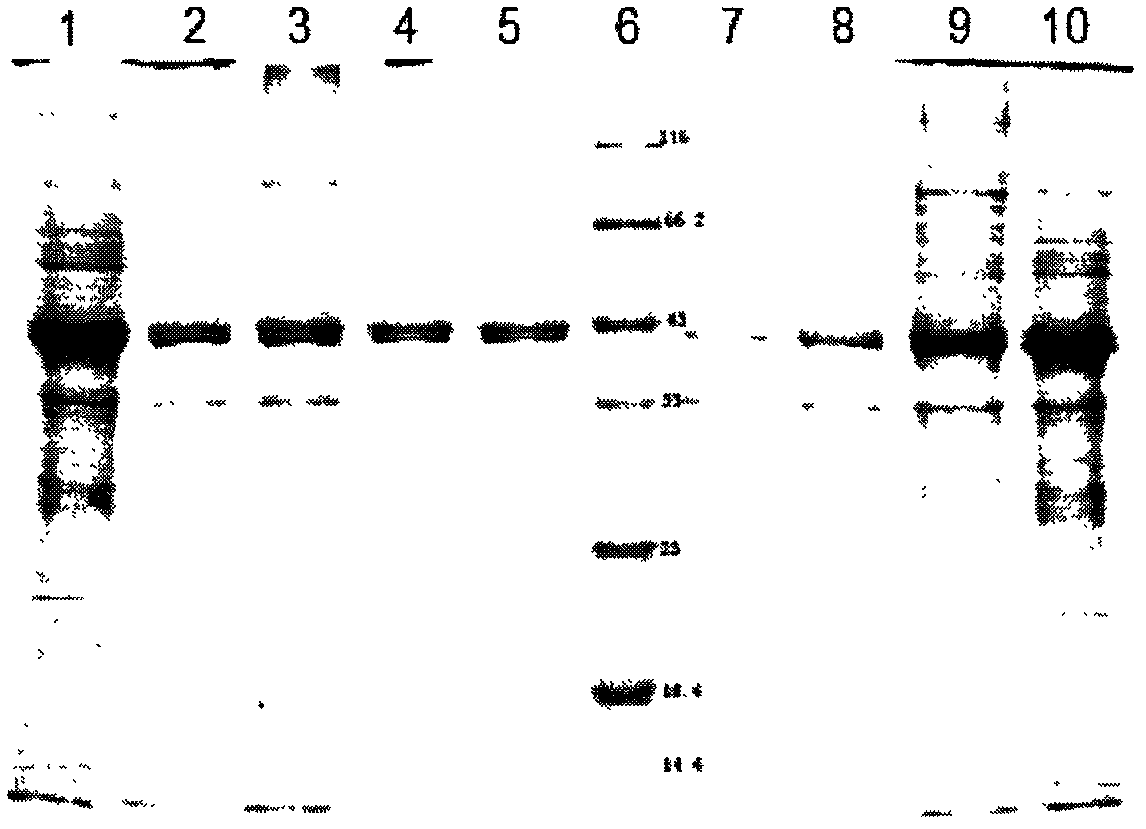
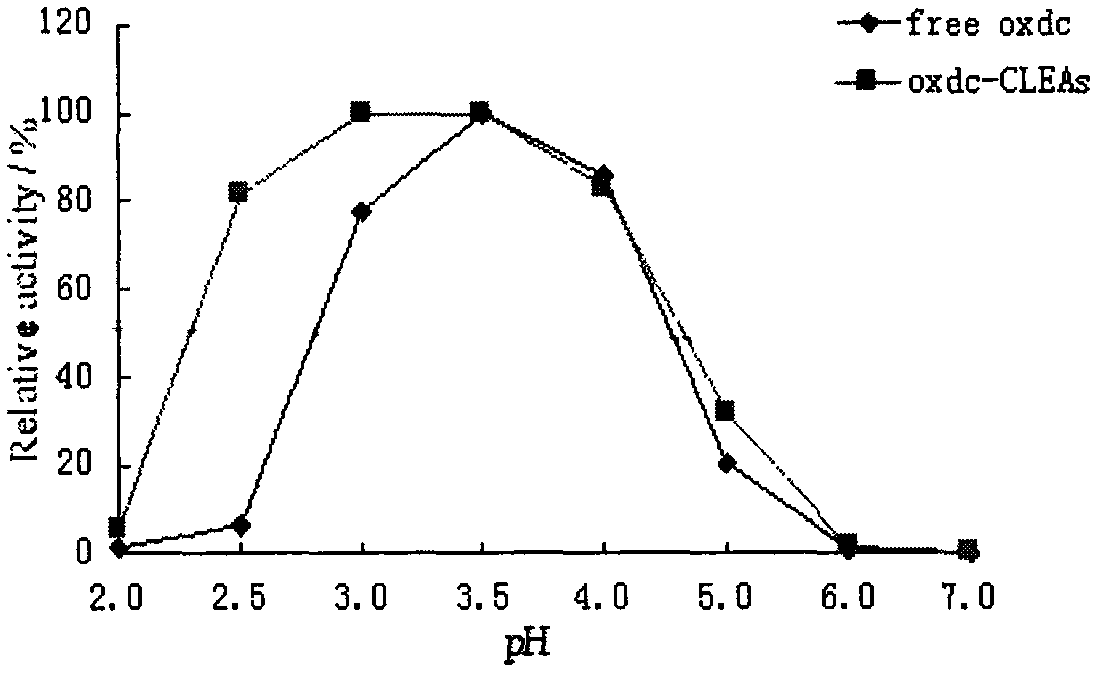
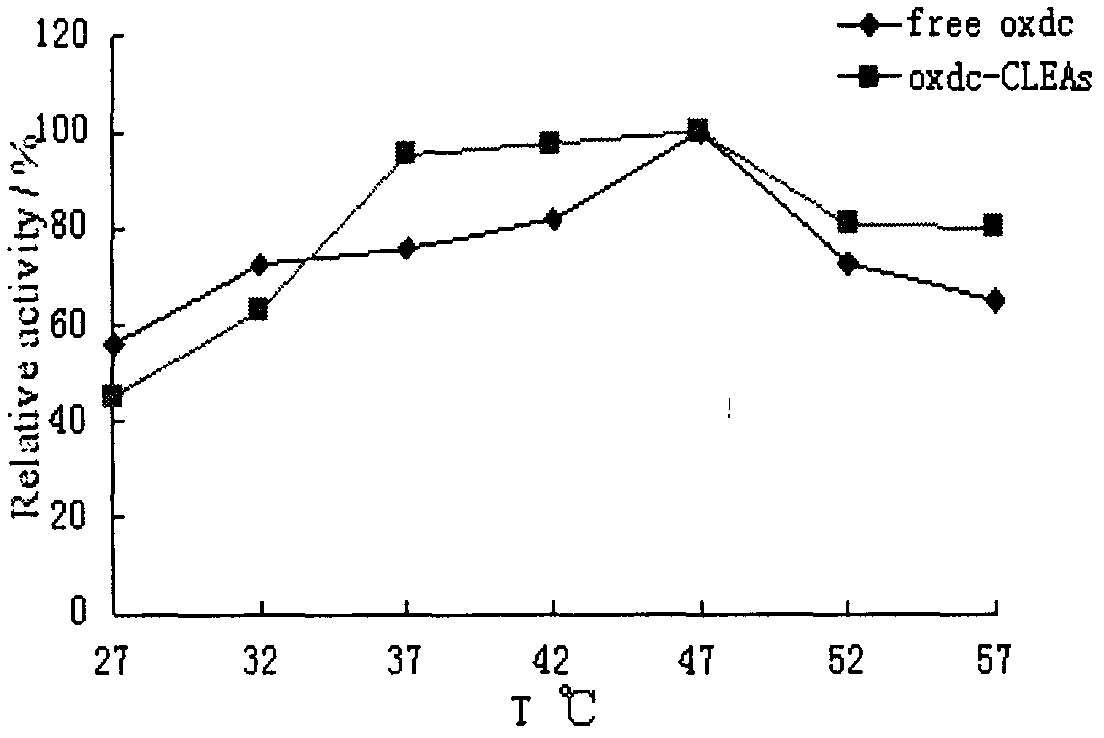
Preparation method of cross-linked oxalate decarboxylase aggregates (CLEAs)
A technology of oxalate decarboxylase and aggregates, which is applied in the field of preparation of cross-linked oxalate decarboxylase aggregates, can solve the problems of high cost and difficult operation, and achieve the effect of high separation efficiency, high purity and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0028] (1) Induced expression of recombinant oxalate decarboxylase
[0029] The genetically engineered bacteria E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET32a / YvrK were inoculated in LB medium containing ampicillin (0.1mg / ml) at 37°C and cultured at 250r / min. Bacteria grow to OD 600 When it is 0.8, add 6mmol / L of MnCl 2 , 0.4mmol / L IPTG, induced expression at 30°C for 8h, centrifuged to collect the bacterial pellet, added 10mL phosphate buffer (50mmol / L, pH 8.0) to resuspend the bacteria per gram of wet weight of the bacteria, and ultrasonically disrupted the bacteria , centrifuged to collect the supernatant as crude enzyme solution.
