Method for preparing positive material fluorine-doped sodium vanadium phosphate of sodium-containing lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery, sodium vanadium fluorophosphate technology, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of not too large input of one-time raw materials, difficult to achieve large-scale production, environmental pollution, etc. Chemical properties, convenient for large-scale production, and the effect of simple and easy methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
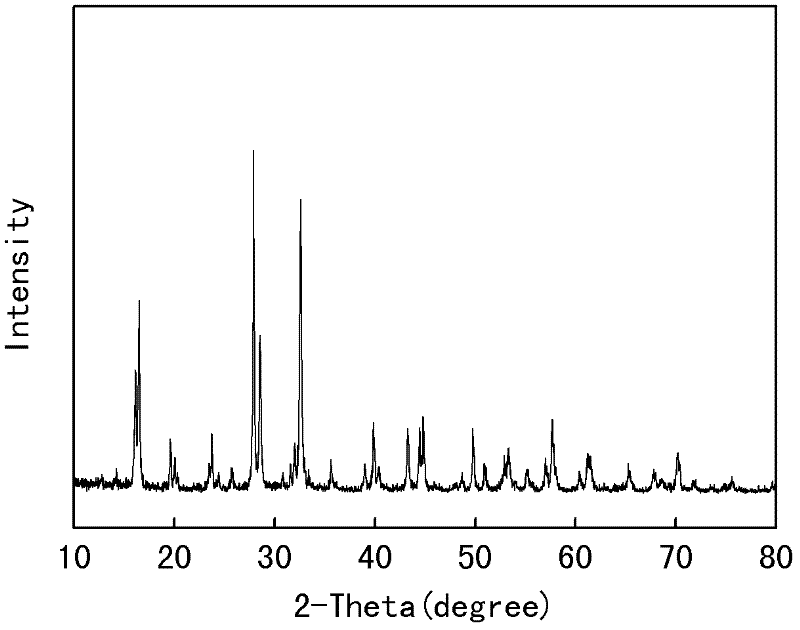
[0032] 0.052mol vanadium pentoxide, 0.156mol ammonium fluoride, 0.156mol sodium bicarbonate, 0.104mol ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and 6g glucose were mixed and dispersed in ethanol, placed in a ball mill, and mechanically Activation for 8h. The mechanically activated material is roasted at 600°C for 24 hours under the protection of argon, and the product Na 3 V 2 (PO 4 ) 2 f 3 / C. The X-ray diffraction analysis of the obtained product is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the analysis shows that the product prepared by this formula also has a small amount of Na 3 V 2 (PO 4 ) 3 In the heterogeneous phase, there is no carbon peak in the spectrum, which shows that glucose is decomposed into amorphous carbon at high temperature. The obtained product was assembled into an experimental button battery, and the electrochemical performance of charge and discharge was tested. The test results showed that the first discharge specific capacity of the material at the rate of 0.5C, ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] 0.052mol vanadium pentoxide, 0.156mol ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.156mol sodium hydroxide and 6g glucose were mixed and dispersed in ethanol, placed in a ball mill, and mechanically activated at 800 rpm for 8 hours. The mechanically activated material was roasted at 900°C for 8 hours under the protection of argon, and the product Na was obtained after cooling. 3 V 2 (PO 4 ) 3 / C. SEM analysis of materials such as image 3 As shown, the analysis showed that the particle size of the product was around 1 μm. The obtained product was assembled into an experimental button battery, and its charge-discharge electrochemical performance was tested at a rate of 0.1C. The test results showed that the first discharge specific capacity was 109mAh·g -1 , and a constant voltage platform appears near the 3.7V voltage, and there is no obvious constant voltage platform near the 4.2V voltage. The first charge and discharge curve of the material at 0.1C is as follows Figure 4 ...
Embodiment 3
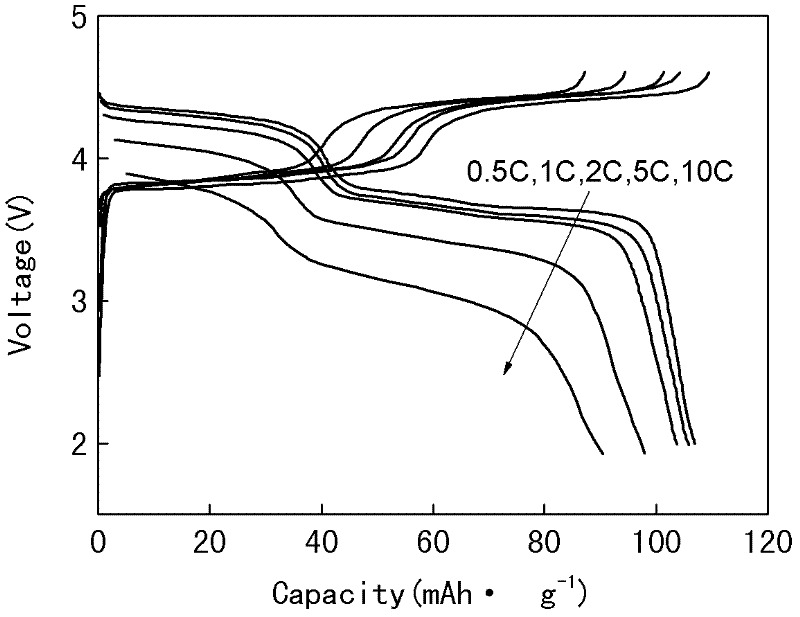
[0036] 0.052mol vanadium pentoxide, 0.13mol ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.156mol sodium hydroxide, 0.075mol ammonium fluoride and 6g glucose were mixed and dispersed in ethanol, placed in a ball mill, and mechanically Activate for 10h. The mechanically activated material was roasted at 700°C for 12 hours under the protection of argon, and the product Na was obtained after cooling. 3 V 2 (PO 4 ) 2.5 f 1.5 / C. The obtained product was assembled into an experimental button battery, and the electrochemical performance of the material was tested. The results showed that the material material not only appeared a constant voltage platform near a voltage of 3.7V, but also appeared a constant voltage platform near a voltage of 4.2V. The first charge and discharge curve of the material at 0.5C rate is as follows Figure 5 As shown, the cycle curve of the material at 5C rate is as follows Image 6 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com