[0030] (2) Precipitation and separation of oxalate decarboxylase
[0031] Add 5ml of crude enzyme solution to a 10ml test tube, add pre-cooled absolute ethanol drop by drop until the ethanol concentration is 10% to 50%, put it in a refrigerator at 4°C overnight, collect the precipitate by centrifugation, and wash with 50mmol / L pH8.0 phosphate The buffer was rediss...
example 2
[0037] (1) Induced expression of recombinant oxalate decarboxylase is the same as example 1
[0038] (2) Precipitation and separation of oxalate decarboxylase
[0039] Add 5ml of crude enzyme solution to a 10ml test tube, add pre-cooled acetone drop by drop to a concentration of 10% to 50%, put it in a refrigerator at 4°C overnight, centrifuge to collect the precipitate, and redissolve it with 50mmol / L pH8.0 phosphate buffer , to obtain purified oxalate decarboxylase.
[0040] Enzyme activity detection and protein concentration analysis showed that acetone precipitation could remove 73.6% of the protein in the crude enzyme solution, the enzyme activity recovery reached 79.2%, and the purification factor was 2.84 times.
[0041] (3) Preparation of cross-linked oxalate decarboxylase aggregates
[0042] Add 5ml of purified enzyme solution to a 10ml centrifuge tube, add absolute ethanol drop by drop until the ethanol concentration is 20% to 50%, put it in a refrigerator at 4°C o...
example 3
[0045] (1) Induced expression of recombinant oxalate decarboxylase is the same as example 1
[0046] (2) Precipitation and separation of oxalate decarboxylase
[0047] Add 5ml of crude enzyme solution to a 10ml test tube, add pre-cooled saturated ammonium sulfate drop by drop to a concentration of 20% to 80%, put it in a refrigerator at 4°C overnight, collect the precipitate by centrifugation, and wash with 50mmol / L pH8.0 phosphate buffer Redissolved to obtain depurified acid decarboxylase.
[0048] (3) Preparation of cross-linked oxalate decarboxylase aggregates
[0049] Add 5ml of purified enzyme solution to a 10ml centrifuge tube, add absolute ethanol drop by drop until the ethanol concentration is 10% to 50%, put it in a refrigerator at 4°C overnight, add BSA to 1.0mg / L~1.5mg / L, drop by drop Add glutaraldehyde solution to 0.01%~0.08%, cross-linking reaction at pH 3~9, 4°C for 0.5~3.5h, centrifuge, discard supernatant, wash with 50mmol / L pH8.0 phosphate buffer until the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com